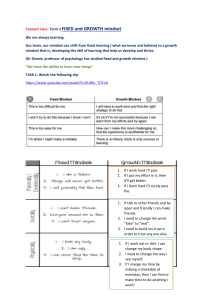
LESSON 11 Setting Goals for Success Guide Questions Is it possible for a person not to have any goal? Is it possible for a person to accomplish all his goals that he has no more goals to achieve? Importance of Goals A goal is a target objective or objective of a motivated and directed change of behavior. ? % & @ Goals may vary an depend on the values and priorities of the individual. Goals are important for behavior to make sense. Importance of Goal Setting Setting goals direct the individuals behavior. Goals can determine the individual’s progress towards accomplishing it. Goals serve as guide to discipline behavior. Goals keep the individual busy. Goals motivate the individual. Self- efficacy Proposed by Albert Bandura The person’s belief about his capacity to exercise some measure of control over his behavior and over events that take place around. Self- efficacy Factors affecting self-efficacy Mastery of learning and skills A good social model A persuasive environment Emotional stability Mindset Carol Dweck’s Types of Mindset Fixed mindset- believes that their character, creativity and intelligence are innate. Growth mindset – does not bank on given qualities for them to be successful but instead they want to be challenged. Final Goal Adler’s types of final Goal Superiority – selfish; lacks social interest or community feeling. Success – success of the community; high social interest or community feeling. Goal – orientation Theory Two types of Goal Orientation Performance – goal – concerned with impressing other people. Learning- goal – concerned with learning something from the experience. CREDITS: This presentation template was created by Slidesgo, and includes icons by Flaticon, and infographics & images by Freepik Locke and Latham’s Goal-Setting Theory FACTORS AFFECTING THE QUALITY OF THE GOAL 01 02 GOAL DIFFICULTY GOAL SPECIFICITY 03 04 05 DEADLINE FEEDBACK GOAL COMMITMENT