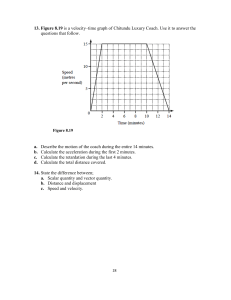
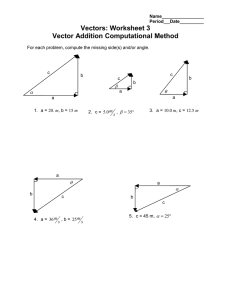
1 Worksheet (AS) Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet. 1 Five speeds are listed. [1] 6 m s−1 6 cm s−1 6 km s−1 6 m h−1 Starting with the smallest, what is the order of increasing magnitude of these speeds? A B C D 2 6 m s−1 → 6 cm s−1 → 6 km s−1 → 6 m h−1 6 cm s−1→ 6 m s−1 → 6 km s−1 → 6 m h−1 6 m h−1 → 6 cm s−1 → 6 km s−1 → 6 m s−1 6 m h−1 → 6 cm s−1 → 6 m s−1→ 6 km s−1 Which of the following correctly lists one scalar and one vector quantity? A B C D 3 Scalar quantity displacement speed speed velocity [1] Vector quantity velocity displacement distance displacement The diagram shows a strip of paper tape pulled at constant speed under a ticker-timer. The ticker-timer makes 50 dots per second. [1] 40 cm What was the speed of the object? A 4 cm s−1 B 10 cm s−1 C 200 cm s−1 D 400 cm s−1 4 A racing car is fitted with a computer that records the distance travelled every second. Which set of readings shows that the car is decreasing in speed? Time / s 0 1 2 A Distance / m 0 25 50 AS and A Level Physics Time / s 0 1 2 B Distance / m 0 50 100 Time / s 0 1 2 C Distance / m 0 40 60 Time / s 0 1 2 [1] D Distance / m 0 25 60 Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1 1 Worksheet (AS) 5 Three velocity vectors, u, v and X are shown in the diagram. [1] Which statement about the vectors is correct? A B C D 6 v added to u produces a resultant X u added to X produces a resultant v the magnitude of v equals the sum of the magnitude of u and the magnitude of X the magnitude of u equals the sum of the magnitude of X and the magnitude of v. Explain what is meant by: a a scalar quantity b a vector quantity. [1] [1] 7 Name any three scalar quantities. [3] 8 a Define the velocity of an object. b Use your answer to a to explain why velocity is a vector quantity. [1] [2] 9 Cannons are being fired in a mock battle scene. The spectators are at a safe distance of 600 m from the cannons. Calculate how long it would take for the sound from the cannons to reach the spectators. (Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.) [2] 10 A small insect travels a distance of 24 cm in a time of 4.0 minutes. Calculate the average speed of the insect in m s−1. [2] 11 The displacement–time graph for an object is shown below. a What does the gradient of a displacement–time graph represent? b Describe the journey of the object. c Calculate the velocity of the object at 2.0 s. [1] [2] [2] 12 A cyclist travels a distance of 3.2 km in 15 minutes. She rests for 30 minutes. She then covers a further distance of 6.2 km in a time of 40 minutes. Calculate the average speed of the cyclist in m s−1: a for the first 15 minutes of the journey b for the total journey. AS and A Level Physics [2] [2] Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 2 1 Worksheet (AS) 13 The diagram shows the displacement–time graph for an object. Calculate the velocity of the object at times: a 4.0 s b 8.0 s. [2] [2] 14 The diagram below shows a stone moving in a horizontal circle of radius 70 cm. The stone takes a time of 0.62 s for each revolution. a Calculate the speed of the stone. (Hint: In a time of 0.62 s, the stone travels a distance equal to the circumference of the circle.) b The stone starts at point A. What is the magnitude of the displacement of the stone from A after a time of: i 0.31 s ii 0.62 s? [2] [1] [1] 15 The table below shows the time taken (t) and the displacement (s) of a trolley rolling down a ramp. Time / s 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 Displacement / 10−2 m 0 0.8 3.0 6.8 12.0 18.9 27.0 a Plot a graph of displacement against time. (Make sure that you sketch a smooth curve.) b Describe the motion of the trolley. Explain your answer. c By drawing tangents to the curve at times 0.2 s and 0.5 s, determine the velocities of the trolley at these times. d The acceleration a of the trolley is given by: a= [2] [2] [2] change in velocity time taken Use the equation above and your answers to c to determine the acceleration a of the trolley. [2] Total: AS and A Level Physics 42 Score: Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 % 3