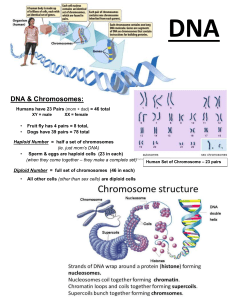
Basic Genetics What is genetic nucleus blueprint DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid RBC Functions of DNA DNA DNA Genetic code Gene Protein synthesis DNA molecules DNA → RNA → Protein Chromosome chromosomes In the ___ of every cell is the genetic information “blueprint” to construct the entire individual Genetic information found in the nucleus of every cell The blueprint is contained in the ___ DNA abbreviation meaning Each of the 100 x 1012 cells in our body contains the entire human genome except __ Genetic code for almost every organism Provide template (mold or form) for protein synthesis refers to the instructions contained in a gene that tell a cell how to make a specific protein is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. ___ are made up of DNA. the process in which cells make proteins The cell nucleus contains chromosomes made from long ___ Is a discrete block of DNA and is one of the basic structures of genome All the nuclear DNA is organized into ___ with the number varying between animal species. made up of genetic material (DNA) from your father and mother Nuclear DNA Karyotypes of some domestic species Karyotype is an individual's complete set of chromosomes Diploid A ___ cell has two complete sets of chromosomes Haploid a cell that contains a single set of chromosomes. Diploid containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. Most cells in humans are diploid, comprising 23 chromosome pairs, so 46 chromosomes in total. Cat 38 Dog 78 Pig 38 Goat 60 Sheep 54 Cattle 60 Horse 64 Alpaca, llama, Rabbit 74 Chicken 78 Chromatids Two identical parts of chromosomes Centromeres Joins chromatids together Basic Genetics Karyotypes Chromosomes are analyzed by organizing them into ___ Sex & chromosome defect Arranged by numbers and helps identify ___ & ___ In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Twenty-two of these pairs, called autosomes, look the same in both males and females. The 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, differ between males and females. The last pair of chromosomes identify the gender of individual Size ___ of the final pair of chromosome identify sex XX Same size ___ XY Different size ___ 46 Normal human will have a total of ___ chromosome Sex determination The difference between the two sexes is the key to ___ XX and XY Mammals has ___ chromosomes XY Male XX Female Sex chromosome X and Y chromosome are known as ____ Bird In ____ sex chromosome are given different names Bird Their relation to sex is opposite of that in mammals (ZZ & ZW) ZZ Male bird ZW Female bird Autosomes Chromosome other than the sex chromosome are called ____ same set Within any species, male and female has the ___ of autosomes occurring in pairs genome The autosome + the sex chromosome is = (the total set of (chromosome) Diploid or haploid cell Diploid cells Cells with full set of chromosomes (paired chromosome) Diploid cells Half of our chromosomes comes from each of our parent (23) Diploid cells Somatic cells are ___ Non-sex Somatic meaning Diploid cells Created by mitosis Haploid cells Cells with one half total number of chromosomes Gametes ___ are the only haploid cells Sex cells: sperm, egg, pollen Gametes are ___ cells ex:___ Haploid cells Created by meiosis Classification of chromosomes based on the location of centromeres Acrocentric Centromere is at one end Sub-metacentric Closer to one end than the other Metacentric In the middle Chromosome bunding (BANDING) Chromosome bunding (BANDING) Stained with Giemsa Reverse of G-banding Centromere are stained Refers to alternating light and dark region along the length of a chromosome, produced after staining with a dye Is an essential technique used in chromosome karyotyping to identify normal and abnormal chromosomes for clinical and research purpose G R C Basic Genetics Stained with quinacrine Telomeres are stained Q T sperm and egg Homogametic (XX) Heterogametic (XY) One 1x1/2 The haploid cell made in meiosis are ___ Female are __ sex Male are ___ sex Chances of female gamete containing an X chromosome is ___ Chances of obtaining XY zygote and XX zygote is ___ Mitosis Mitosis Is used for almost all of your body’s cell division needs It adds new cells during development and replace old and worn-out cells through out your life The goal of mitosis is to produce ____ genetically identical to their mother Chemically, chromosomes are consisted of mostly ___ with small amount of protein called ___ Structural function Constitute the genetic information that is passed from parent cell to offspring during mitosis, from one generation to the next through meiosis Consist of ___ strand – each is a linear arrangement of ___ Base A & G Base T and C - Daughter cell DNA; histone Histone DNA Two; nucleotides (gene) Purines Pyramids Basic Genetics 20 ____ different amino acid for the synthesis of protein Gene All the cells in the body contain the same ___ Instructions: protein coding Every gene compromise of the particular set of___ for a particular function or ___ Gene regulation The process of turning genes on and off Gene regulation Ensured that appropriate gene are expressed at the proper time Gene regulation Help and organism respond to its environment Different cell in multicellular organism may express very different set of genes, even through they contain the same DNA Mutation Uncorrected mistakes in DNA replication are called Substitution Insertion Changes the code of a single triple Changes the genetic code of all triplets following the mutation Deletion Changes the genetic code of all triplets following the mutation Locus or loci A unique chromosomal location defining the position of an individual gene or DNA sequence Two alternate forms on a gene on a pair of homologous chromosome When identical alleles of gene are present on both homologous chromosom. Homozygote Alleles Homozygous Heterozygous Gene contains different alleles of a gene. heterozygote One wild type alleles and one mutant alleles