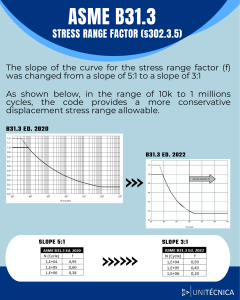
B31.3 (Process Piping) T: Minimum thickness in accordance with purchase specifications tm: minimum required thickness c: sum of allowances; corrosion, erosion, mechanical (thread depth, groove depth…) t: pressure design thickness T> tm + manufacture tolerance (usually 12.56% for seamless pipes and 0.3% for welded pipes) tm=t+c t formulas 3a & 3b (page 47) (for t<D/6 & P>0.385SE) S: basic allowable stress; Table A-1 (page 194) E: Quality factors - Casting quality factor Ec: Table A-1A (page 375); when extensive surface examination is to be applied those factors can be reduced as per Table 302.3.3C (page 43) Longitudinal Weld Joint Quality Factor Ej: Table A-1B (page 376); when extensive joint examination is to be applied those factors can be reduced as per Table 302.3.4 (page 45) W: Weld Joint Strength Reduction Factor, for elevated temperatures and only applicable for longitudinal welds (straight or helical) (page 48). It accounts for possible reduction in long-term strength of joints compared to base materials. Y: Coefficient from Table 304.1.1 for t<D/6 (page 50). Whenever d appears in formulas, it refers to measured inside diameter. For pressure design calculations it refers to the maximum allowable wall thickness under purchase specifications. Table 314.2.1 (page 64): minimum schedule of components with external threads t tm T (0.875T>=tm)x(choosing T) + (0.875T<tm)x(choosing T’>T) External Pressure & stiffening requirements: same as pressure vessels (ASME 8 div1 UG28-30) Bends: 𝑃𝐷 𝑡= 𝑆𝐸𝑊 2( + 𝑃𝑌) 𝐼 I depends on the bend radius (intrados: 4𝑅1 −1 𝐷 4𝑅1 −2 𝐷 4𝑅1 𝐷 ; extrados: 4𝑅1 𝐷 +1 +2 ; where R1 is the centreline radius) B31.8 (Gas transmission) The design wall thickness is determined by the formula: 𝑡𝑑 = 𝑃𝐷 2𝑆𝐸𝐹𝑇 But S here refers to specified minimum yield strength (SMYS) Table D-1 (page 161) T: temperature de-rating factor Table 841.1.8-1 (page 64) E: Table 841.1.7-1 (page 64) F: Design factors accounting for population density around the pipeline area. Its basic values are specified in Table 841.1.6-1 (page 62) Location classes: 840.3 (page 59) B31.4 (Liquids and slurries) The design wall thickness is determined by the formula: 𝑡𝑑 = 𝑃𝐷 2𝑆𝐸𝐹 S: specified minimum yield strength (SMYS) refer to ASME B31.8 E: Weld joint factor Table 403.2.1-1 (page 38) F: Design factors accounting for population density around the pipeline area. Its basic values are specified in Table 403.3.1- 1 (page 39) Sustained loads 𝑆𝐿 = √(|𝑆𝑎 |2 + 𝑆𝑏 )² + (2𝑆𝑡 )² 𝑆𝑎 = √(𝐼𝑖 𝑀𝑖 )² + (𝐼𝑜 𝑀𝑜 )² 𝐼𝑎 𝐹𝑎 𝐼𝑡 𝑀𝑡 ; 𝑆𝑡 = ; 𝑆𝑏 = 𝐴 2𝑍 𝑍 The calculated stress is to be compared to Sh (Table A-1 -page 194- & Table A-1M). Displacement loads 𝑆𝐸 = √(|𝑆𝑎 |2 + 𝑆𝑏 )² + (2𝑆𝑡 )² Stresses due to axial forces, bending and torsion moments are calculated as for sustained loads except that the forces and moments indexes are replaced by SIF (ASME B31J). The stress calculated according to the previous formula is to be compared to the allowable stress range: 𝑆𝐴 = 𝑓(1.25𝑆𝑐 + 0.25𝑆ℎ ) 𝑓 = 6. 𝑁 −2 ≤ 𝑓𝑚 fm : maximum value of stress range factor; Ferrous material + SPMTS ≤517 MPa + metal temperatures ≤371°C fm=1.2 Otherwise fm = 1.0 N: equivalent number of full displacement cycles during the expected service life of the piping system