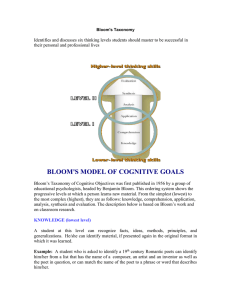
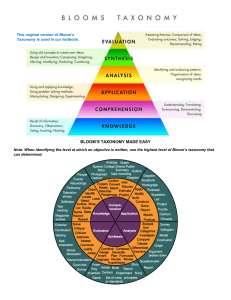
Bloom et al.'s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain LEVEL KNOWLEDGE COMPREHENSION DEFINITION Student recalls or recognizes information, ideas, and principles in the approximate form in which they were learned. Student translates, comprehends, or interprets information based on prior learning. SAMPLE VERBS SAMPLE BEHAVIORS Write List Label Name State Define The student will define the 6 levels of Bloom's taxonomy of the cognitive domain. Explain Summarize Paraphrase Describe Illustrate The student will explain the purpose of Bloom's taxonomy of the cognitive domain. Bloom et al.'s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain LEVEL DEFINITION SAMPLE VERBS SAMPLE BEHAVIORS APPLICATION Student selects, transfers, and uses data and principles to complete a problem or task with a minimum of direction. Use Compute Solve Demonstrate Apply Construct The student will write an instructional objective for each level of Bloom's taxonomy. ANALYSIS Student distinguishes, classifies, and relates the assumptions, hypotheses, evidence, or structure of a statement or question. Analyze Categorize Compare Contrast Separate The student will compare and contrast the cognitive and affective domains. Bloom et al.'s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain SAMPLE VERBS SAMPLE BEHAVIORS SYNTHESIS Student originates, integrates, and combines ideas into a product, plan or proposal that is new to him or her. Create Design Hypothesize Invent Develop The student will design a classification scheme for writing educational objectives that combines the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. EVALUATION Student appraises, assesses, or critiques on a basis of specific standards and criteria. Judge Recommend Critique Justify The student will judge the effectiveness of writing objectives using Bloom's taxonomy. LEVEL DEFINITION In general, research over the last 40 years has confirmed the taxonomy as a hierarchy with the exception of the last two levels. It is uncertain at this time whether synthesis and evaluation should be reversed (i.e., evaluation is less difficult to accomplish than synthesis) or whether synthesis and evaluation are at the same level of difficulty but use different cognitive processes. In any case it is clear that students can "know" about a topic or subject at different levels. While most teacher-made tests still test at the lower levels of the taxonomy, research has shown that students remember more when they have learned to handle the topic at the higher levels of the taxonomy. This is because more elaboration is required, a principle of learning based on finding from the information processing approach to learning The revised taxonomy (Anderson and Krathwohl, 2001) incorporates both the kind of knowledge to be learned (knowledge dimension) and the process used to learn (cognitive process), allowing for the instructional designer to efficiently align objectives to assessment techniques. Both dimensions are illustrated in the following table that can be used to help write clear, focused objectives. For teachers, the objectives for an entire unit can be plotted out on the taxonomy table, ensuring that all levels of the cognitive process are used and that students learn different types of knowledge. For example, if a math teacher were planning a comprehensive unit, he or she could use the taxonomy table to make sure that students not only learned different mathematical procedures, but also learned how to think (meta-cognition) about the best way to solve math problems. Teachers may also use the new taxonomy dimensions to examine current objectives in units, and to revise the objectives so that they will align with one another, and with assessments. Using the revised taxonomy by referring to the charted dimensions may give teachers a place to start when revising units to better align with new standards-based requirements as well. Remember: Recognizing, Recalling Understand: Interpreting, exemplifying, classifying, summarizing, inferring, comparing, explaining Apply: Executing, implementing Analyze: Differentiating, organizing, attributing Evaluate: checking, critiquing Create: generating, planning, producing How can the new table help instructional designers and teachers? Bloom's Taxonomy The Cognitive Process Dimension The Knowledge Dimension Remember Understand Apply Analyze Evaluate Factual List Summarize Classify Order Rank Knowledge Conceptual Describe Interpret Experiment Explain Assess Knowledge Procedural Tabulate Predict Calculate Differentiate Conclude Knowledge MetaAppropriate Cognitive Execute Construct Achieve Action Use Knowledge Create Combine Plan Compose Actualize EXAMPLES • Remember: Describe where Goldilocks lived. • Understand: Summarize what the Goldilocks story was about. • Apply: Construct a theory as to why Goldilocks went into the house. • Analyze: Differentiate between how Goldilocks reacted and how you would react in each story event. • Evaluate: Assess whether or not you think this really happened to Goldilocks. • Create: Compose a song, skit, poem, or rap to convey the Goldilocks story in a new form. Remembering: Retrieving, recognizing, and recalling relevant knowledge from long-term memory. Understanding: Constructing meaning from oral, written, and graphic messages through interpreting, exemplifying, classifying, summarizing, inferring, comparing, and explaining. Applying: Carrying out or using a procedure through executing, or implementing. Analyzing: Breaking material into constituent parts, determining how the parts relate to one another and to an overall structure or purpose through differentiating, organizing, and attributing. Evaluating: Making judgments based on criteria and standards through checking and critiquing. Creating: Putting elements together to form a coherent or functional whole; reorganizing elements into a new pattern or structure through generating, planning, or producing. Layer one is Remembering where memory is used to produce definitions, fact charts, lists, or recitations. Layer two, Understanding , includes producing drawings or summaries to demonstrate understanding Layer three, Applying where concepts are applied to new situations through products like models, presentations, interviews or simulations. Distinguishing between the parts is the focus of Layer four, Analyzing , by creating spreadsheets, surveys, charts, or diagrams. Layer five is Evaluating Critiques, recommendations, and reports are some of the products that can be created to demonstrate Layer six, Creating , puts the parts together in a new way with products such as puppet shows, cartoons, or new games. All of the levels of the Revised Bloom's Taxonomy come together to form a complete learning experience just as the animation comes together to form a complete cake. Animation developed and created by Melanie Argiro, Mary Forehand I. KNOWLEDGE LEVEL • DEFINED AS THE REMEMBERING OF PREVIOUSLY LEARNED MATERIAL. • May involve the recall of a wide range of material (from specific facts to complete theories) but all that is required is the bringing to mind of the appropriate information. • Represents the lowest level of learning outcomes in the cognitive domain. KNOWLEDGE Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers • - KEY WORDS: Who - what When - omit Which - choose How - define Show - spell Match - name Tell - recall -why -where - find - label - list - relate - select KNOWLEDGE LEVEL QUESTIONS • • • • • • • What is …? Where is …? How did ________ happen? Why did … ? How would you show …? Who were the main …? Which one …? KNOWLEDGE LEVEL QUESTIONS • • • • • • • How is … ? When did ____ happen? How would you explain … ? How would you describe …? Can you recall …? Can you list three …? Who was …? 1. MEMORY LEVEL • QUESTIONS WHICH REQUIRE THE LEARNER TO RECALL OR RECOGNIZE INFORMATION. • Tell - who • List - what • Where - does • State - describe COMPREHENSION LEVEL • ABILITY TO GRASP THE MEANING OF A MATERIAL. • Translating the material from one form to another. • Interpreting the material (explaining or summarizing) • Estimating future trends/predicting consequences of effects. COMPREHENSION LEVEL • Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by: - organizing -comparing -translating -interpreting -giving descriptions and -stating main ideas. COMPREHENSION LEVEL KEY WORDS • • • • • • • • Compare -contrast Demonstrate -interpret Explain -extend Illustrate -infer Outline -relate Rephrase -translate Summarize -show classify COMPREHENSION QUESTIONS • • • • • • • How would you classify the type of…? How would you compare…? Contrast…? Will you state or interpret in your own words …? How would you rephrase the meaning of …? What facts or ideas show …? What is the main idea of …? Which statements support…? COMPREHENSION QUESTIONS • Can you explain what is happening …? What is meant …? • What can you say about…? • Which is the best answer …? • How would you summarize …? 2.TRANSLATION LEVEL • QUESTIONS WHICH REQUIRE THE LEARNER TO CHANGE INFORMATION INTO DIFFERENT SYMBOLIC FORM OR LANGUAGE. • Tell in your own words… • Construct a graph with the information contained in the paragraph… • Write a paragraph about the information in the table… • Complete the following paragraph with reference to the diagram… • Design a poster illustrating the different types of … APPLICATION LEVEL • THE ABILITY TO USE LEARNED MATERIAL IN NEW AND CONCRETE SITUATIONS. • Include the application of such things as rules, methods, concepts, principles, laws and theories. • Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques, and rules in a different way. APPLICATION KEY WORDS • • • • • • • • Apply Construct Make use of Identify Experiment with SelectInterview Model -choose -plan -utilize -solve -build -develop -organize APPLICATION QUESTIONS • How would you use …? • What examples can you find to …? • How would you solve … using what you’ve learned …? • How would you organize … to show …? • How would you show your understanding of …? • What approach would you use to …? • How would you apply what you learned to develop…? APPLICATION QUESTIONS • • • • • What other way would you plan to …? What would result if …? Can you make use of the facts to …? What facts would you select to show …? What questions would you ask in an interview with …? 3.INTERPRETATION LEVEL • REQUIRE THE LEARNER TO DISCOVER RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FACTS, GENERALIZATIONS, DEFINITIONS AND SKILLS. • Compare and contrast … • Find the implications … • Explain the relationship … • Show cause and effect … • Give evident items in the list … • Find the relevant items in the list … • Draw conclusions from the figures in the table … 4. APPLICATION LEVEL • QUESTIONS THAT REQUIRE THE LEARNER TO SOLVE A LIFE-LIKE PROBLEM THAT REQUIRES THE IDENTIFICATION OF THE ISSUES AND THE SELECTION AND USE OF APPROPRIATE GENERALIZATIONS AND SKILLS. APPLICATION LEVEL • • • • DEMONSTRATE … USE THE GIVEN INFORMATION TO SOLVE … SHOW HOW YOU MIGHT USE … WRITE A RESEARCH PAPER ACCORDING TO THE PROCEDURE THAT HAVE BEEN CAUGHT … • CONSIDER THE IMPLICATION OF … ANALYSIS LEVEL • ABILITY TO BREAK DOWN A MATERIAL INTO ITS COMPONENT PARTS SO THAT ITS ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE MAY BE UNDERSTOOD. • Include: 1. Identification of the parts 2. Analysis of the relationships between the parts. 3. Recognition of the organizational principles involved. REQUIRE AN UNDERSTANDING OF BOTH CONTENT AND STRUCTURAL FORM ANALYSIS • EXAMINE AND BREAK INFORMATION INTO PARTS BY IDENTIFYING MOTIVES OR CAUSES. • MAKE INFERENCES TO FIND EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT GENERALIZATIONS. ANALYIS – KEY WORDS • • • • • • • • • • • • • ANALYZE CLASSIFY CONTRAST DISSECT EXAMINE SIMPLIFY TAKE PART IN DISTINGUISH LIST THEME FUNCTION INFERENCE CONCLUSION -CATEGORIZE -COMPARE -DISCOVER -DIVIDE -INSPECT -SURVEY -TEST FOR -LIST -DISTINCTION -RELATIONSHIPS -MOTIVE -ASSUMPTION ANALYSIS - QUESTIONS • • • • • • • • What are the parts or features of …? How is … related to …? Why do you think …? What is the theme …? What motive is there …? Can you list the parts …? What inference can you make …? What conclusions can you draw …? ANALYSIS - QUESTIONS • • • • • • • How would you classify …? How would you categorize …? Can you identify the different parts …? What evidence can you find …? What is the relationship between …? What is the function of …? What ideas justify …? 5. ANALYSIS LEVEL • REQUIRE THE LEARNER TO SOLVE PROBLEMS IN THE LIGHT OF CONSCIOUS KNOWLEDGE OF THE PARTS AND FORMS OF THINKING. ANALYSIS LEVEL • • • • • • • • • • • HOW … WHY … REASON FOR … WHAT ARE THE CONDITIONS … SPECIFY THE CAUSES … ARRANGE … WHAT ARE THE STEPS IN THE PROCESS … LIST ALL THE PROBLEMS … ANALYZE THE EVIDENCE TO EACH CONCLUSION … WHICH CONDITIONS ARE NECESSARY FOR … APPLY SCIENTIFIC METHOD … SYNTHESIS LEVEL • ABILITY TO PUT PARTS TOGETHER TO FORM A NEW WHOLE. • May involve: 1. Production of a unique communication (theme of speech) 2. A plan of operation (research proposal) 3. A set of abstract relations (scheme of classifying information). SYNTHESIS • STRESS CREATIVE BEHAVIOR WITH MAJOR EMPHASIS ON THE FORMULATION OF NEW PATTERNS OF STRUCTURES. • COMPILED INFORMATION TOGETHER IN A DIFFERENT WAY BY COMBINING ELEMENTS IN A NEW PATTERN OR PROPOSING ALTERNATIVE SOLUTIONS. SYNTHESIS – KEY WORDS • • • • • • • • • • • • Build Compile Create Invert Plan Solve Discuss Improve Choose Imagine Suppose Delete -estimate -solution -original -modify -minimize -improve -theorize -maximize -compose -elaborate -design -happen -formulate -combine -make-up -construct -predict -develop -originate -propose -change -adapt -test -change SYNTHESIS - QUESTIONS • What changes would you make to solve …? • How would you improve…? • What would happen if …?can you elaborate on the reason …? • Can you propose an alternative …? • Can you invent …? • How would you adapt ___ to create a different …? • How would you change (modify) the plot/plan …? SYNTHESIS - QUESTIONS • What could be done to minimize (maximize) …? • What way would you design …? • What could be done to improve (change) …? • Suppose you could … what would you do …? • How would you test …? • Can you formulate a theory for …? SYNTHESIS -QUESTIONS • Can you predict the outcome if …? • How would you estimate the results for …? • What facts can you compile …? • Can you construct a model that would change …? • Can you think of an original way for the …? 6. SYNTHESIS LEVEL • QUESTIONS THAT REQUIRE THE LEARNER TO SOLVE A PROBLEM THAT REQUIRE ORIGINAL, CREATIVE THINKING. • REQUIRES PRODUCTIVE THINKING, ORIGINALITY AND IMAGINATION. SYNTHESIS LEVEL • • • • • • • Create … - Devise … Design … - Suppose … Develop … What are the possible courses of action What hypothesis can you suggest … Think of all the different ways … In what ways can you improve … EVALUATION LEVEL • ABILITY TO JUDGE THE VALUE OF A MATERIAL, STATEMENT, NOVEL, POEM, RESEARCH REPORT, ETC. FOR A GIVEN PURPOSE. • Judgments are based on a definite criteria. • Internal criteria – organization • External criteria – relevance to the purpose. EVALUATION • Highest in the cognitive hierarchy because they contain elements of all the other categories plus value judgments based on clearly defined criteria. • Present and defend opinions by making judgmen5ts about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. EVALUATION – KEY WORDS • • • • • • • • Award -choose -prove Criticize -determine -decide Compare -recommend -judge Opinion -influence -agree Estimate -support -justify Rule on -appraise -deduct Interpret-perceive -value Disprove-prioritize -assess EVALUATION – KEY WORDS • • • • • • Dispute Importance Defend Measure Select Explain -mark -conclude -evaluate -rate -prioritize -criteria EVALUATION - QUESTIONS • Do you agree with the actions …? with the outcome …? • What is your opinion of …? • How would you prove …? Disprove …? • Can you assess the value or importance of …? • Would it be better …? EVALUATION - QUESTIONS • • • • Why did they (the character) choose …? What would you recommend …? How would you rate the …? what would you cite to defend the actions …? • How would you evaluate …? • How could you determine …? • How would you prioritize …? EVALUATION - QUESTIONS • What choice would you have made …? • What would you select …? • What judgment would you make about …? • Based on what you know, how would you explain …? • What information would you use to support the view …? EVALUATION - QUESTIONS • How would you justify …? • What data were used to make the conclusion …? • Why was it better that …? • How would you prioritize the facts …? • How would you compare the ideas …? People …? 7. EVALUATION LEVEL • QUESTIONS THAT REQUIRE THE LEARNER TO MAKE JUDGMENT OF GOOD OR BAD, RIGHT OR WRONG, ACCORDING TO STANDARDS HE DESIGNATES. • The learner judges a material in accordance with a standard or set of criteria. TAXONOMY OF QUESTIONS THEY ARE SEQUENTIAL AND CUMMULATIVE