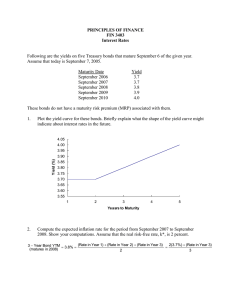
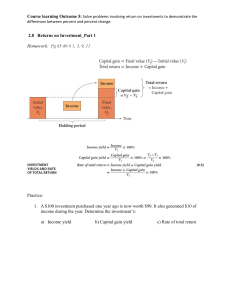
Test Bank for Ch 04 and 05 1. 2. 3. Risk that is associated with a government holding too much debt would be considered A) part of foreign exchange risk; B) country risk; C) translation exposure; D) uncovered. When investigating the term structure of interest rates, the bonds compared are A) identical except for their maturity dates; B) identical in maturity, but differ in terms of liquidity and risk; C) identical in terms of risk, but differ in terms of tax characteristics; D). identical except for their liquidity Which of the following theories does not help to explain the why the yield curve follows its traditional shape? A) the Segmented Markets theory; B) the Rational Expectations theory; C) the Preferred Habitat theory; D) All of these help to explain the yield curve's shape. 4. Which of the following bond offerings would be most likely to experience excess returns? A) a Vietnam bond offering in Dong; B) a German bond offering in euros; C) a Japanese bond offering in yen; D) an Australian bond offering in British pounds 5. Real interest rate parity implies that A) real rates of return will be equal when expected inflation rates converge; B) uncovered interest rate parity will never hold; C) real rates of return on similar financial instruments in two different nations should be equal; D) absolute purchasing power parity holds. 6. 7. Which securities will require for higher default risk premium? A) US Treasury bond; B) Mexico government bonds; C) Apple’s corporate bonds; D) A corporate bond issued by a small company. If an investor expects to get a higher yield for a longer-termed instrument, it is called a A) risk preference; B) risk premium; C) yield curve; D) term premium. 8. If the nominal interest rate is 1% and the expected rate of inflation is 3.5%, then the real interest rate is A) -2.5%; B) 0%; C) 2.5%; D) 4.5%. 9. How do you determine is a foreign exchange market is efficient? A) See if the market rates adjust quickly to new and relevant information; B) See if systematic profit opportunities are quickly eliminated; C) See if forward rates are equal to expected future spot rates; D) All of the above should be true if a foreign exchange market is efficient. 10. Based on the covered interest parity (CIP) model analysis, investors move their capital from abroad to domestic economy. You will observe that A) a rise in domestic interest rate; B) a rise in foreign interest rate; C) a depreciation in domestic currency; D) an appreciation in foreign currency. 11. What is the difference between international money markets and international capital markets? A) the direction of financial flows in the market; B) the risk premium of the instruments in the market; C) the length of maturities for the instruments; D) the countries that participate in the markets 12. A Eurocurrency is a A) bank account located in England; B) bank account in the eurozone; C) bank account denominated in euros in the EU; D) bank account denominated in a currency other than the nation in which the deposit is located. 13. Suppose an individual firm is comparing two investments, a one year bond from a U.S. firm paying 4% or a one year bond from a German firm which is paying 6%. The current dollars-per-euro rate is 0.75, and the expected rate in one year is 0.72. If the expected rate is correct, which investment will receive the higher return? A) The U.S. Bond; B) The German Bond; C) They will have the same return; D) This cannot be determined from the information given. 14. Maturity Yield 1 year 1.1 2 years 1.05 5 years 1.025 10 years 1.01 30 years 1 Suppose the table above represents the average current yield for various international bonds, what would the shape of the yield curve show? A) a normal, upward sloping yield curve B) a normal, inverted yield curve C) an unusually inverted yield curve D) a downward sloping yield curve