Budgetary Control & Responsibility Accounting Learning Objectives
advertisement

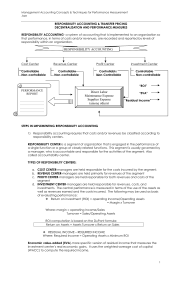
BUDGETARY CONTROL AND RESPONSIBILITY ACCOUNTING LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Describe budgetary control and static budget reports. Budgetary control consists of (a) preparing periodic budget reports that compare actual results with planned objectives, (b) analyzing the differences to determine their causes, (c) taking appropriate corrective action, and (d) modifying future plans, if necessary. Static budget reports are useful in evaluating the progress toward planned sales and profit goals. They are also appropriate in assessing a manager’s effectiveness in controlling costs when (a) actual activity closely approximates the master budget activity level, and/or (b) the behavior of the costs in response to changes in activity is fixed. 2. Prepare flexible budget reports. To develop the flexible budget it is necessary to: (a) Identify the activity index and the relevant range of activity. (b) Identify the variable costs, and determine the budgeted variable cost per unit of activity for each cost. (c) Identify the fixed costs, and determine the budgeted amount for each cost. (d) Prepare the budget for selected increments of activity within the relevant range. Flexible budget reports permit an evaluation of a manager’s performance in controlling production and costs. 3. Apply responsibility accounting to cost and profit centers. Responsibility accounting involves accumulating and reporting revenues and costs on the basis of the individual manager who has the authority to make the day-to-day decisions about the items. The evaluation of a manager’s performance is based on the matters directly under the manager’s control. In responsibility accounting, it is necessary to distinguish between controllable and noncontrollable fixed costs and to identify three types of responsibility centers: cost, profit, and investment. Responsibility reports for cost centers compare actual costs with flexible budget data. The reports show only controllable costs, and no distinction is made between variable and fixed costs. Responsibility reports show contribution margin, controllable fixed costs, and controllable margin for each profit center. 4. Evaluate performance in investment centers. The primary basis for evaluating performance in investment centers is return on investment (ROI). The formula for computing ROI for investment centers is Controllable margin ÷ Average operating assets. a 5. Explain the difference between ROI and residual income. ROI is controllable margin divided by average operating assets. Residual income is the income that remains after subtracting the minimum rate of return on a company’s average operating assets. ROI sometimes provides misleading results because profitable investments are often rejected when the investment reduces ROI but increases overall profitability.