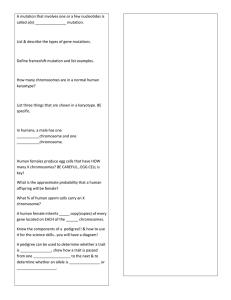
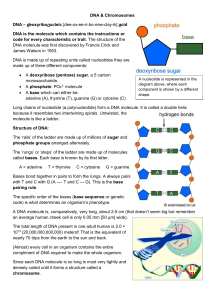
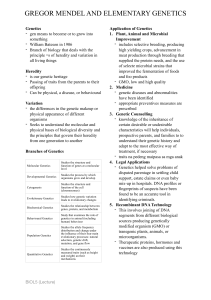
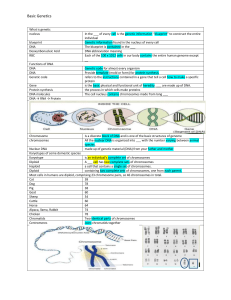
Alleles gene organism Breeding organisms by humans for specific phenotypic characteristics
advertisement

Alleles Alternate forms of a gene or DNA sequence, which occur on either of two homologous chromosomes in a diploid organism Artificial selection Breeding organisms by humans for specific phenotypic characteristics Codominance An inheritance relationship in which neither of two alleles of the same gene totally mask the other Deletion Chromosome abnormality in which part of the chromosome is missing; loss of one or more base pairs from DNA which can result in a frameshift Dominance A characteristic in which an allele that expresses its phenotype even in the presence of a recessive allele Frameshift mutation Genome A mutation that results in the misreading of the code during translation because of the change in the reading frame Genotype The structure of DNA that determines the expression of a trait Human Genome Project A project coordinated by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Department of Energy (DOE) to determine the entire nucleotide sequence of the human chromosomes Incomplete dominance A condition where a heterozygous off- spring has a phenotype that is distinctly different from, and intermediate to, the parental phenotypes Independent assortment Karyotype The law stating that pairs of genes separate independently of one another in meiosis The complete genetic material contained in an individual; the genetic complement contained in the chromosomes of a given organism, usually the haploid chromosome state All of the chromosomes in a cell or an individual organism, visible through a microscope during cell division