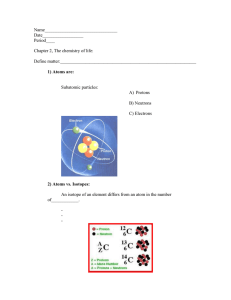
3. Atoms, Elements and Compounds Date 0620 RM 3.1 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table 3.1 Atomic structure and the Periodic Table Core State the relative charges and approximate relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons Define proton number and nucleon number Use proton number and the simple structure of atoms to explain the basis of the Periodic Table (see section 9), with special reference to the elements of proton number 1 to 20 Define isotopes State the two types of isotopes as being radioactive and non-radioactive State one medical and one industrial use of radioactive isotopes Describe the build-up of electrons in 'shells' and understand the significance of the noble gas electronic structures and of valency electrons (the ideas of the distribution of electrons in s and p orbitals and in d block elements are not required.) (Note: a copy of the Periodic Table, as shown in the Appendix, will be available in Papers 1, 2 and 3) Atoms consist of protons, neutrons and electrons. Particle O proton neutron electron Mass/atomic mass units Charge 1 +1 1 O 1/1840 → 0 -| Proton number /atomic number: number of protons in an atom nucleon number: number of protons and neutrons in an atom Le relative atomic mass The periodic table is ordered by proton number • columns indicate groups with similar reactions / properties • rows are called periods grange A'ZONE e.g 0580 MA Isotop es Isotopes are atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons (same proton number) 12 6 2( 136 13 (14C Radioactive (radioisotope) nucleus is unstable so it decays to give off radiation 6 non-radioactive 6 Uses of radioisotopes: Cancer treatment (cobalt-60) - radiation destroys cancerous cells • Detecting leaks - added to oil or gas in pipeline -radiation can be detected with GMtube O Electron Electrons build up in 'Shells' Valency electrons are the elections in the outer shell-they dictate how an element reacts to bomo Corton XX 1st shell holds max. 2 electrons 2nd shell holds max 8 electrons Noble gases (Group 0) have a full valence shell - unreactive 3.2 Bonding: the Structure of Matter 3.2 Bonding: the structure of matter Core Describe the differences between elements, mixtures and compounds, and between metals and non-metals Describe an alloy, such as brass, as a mixture of a metal with other elements O stosibat camuls. Looney ballos 9 No. 0620 " Date RM. Element: -contains only one type of atom od fotsin at Compound: more than one type of atom chemically bonded @ atoma bonded in same ratio • cannot be separated by physical means ·Mixture: - can contain any number of substances in any ratio • not joined by chemical bonds nobl Metals and nonmetals . Metal s • readily conduct electricity & heat •Mostly malleable and ductile s to H of Mibod Non-metal ・do not conduct electricity and heat ・ usually brittle normally shiny! noitsoil. look dull when solid 0 tend to have high density 0 higher m.p and b.p • low density •form positive ions • usually form basic oxide, low melting points • form negative ions •usually form acidic oxides Alloys are mixtures of metals with other elements. AGM Custom 3.2 (a) Ions and Ionic Bonds solo as • 3.2(a) 3.2 (a) lons and ionic bonds Core Describe the formation of ions by electron loss or gain Describe the formation of ionic bonds between elements from Groups I and VII Knot Tons are formed by - electron loss electron gain = Supplement Describe the formation of ionic bonds between metallic and non-metallic elements Describe the lattice structure of ionic compounds as a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions electron transfer positive ion had tas Love) negative ion bomot of nos eting Tonic bonds only form between a metal and a non-metal, where A'ZONE green range 0.00 sodium atom the metal loves elections (becoming positive) and the non-metal gains elections (becoming negative) out sho Tonic bonding between Group I and Group VII. Sodium loses election, chlorine gains electron sutxi M chlorine atom sodium ion chlorine ion Na election Cl Na transfers O slit such bow both have full outer shell 2, 8, 1 Hool for Due to their electrostatic attraction, the two ions are attracted to each o + her list wall Lattice structure on t white hos min love w dad of brot 4.01 isdeld cabixo sical mot ullover Many ions group together, forming a giant ionic lattice with a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions. 3.2(0) Molecules and Covalent Bondso 3.2 (b) Molecules and covalent bonds Core Describe the formation of single covalent bonds in H2, CL, H2O, CH, and HCl as the sharing of pairs of electrons leading to the noble gas configuration Describe the differences in volatility, solubility and electrical conductivity between ionic and covalent compounds Supplement Describe the electron arrangement in more complex covalent molecules such as N2, C2H, CH,OH and CO Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. can be formed between atoms of the jame non-me tal can be formed between atoms of different nonmetals. The bonded atoms form units - molecules Simple molecular compounds have weak inter-molecule bonds, strong intra-molecule covalent bonds. No. 0620 Date RM. Formation of single covalent bonds H + H2 HAH sharing elections lead, to gas configuration noble two single covalent bonds More complex covalent molecules HAC H CH4 ON2 EN ON three pairs of XN) N⚫ shared electron -triple bond G2 H 4 H N =N H H Hon H (=C . CO 2 CH2O H H Xo HOC H 0=C=0 -double bond, 0° -linear H X CH H-C-O-H H Comparing ionic and simple molecular compounds IONIC MOLECULAR High m.p & b.p-strong attractions • Low m.p fb.p -weak attractions •are not volatile • conduct electricity when liquid -presence of charged particles • soluble in water 1• hard are volatile do not conduct electricity - no Tcharged particles insoluble in water grange A'ZONE 32(c) Macromolecules 3.2 (c) Macromolecules Core Describe the giant covalent structures of graphite and diamond Relate their structures to the use of graphite as a lubricant and of diamond in cutting Supplement Describe the macromolecular structure of silicon(IV) oxide (silicon dioxide) Describe the similarity in properties between diamond and silicon(IV) oxide, related to their structures Graphit e Carbon a tom electron strong covalent bonds -weak forces 1. Each carbon atom bonded with three others. There is a free electron • Covalent bond, within layers are strong • Weak forces between layers • O Used as a lubricant - lagers can slide • Used as electrodes - can conduct electricity due Each carbon atom becomes part of a flat hexagonal ring to delocalbed electron Diamond strong covalent bonds Each carbon atom forms a tetrahedron with four other carbon atoms. . • Each carbon atom joined with four others with strong covalent bonds, forming a giant covalent lattice • All bond, are identical, no weak bonds • Used in cutting tools - hardest natural O substance as 0 Used in jewellery - shiny and translucent Silicon (IV) oxide (silicon dioxide) antic Similar structure to diamond, tetrahedral in shape. • each silicon atom covalently bonded with four oxygens • each oxygen bonded with two silicons Similar properties to diamond: • high melting point and very hard non-conductor of electricity and insoluble in water Used in sandpaper and to line furnaces silicon охудет 3.2(d) Metallic Bonding famous metal 107 electron 3.2 (d) Metallic bonding Supplement Describe metallic bonding as a lattice of positive ions in a 'sea of electrons' and use this to describe the electrical conductivity and malleability of metals No. 0620 Date RM. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons leave the metal atoms, giving stable metal ions with full outer shells. + + + Giant lattice of positive metal ions in a sea of delocalised electrons • Bonds are strong- electrostatic attraction between positive ions and negative electron s Explaining metal properties. • High • High mp and b.p- strong electrostatic attraction therefore strong bonds • Electrical conductors -delocalised electrons carry charge through metal Thermal conductor) -delocalised electrons carry thermal energy through metal Malleable and ductile - layers of ions can slide over eachother O green range A'ZONE