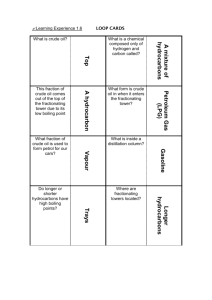
Crude oil Formation 1. Plankton die and fall to the bottom of the sea 2. Sediemnts build up on the plankton over millions of year, heat and pressurise them, turns the plankton into oil 3. Crude oil rises up though porous rock 4. Crue oil becomes trapped by non-porous ruck 5. Crude oil is collected by drilling though layers of rock What is crude oil? - Crude oil is made almost entirely from hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons only contain only Carbon and Hydrogen How is crude oil separated? 1. The crude oil evaporated 2. The vaporised crude oil will enter the fractionating column 3. As it cools it will either collect on meshes or rise until it cools to a liquid The longer the chains the more intermolecular bonds you have and the higher the boiling point There is a temperature gradient so the hydrocarbons with high boiling points will condensate at the lower, hotter, areas. What is crude oil How does the size of the hydrocarbons affect its properties A mix of hydrocarbons at different chain lengths Small Big hydrocarobons hydrocarbons Boiling Lower Higher points Flammability Higher Lower Clenliness of Cleaner Dirtier flame Viscosity Lower Higher Gas - Cookers Petrol - Cars Kerosene - Aircraft Diesel – Trains, cars, lorries Heavy fuel Bitumen – Road surface Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons. What is a mixture? What are hydrocarbons? A mixture is a collection of different molocules, hydrocarbons only contain hydrogen and carbon The hydrocarbons have different properties. Which of these properties does separtoin by fractional distaillation depend on? Boiling point Two hydrocarbons include decane and pentane. Decane has a larger size Decane has a higher boiling point Pentane is more runny Pentane catches fire more easlity Decane burns with the smokier flame Pentane collects higher up the fractionating column Kerosene is a fraction of crude oil used for aeroplanes. Is kerosene a pure substance or a mixture. Kerosene is a mixture as it is separated based on having a range of sizes, and not all of the liquid is identical