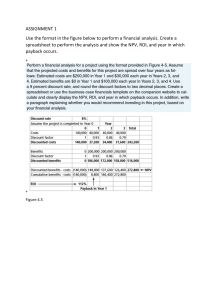
Strategic Cost Management JPFranco Lecture Note in Responsibility Accounting Centralization exists when decisions rest only to the top management. Decentralization happens when the authority to make decisions is delegated to responsible officers in different organizational units. Either decision model provides great results. Authority is the power to do or not to do, to give orders, to give command and to give instructions or make decisions. Responsibility is the duty to do or not to do an activity according to the given order. Accountability is the answerability on the consequences of what had been done, undone, or had not been done. Authority and responsibility must always go together. Authority without responsibility is absolute power and absolute power corrupts absolutely. As authority is shared to trusted men, responsibility must be performed in line with the principle of accountability, that is, when authority is exercised, the effects must be evaluated. Without accountability, there would be no compelling reason to evaluate performance fairly and objectively. Authority and responsibility would loose their intrinsic meanings without accountability. Thus, AUTHORITY = RESPONSIBILITY = ACCOUNTABILITY In a decentralized decision-making model, divisions, departments, segments, or units are considered responsibility centers or strategic business units. Each center is managed by a responsible officer – he is held accountable for its operation and resources. A responsibility center could be a cost center, a revenue center, a profit center or an investment center. Commonly, organizations are designed to emphasize functional, product line or geographical responsibility. The span of authority given to a manager or responsible officer defines the area over which he has controls. Controllability refers to the power of the manager to decide or influence the incurrence or non-incurrence of an item, event, or activity. The authority entrusted to a manager should commensurate with the responsibility assigned to him. Consequently, he is accountable to his action or inaction. His performance should be evaluated in line with the established objectives and standards over his center. One way is through the performance or information report submitted to and gathered by the responsible manager or officer. Basis Used in Evaluating Responsibility Centers Responsibility Center Description Cost center Controls or influence the incurrence of costs Revenue center Controls the generation of revenues Profit center Controls both the generation of income and incurrence of costs Evaluation Technique Cost variance analysis Revenue variance analysis Segment margin analysis Page 1 of 7 Investment center Decides on which strategic Return on Investment (ROI) business opportunity should the Residual Income (RI) company undertake Economic Value Added (EVA) Revenue Center A revenue center manager has control or influence in generating revenue but not costs. His performance report should show the variances between actual revenue and budgeted revenue. When the actual revenue is greater than budgeted revenue, there is favorable revenue variance, and vice-versa. A favorable variance may be given commensurate reward and recognition. Cost Center A cost center manager has control or influence over the incurrence or non-incurrence of costs, but not over revenue or the use of investment funds. The cost center manager reports should separate the controllable from the non-controllable costs and should highlight the variances between the actual and budgeted costs. Variances may be favorable or unfavorable. Favorable variances mean savings while unfavorable variances could indicate excessive costs and both must be investigated. Service departments such as accounting, finance, general administration, legal and personnel are classified as cost centers. Manufacturing facilities are often treated as cost centers. The managers of cost centers are expected to minimize costs while providing the level of products and services needed by other parts of the organization. Profit Center A profit center manager has control over revenue and costs, but not over the use of investment funds. His performance is evaluated based on controllable margin while the center’s performance is evaluated based on segment or direct margin. The difference between controllable margin and segment margin is fixed costs and expenses controllable not by the responsible manager but by others. Thus, Contribution margin Less: Controllable (Traceable) Direct Fixed Costs Controllable margin Less: Non-controllable (Traceable) Direct Fixed Costs Segment margin Pxx xx xx xx Pxx Investment Center Investment center manager has authority to decide over which investment opportunity should be considered and pour in the funds for investments. He is responsible for earning an adequate return on investment. The cost-benefit criterion plays a vital role in this decision process. The benefit refers to the returns derived from investments while the cost refers to the amount used in undertaking the opportunity. Page 2 of 7 The Return on Investment (ROI) Model The return on investment is sometimes referred as return on assets (ROA) or accounting rate of return (ARR). The higher a business segment’s return on investment, the greater the profit earned per peso invested in the segment’s operating assets. The segment margin or net operating income is income before interest and taxes (EBIT). Segment investment or average operating assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, plant and equipment, and all other assets held for operating purposes. Non-operating assets include land held for future use, an investment in another company, or a building rented to someone else – these are not included in operating assets in computing ROI. Average operating assets beginning balance plus ending balance at the end of the year divided by two. The formula is: ROI = Segment Income / Segment Investment The Du Pont Model An extended model of ROI is expressed as: ROI = Net Profit / Net Sales x Net Sales / Investment ROI = Return on Sales x Asset Turnover This model encourages investment center managers to wisely take investments only for those which are of relevance to operations. This will result to efficiency in allocating investment funds. In other words, only those investment of which the investment center manager has control and use in operations shall be included in the ROI determination. All other things the same, margin or return on sales is improved by increasing selling prices, reducing operating expenses, or increasing unit sales. Increasing selling prices and reducing operating expenses increases net operating income. Increasing unit sales increases operating leverage! A given increase in the number of units sold will lead to an even larger increase in net operating income. However, excessive funds tied up in operating assets depress turnover and thus lower ROI. The Residual Income Model The residual income is computed as follows: Segment Income Less: Minimum Required Income Residual Income Pxx xx (investment x implied interest rate) Pxx The segment income is income expressed before tax or earnings before interests and tax (EBIT) or the operating income. The minimum required income is also referred as imputed income, implied income, or desired income. Page 3 of 7 The imputed interest rate is based on the prevailing market rate from which the business generates profit without accepting a high business risk. This is a pre-tax cost of capital and in principle, should reflect the degree of risk the reporting responsibility center is willing to accept. Assessment using residual income is considered superior than ROI because of 1) the compliance to a minimum return; and 2) the size of the excess over the minimum return. The Economic Value-Added (EVA) Model This is a more specific after-tax version of residual income. EVA is after-tax operating income minus the total annual cost of capital. It represents the business unit’s “true” economic profit. It is a measure of the management effectiveness in increasing investors’ “value.” If EVA is positive, the company is creating wealth. If it is negative, then the company is destroying wealth. The best investment based to use is the market value of the long-term financing (Total Assets – Current Liabilities). Net Operating Income After Tax Less: Minimum Required Income (Investments based on Market Values x Cost of Capital) Economic Value Added Pxx xx Pxx Illustrative Problem 1 Torres Company is a decentralized company with five autonomous divisions. Operating results for the company’s Division A are given below: Sales P24,500,000 Less: Variable costs 14,700,000 Contribution margin 9,800,000 Less: Fixed costs 8,000,000 Net operating income P 1,800,000 The company had an overall ROI of 24% last year. Division A used an investment of P6,000,000 at the start of the year. Division A has an opportunity to add a new product line that would require an investment of P4,000,000. The cost and revenue characteristics of the new product line per year would be: Sales P 8,000,000 Variable costs 60% of sales Fixed costs P 2,240,000 Required: 1. Compute the Division A’s ROI for last year. 2. Compute the Division A’s ROI if the new product is added. 3. If you were Division A’s manager, would you accept the new product line? 4. If you were the Chief Executive Officer of Torres Company, would you advise Division A manager to add the new product line? 5. Suppose that the company sets a minimum return of 20% on its invested assets and that the divisional performance is evaluated by the residual income approach: Page 4 of 7 a. Determine the residual income of Division A last year and its new residual income if the new product line is accepted. b. Under these circumstances, if you are the Division A manager, would you accept the new product line? Answer and Solution: 1. Division A’s ROI last year is computed as follows: Return on Investment = Net Operating Income / Investment = P1,800,000 / P6,000,000 = 30% 2. If the new product line is accepted, the new ROI will be: New ROI = (P1,800,000 + P960,000*) / (P6M + P4M) = P2,760,000 / P10,000,000 = 27.60% *Sales Less: Variable costs Contribution margin Less: Fixed costs Net operating income P8,000,000 4,800,000 3,200,000 2,240,000 P 960,000 3. No, because the new product line would decrease Division A’s ROI of 30%. 4. Yes, because the new product line’s ROI of 24% (P960,000/P4,000,000) is not lower than the overall ROI of the company which is also 24%. 5. A. Last Year With New Product Line Operating Income P1,800,000 P2,760,000 Less: Minimum Income (P6M x 20%) 1,200,000 (P10M x 20%) 2,000,000 Residual Income P 600,000 P 760,000 B. Yes, because the new product line provides additional residual income of P160,000. Illustrative Problem 2 Costa Company had three autonomous divisions: King, Queen, and Jack. Presented below are the available data: Division Sales Revenue Net Operating Income Invested Assets King P 60,000,000 P3,000,000 P20,000,000 Queen P 9,000,000 P3,600,000 P18,000,000 Jack P135,000,000 P6,750,000 P45,000,000 Page 5 of 7 Required: 1. Compute the ROI for each division. 2. Compute the residual income for each division using an imputed rate of 16%. 3. Suppose that Costa Company is using a total of P40,000,000 in bonds with 9 percent interest and P60,000,000 of ordinary shares with cost of equity at 12%. Costa has 30% tax rate. Analysis of each division shows the following current liabilities: King P 400,000 Queen 1,000,000 Jack 600,000 Total P2,000,000 Compute the EVA of each division. Answer and Solution: 1. The ROI for each division is computed as follows: King Net operating income P3,000,000 Divided by: Invested Capital P20,000,000 ROI 15% Queen P3,600,000 P18,000,000 20% 2. The residual income for each division is computed as follows: King Queen Net operating income P3,000,000 P3,600,000 Less: Minimum income (P20,000,000 x 16%) P3,200,000 (P18,000,000 x 16%) P2,880,000 (P45,000,000 x 16%) Residual income P (200,000) P 720,000 Jack P6,750,000 P45,000,000 15% Jack P6,750,000 P7,200,000 P (450,000) 3. First, compute the weighted average cost of capital used by Costa Company: Ratio Effective rates Weighted Bonds P 40,000,000 40% x 9% x (1-30%) = 6.3% 2.52% Stocks 60,000,000 60% x 12% 7.20% P100,000,000 100% 9.72% Second, use the weighted average cost of capital to get the minimum income and thus compute the EVA: King Queen Jack Net operating income, after tax P2,100,000 P2,520,000 P4,725,000 Less: Minimum income (P20,000,000 – P400,000) x 9.72% P1,905,120 (P18,000,000 – P1,000,000) x 9.72% P1,652,400 (P45,000,000 – 600,000) x 9.72% P4,315,680 Economic Value Added P 194,880 P 867,600 P 409,320 Page 6 of 7 Illustrative Problem 3 Pullman, Inc. had an after-tax operating income last year of P1,583,000. Three sources of financing were used by the company: P2 million of mortgage bonds paying 8 percent interest; P3 million of unsecured bonds paying 10 percent interest, and P10 million of ordinary shares, which was considered to be no more or less risky than other stocks. Stockholders, on the average, received six percentage points higher than the return on long-term government bonds. The Philippine Treasury is issuing bonds at 6 percent. The tax rate of Pullman is 40%. Required: 1. Compute the cost of capital in using mortgage bonds. 2. Compute the cost of capital in using unsecured bonds. 3. Compute the cost of capital in using ordinary shares. 4. Compute the weighted average cost of capital. 5. Compute the EVA for last year. 6. Assume instead that Pullman, Inc. had P15 million in ordinary shares with no mortgage bonds or unsecured bonds, what will be the EVA? Answer and Solution: 1. Cost of Capital using Mortgage Bonds = 8% x (1-40%) = 4.80% 2. Cost of Capital using Unsecured Bonds = 10% x (1-40%) = 6.00% 3. Cost of Capital using Stocks = 6%(risk-free rate) + 6%(growth rate) = 12.00% 4. Weighted-Average Cost of Capital: Mortgage Bonds P 2,000,000 Unsecured Bonds P 3,000,000 Ordinary Shares P10,000,000 P15,000,000 5. Economic Value Added for Pullman last year: After-tax operating income Less: Minimum Income Required (P15,000,000 x 9.84%) Economic Value Added 6. After-tax operating income Less: Minimum Income Required (P15M x 12%) EVA 2/15 x 4.80% 3/15 x 6.00% 10/15 x 12.00% = 0.64% = 1.20% = 8.00% = 9.84% P1,583,000 P1,476,000 P 107,000 P1,583,000 P1,800,000 P (217,000) Page 7 of 7