Describing Motion
advertisement

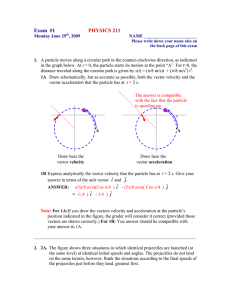
Describing Motion Picturing Motion Motion Diagrams – A series of images of a moving object Particle Model Particle Model – Replacing an object by a single point. – Example Ticker Timer Lab Vectors and Scalars A quantity that has only magnitude is referred to as a scalar quantity A quantity that has magnitude and direction is referred to as a vector quantity – The arrow head indicates direction, while the length of the arrow indicates magnitude Vector Diagrams Interpret the motion of the following diagram. What would a gradually increasing velocity vector look like? Draw it. Time Intervals and Displacement Displacement is the change in position of an object (defines the distance and direction between two positions) – Therefore d =df - di Time interval is the difference between ti and tf – Therefore t =tf – ti Velocity and Acceleration Average Velocity – Simply the slope of a Position vs. Time Graph V = d / t = (df – di) / (tf – ti) Average Acceleration – Simply the slope of a Velocity vs. Time Graph a= v / t = (vf – vi) / (tf – ti)