Market Structures
advertisement

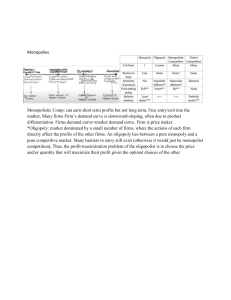
Microeconomics MARKET STRUCTURES Four Types of Competition Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Monopoly Key Terms Commodity - PC Economy of Scale - M Franchise - M Differentiation - O Collusion - O Cartel – O Regulation - MC Merger - MC commodity Product that is the same no matter who produces it Economy of scale Factors that cause a producer’s average cost per unit to fall as output rises franchise Right to sell a G/S in an exclusive market differentiation Making a product different from other similar products collusion Agreement among firms to divide market, set prices, or limit production cartel Formal organization of producers that agree to coordinate prices and production O.P.E.C. – Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries regulation Government intervention in a market that affects the production of a good merger Combination of 2 or more companies into a single firm 3 types of mergers V e C Horizontal t n i g c l a o l m e r a t e Altering Competition Price Fix – agreement among firms to charge one price for the same good Price War – series of competitive price cuts that lowers the market price below cost of production Market Structure Table firms PC MC O M goods price barriers costs regulation example graph Comparing Market Structures Category Description Numbers of firms – amount of choice for the consumer Variety of goods – amount of difference in brands Control over prices – influence each firm has on the market Barriers to entry/exit – cost of production, effects of company on the market Comparing Market Structures Category Description Start-up costs – type of G/S, knowledge and cost to produce first unit Regulation – amount of government intervention, how many rules, licensing, subsidies Example – G/S in that type of market place Demand curve – compared to a market demand Market Demand Curve $ S E D Q Perfect Competition Many, virtually unlimited None, commodity None, too many choices for individuals, firms None, low costs, easy to make, no effect Low, inexpensive lay-out None, safe, high quality Tomatoes, craft show Perfect Competition $ Firm Demand Curve S E D Q Monopolistic Competition Many firms Differentiated products Little price control Small knowledge-base Production, Distribution, Final G/S Relatively low, flat marginal returns Minimal regulation Clothing, toiletries, autos Monopolistic Competition $ S E Firm Demand D Q Oligopoly Few firms Differentiated products Some control over prices, market control Specialized knowledge Production, Distribution, G/S High start-up costs, good marginal returns Much regulation Phone, airlines, banking, entertainment Oligopoly $ S Firm Demand D Q Monopoly One firm No variety of good, only one in market Complete price control, unregulated No new competition, can’t leave industry High costs, economy of scale Public corporation Licensing, pricing, subsidized Utilities Monopoly $ S E Firm Demand D Q