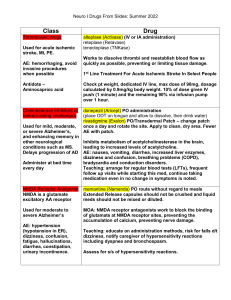
3️⃣ Parkin & MS Subject 106 Video Axons = Myeline Sheets Sclerosis - brain and spinal cord (disease in CNS), autoimmune disorder results in sensory and motor problems protected by blood brain barrier Discussion: Types of Multiple Sclerosis 1. Replasing - Remitting (RRMS) = common cause of inflamed t-cells 2. Secondary Progressive (SPMS) 3. Primary Progressive (PPMS) 4. Progressive - Relapsing (PRMS) Symptoms: 20-40yrs Charcotic Neurologic Triad = Dysarthria, Nystagmus, Intention Tremors Have Plaques (in ANS) Lhermiette’s Signs = electric signs Diagnosis is MRI Multiple Sclerosis - myeline sheet protects axons chronic typically progressive disease involving damage to the sheaths of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord slow growing infection attack myelin sheath muscle weakness, spasticity, diplopia (two images) elevated IgG in CSF, (MRI reveals lesions Treatment Goal: = decrease inflammatory process Symptoms: hearing, blurred vission, dysarthria, dysphagia, constipation 1. Acute Attack = (exacerbation (worsening), motor weakness, optic neuritis, spasticity Medications: prednisone - glucocorticoids, ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) 2. Remission = spasticity, clinical MS Parkin & MS 1 Medications: Betaseron, Imuran-suppress 3. Chronic Progressive (wheel chair-bond) - paraplysis -progress Medications: Cytoxan, ACTH 1. Centrally Acting Muscle Relaxants Baclofen - to treat muscle spasticity (drowsiness, headache, diarrhea, abdo disease) 2. Peripherally Acting Muscle Dantrolene (Dantrium) - to treat spasticity TEST: 1. Dystthira, 2. Nystagmus Diagnostic is = MRI, 3 .prednisone, 4.multiple sclerosis, 5.prenisone, 6.Betaseron, 7.Dysarthria, 8.Baclofen, 9.Dantrium, 10.Nystagmus Lesson 5: Parkinson’s Disease (PD) = Neurotransmitter: Dopamine 1st Video: PD 600k to 1M 60k per year has PD happens when age increase Test Lab Test Cholesterol Medical History Motor Movement Signs Resting Tremors Stiffness Slow movement Other SIgns Consti, depression, cognitive, loss of smell Dopamine stops in the brain Factors affecting PD is unknown but it can be genetic or environmental Parkin & MS 2 To ease symptoms: Have movement disorder specialist Individualized 2nd Video: Dopamine produces in 3 parts = substansia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus made in tyrosine purpose is to feel pleasure, shopping, smelling 4 Types: Reward Reinforcement Movement Prolactin = SE: low dopamine, postpartum depression re-uptake of dopamine by postsynaptic vesicles presynaptic 3rd Video: MAO Inhibitor treats depression synaptic cleft Dopamine Synthesis: Levodopa → dopamine Monoamine Oxidase MAO & COMT Inhibitor (enzymes) degrade dopamine Earliest develop anti-depressant SE: Increase BP & blood sugar levels SE of MOA: Insomia, headache, dry mouth Can be combine with MAOI painkiller cold & allergies antidepressants Discussion Parkinson’s Disease neurologic disorder by muscle rigidity, tremor, bradykinesia, loss of postural chronic progressive involving substansia nigra & basal ganglia resulting in decease dopa and increase acetylcholine Dopamine: Inhibitory neurotransmitter Parkin & MS 3 Acetylcholine: Excitatory “” Signs & Symptoms muscle rigidity/stiffness = passive movement tremor = pill rolling bradykinesia = arms, eyes decrease blink, loss smell Tyrosine → Levodopa → Dopamine Goal: aimed at correcting the neurotransmitter imbalance all forms of treatment for PD are palliative, not curaitve DRUGS: 1. Anticholinergic (Symphathetic) reduces excessive cholinergic activity cliemts with minimal symptoms decrease rigidity decrease some tremors but minimal effect on bradykinesia Drug of Choice = Cogentin (Benztropine Mesylate) SE: nausea, dry mouth, nervousness, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention Caution: narrow-angle glaucome, GI obstruction, ulcerative colitis, benign prostoratic, hyperplasia(BPH) NR: monitor vs, urine output, bowel sounds, increase fiber/fluid in diet provide candies, gum, eye examination 2. Dopaminergics (Dopamine Agonist)) - stimulate dopamine receptor a. Levodopa - amino acid like tyrosine most effective drug dopamine replacement agent precursor of dopamine given in increase dosage (DOPA DECARBOXYLASE) short half life (3-4x day) initially low does then gradually increase weekly maximum effect after 2-4mos b. Carbidopa alternative to levodopa inhibits the enzymes DOPA DECARBOXYLASE periphery → periphery →more→ levodopa reaches the blood brain barrier combined with levodopa in a ratio of 1:10 sinemet 10-100 )brand name) Advantage: more dopa reaches the basal ganglia, single dose/day of levodopa to achieved desired effect SE: n/v, dystonic movement, psychotic, behavior, cardiac, dysrhythmia, palpitation & orthostatic hypertension 3. Dopamine Agonists - stimulate the dopamine receptors Parkin & MS 4 a. Amantadine HCI symmetrical (brand name) (anti-parkinsons) believe to release dopa & noreph SE: GI Distress, nervoucness, anxiety, Livdeo Reticularis b. Parlodel (Bromocriptine Mesylate) Ergot derivative with potent dopa recpetor agonist activity in CNS, CV, & GI systems activity postsynaptic dopa receptors in the corpus stratum substitute for levodopa 4. Monoamine Oxidase - B (MAO-B) Inhibitors Enzyme causes the catabolism of dopa increase the activity of dopa a.Selegine HCI (Eldepyl, Carbex) inhibits MAO-B thus prolong effect of Levodopa Drug Interactions: VIT-B increase DOPA DECARBOXYLASE action Anti-psychotic drugs - block dopamine receptors Large dose of Selegiline = Hypertensive Crisis 5. Cathecol-o-methyl Trasferase (COMT) Inhibitors enzyme that inactie dopamine Increase amount of levodopa concentration in brain Tolcapone, Entacapone SE: dyskinesia, urine discoloration, anxiety, abdo pain, consti, dyspeia, dizzness NR: obtain baseline data, taking levodopa should be monitored for orthosatic hypertension, cardiac dysrhythmia, psychotic disturbance. receiving dopaminergic = closely monitor for dizziness and risk for fall agents should not be stooped abruptly urine maybe disclosed & wlll obtain darken with air exposure, perspiration may be dark = harmless Decrease intake of protein rich foods interfering drug transport COMT inhibitor should not be take with MAOB Inhibitor SGOT & SGPT Test: Major Signs of Parkinson’s Disease tremors muscle stiffness impaired balance & coordination Face of pt. with PD = expressionless tremors description = pill rolling Drug of choice for anti-cholinergic drug = congentin 2 symptoms can be treated for= tremors, muscle stiffness & rigidity Most effective dopaminergic drug = levodopa Parkin & MS 5 levodopa is the best drug choice instead of dopamine where = blood brain barrier enzyme that converts levodopa to dopamine = DOPA DECARBOXYLASE drugs given in combine with levodopa = caridopa substitute for levodopa = parlodel 2 enzymes that catabolyized dopamine = MAO & COMT increase BP selegilin cant be take bcoz of = anti-psychotic drug has a label warning of what = hepato - toxicity Causes of Parkinson = Genetic & Enviromental Precursor of levodopa = tyrosine funcitons of dopamine = reward, reinforcement, movement, prolactin 3 peripheral symptoms of PD = pain, numbness, tingling or muscle weakness, enzyme = SGOT & SGPT neurotransmitter = dopamin Parkin & MS 6