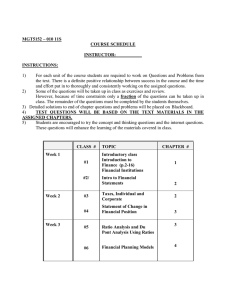
Course syllabus Course: Advanced Corporate Finance Description of Course The main aim of this Course is to provide a rigorous grounding in the theory and practice of corporate finance at an advanced level, and a thorough synthesis of the most important current research in corporate finance, with an emphasis on the applications of the principles. Both normative and positive aspects of the theory are examined, together with supporting descriptive and empirical evidence. Course Objectives: Upon completion of the Course, you should have: advanced knowledge and critical understanding of essential components of modern finance theory and associated current research; explored, understood and appreciated the complexity and contradictions of the current academic literature and its implications for professional practice, and be able to identify open questions for their own research; demonstrated ability to learn and work independently in corporate finance, exercising critical judgment and discrimination in the resolution of complex problematic situations; used highly specialized and advanced technical, professional and academic skills in the analysis of relevant specific problems in corporate finance; Have the opportunity to apply problem solving and analytical skills to issues in corporate finance in a complex specialized context. Course Content Chapter One Introduction to Financial Theories 1.1. An overview of Finance 1.2. Objectives and Goals of Finance 1.3. Functions of financial management 1.4. Role of corporate finance manager 1.5. Financial Assets/ Instruments and Markets Chapter Two Investment Decision and Capital Budgeting 2.1. Introduction to investments and capital budgeting 2.2. Investment appraisal techniques 2.3. Non Discounted cash flow techniques 2.4. Payback period 2.5. Accounting rate of returns 2.6. Discounted cash flow techniques 2.7. Net present Value(NPV) 2.8. Internal Rate of Returns(IRR) 2.9. Comparison of the NPV and IRR Methods 2.10. Multiple IRRs and Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) 2.11. Profitability Index(PI) 2.12. Conclusions on Capital Budgeting Methods and Business Practice Chapter Three Valuation of Stock and Bonds 3.1.1. 3.1.2. 3.1.3. 3.1.4. 3.1.5. 3.1.6. 3.1.7. 3.2.1. 3.2.2. 3.2.3. 3.2.4. 3.2.5. 3.2.6. Legal Rights and Privileges of Common Stockholders Types of Common Stock Common Stock Valuation Constant Growth Stocks and Expected Rate of Return on a Constant Valuing Stocks That Have a Non constant Growth Rate Stock Valuation by the Free Cash Flow Approach Preferred Stock Bond valuation Who Issues Bonds? Key Characteristics of Bonds Bond Valuation Bond Yields Changes in Bond Values over Time Chapter Four Risk and Return analysis and Portfolio theory 4.1. Risk Analysis & Management 4.2. Uncertainty and Risk 4.3. Types of Risk 4.4. Measurement of Risk (Standard Deviation and Beta) 4.5. Systematic and Unsystematic Risk (Measurement and Analysis) 4.6. Diversification and Portfolio Risk 4.7. The Security Market Line (SML) 4.8. Markowitz’s portfolio theory 4.9. The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and Arbitrage pricing theory (APT) Chapter Five Cost of Capital 5.1. The Cost of Equity 5.2. The Cost of Debt 5.3. The cost Preferred Stock 5.4. The Weighted Average Cost of Capital Chapter Six Market Efficiency and Efficient Market Hypothesis: 6.1. Classification of financial markets and Market Efficiency 6.2. Forms of efficiency 6.3. Efficient market hypothesis Chapter Seven Corporate Valuation And Financial Analysis 7.1. Corporate Value Creation 7.2. What should be the goal of management? 7.3. Accounting profits and economic profits 7.4. Residual income 7.5. Some evidence 7.6. EVA and MVA 7.7. Other measures of value creation 7.8. Corporate Valuation and Ratio Analysis 7.9. Market Value Ratios 7.10. Trend Analysis, Common Size Analysis, and Percentage Change Analysis 7.11. The Du Pont Equation 7.12. Comparative Ratio and Bench marking 7.13. Uses and Limitations of Ratio Analysis