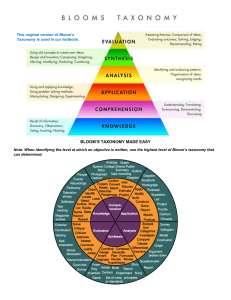
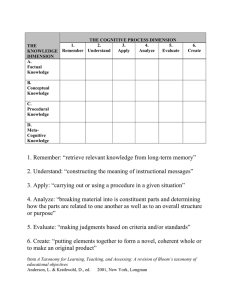
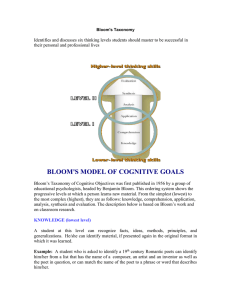
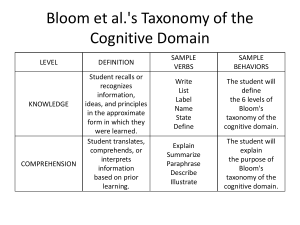
Blooms Taxonomy Bloom's Taxonomy is a hierarchical framework that classifies educational objectives and cognitive skills based on their complexity. It was developed by Benjamin Bloom in the 1950s and has become widely used in education to guide curriculum design, assessment, and instruction. Bloom's Taxonomy consists of six levels, which are arranged in a pyramid-like structure, with each level building upon the previous one. The levels, listed in ascending order of complexity, are: 1. Knowledge: This level represents the basic recall or recognition of information. It involves remembering facts, terms, or concepts. Examples of activities at this level include defining terms, listing facts, or identifying elements. 2. Comprehension: This level involves understanding the meaning or interpretation of information. It goes beyond simple memorization and requires the ability to explain ideas or concepts in one's own words. Activities at this level include summarizing, paraphrasing, or interpreting information. 3. Application: At this level, learners can apply their knowledge and understanding to solve problems or complete tasks. They can use acquired information in new situations and demonstrate practical application of concepts. Examples of activities at this level include solving mathematical equations, conducting experiments, or applying principles to real-world scenarios. 4. Analysis: This level involves breaking down complex information into its constituent parts and examining their relationships. Learners at this level can identify patterns, analyze data, and make connections between different elements. Activities at this level include categorizing, comparing and contrasting, or identifying cause and effect relationships. 5. Synthesis: At this level, learners can integrate and combine elements to create something new. They can generate original ideas, design solutions, or develop alternative approaches. Activities at this level include designing experiments, creating artwork, or writing essays that require the synthesis of various concepts. 6. Evaluation: This level represents the highest level of cognitive complexity. Learners at this level can make judgments and assessments based on criteria or standards. They can critically evaluate information, arguments, or methods and provide reasoned judgments. Activities at this level include critiquing, defending a position, or assessing the validity of a hypothesis. Bloom's Taxonomy provides educators with a framework for designing learning objectives, developing appropriate assessments, and selecting instructional strategies that align with the desired level of cognitive engagement. It encourages higher-order thinking skills and promotes deeper understanding and application of knowledge.