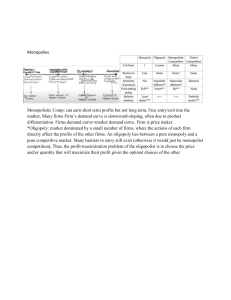
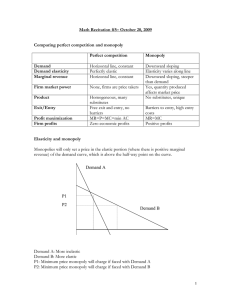
Market Structure Review Questions 1. Which market structure(s) will have zero economic profits in the long run? - The perfect competition market and the monopolistic competition market will have zero economic profits in the long run. 2. Which market structure(s) will be a price maker and have barriers to entry? - The monopoly market and oligopoly market will be price makers and have barriers to entry. 3. There are currently 8 firms in a particular market. Their firm sales are given in the table below. (1) What is the four-firm concentration ratio for this industry? (2) Would you classify it as an oligopoly? Firm 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Sales $1,000 $1,500 $2,000 $2,500 $3,000 $1,000 $500 $2,500 4 Largest Firms’ Sales = 3,000 + 2,500 + 2,500 + 2,000 = $10,000 Industry Sales = 1,000+1,500+2,000+2,500+3,000+1,000+500+2,500 = $14,000 Concentration Ratio (CR) = 10,000/14,000 = 0.7143 = 71.43% CR = 71,43% > 60% => It is an oligopoly 4. Although market structures vary widely in their characteristics, (1) what is one common aspect among all of them? (2) What is the potential calculation for your previous answer? - The common aspect among all is the principle of supply and demand. - Potential calculation for market equilibrium: + Quantity supplied (QS): the amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer at a given price. + Quantity demanded (QD): the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing to purchase at a given price. When QS = QD, the market reaches equilibrium, meaning that the market is efficiently allocating resources and satisfying consumer demand. 5. In the long run, (1) which market structures are likely to have their average cost curve just sit on top of their demand curve? (2) What does this imply for each market structure? (3) Are there any differences in the market structures you gave in your previous answer? - Two market structures are likely to have their average cost curve just sit on top of their demand curve: + Monopoly: There is only one seller with no competitors in the monopoly market. The monopolist can set its own price, and it will not have to worry about rivals. As a result, the monopolist's average cost curve will be tangent to its demand curve at the profit-maximizing output level. + Perfect competition: In perfect competition, there are many buyers and sellers, and all firms produce a homogeneous product. This means that no firm has any market power, and all firms must take the market price as given. As a result, the average cost curve for all firms in a perfectly competitive industry will be tangent to the market demand curve at the industry output level that maximizes profits for all firms. - Different between monopoly market and perfect competition market: Market power Monopoly Only one seller Yes Profit Can make economic profits Efficiency Monopolists may not be efficient because they do not have the same incentives to be efficient as firms in perfectly competitive market. Perfect competition Many sellers with identical products or services No Cannot make economic profits in the long run because new firms will enter the market Firms in perfectly competitive market are efficient because they are constantly competing with each other to produce goods and services at the lowest possible cost. 6. What market structure(s) are likely to cause a net loss to societal welfare? - Monopoly market is likely to cause a net loss to societal welfare.