Biology Study Guide: Characteristics of Life & Cell Structure
advertisement

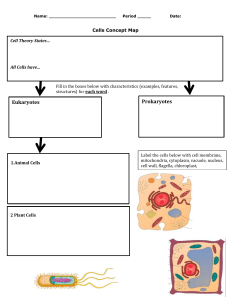
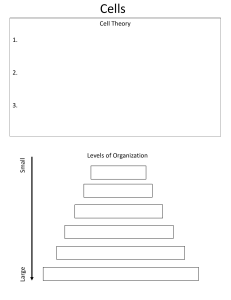
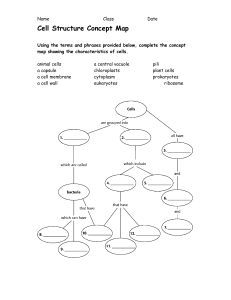
What is the study of biologically important molecules concerned with? Composition, structure, and chemical reactions. What is the structure of DNA? Helical and double-stranded. What is the first characteristic of life? Order, consisting of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. What is the second characteristic of life? Sensitivity or response to stimuli, such as the leaves of the sensitive plant drooping when touched. What is the third characteristic of life? Reproduction, with organisms having parts or organs for reproduction. What is the fourth characteristic of life? Growth and development, with organisms changing over time. What is the fifth characteristic of life? Regulation, with organs reacting to foreign matter to regulate the body. What is the sixth characteristic of life? Homeostasis, the balance in an organism's body with internal control. What is the seventh characteristic of life? Energy processing, with plants gathering energy from the sun to make food. What must be present for an organism to be called a living organism? All seven characteristics of life. What is the biological level of organization? The hierarchy of living things from atoms to ecosystems. What are the six distinct levels of increasing complexity in the structural organization of the human body? There are six distinct levels of increasing complexity in the structural organization of the human body. What is the most abundant element in the human body? The most abundant element in the human body is oxygen. What are cells? Cells are the building blocks of all organisms. What are the four components that all cells have? Regardless of the type, all cells have an enclosing plasma membrane which separates the cell's interior from the environment, cytoplasm made of cytosol in which other components of the cells are found, DNA, which is the genetic material of the cell, and ribosomes which synthesize proteins. What is the cell theory? The cell theory states that cells are the basic units of life, all living organisms are made of cells, and all cells come from preexisting cells. How do prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes? Prokaryotes are single-celled, while only eukaryotic cells can be multicellular. Prokaryotes may stick together to form colonies, but they do not have specialized structures like eukaryotes. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Prokaryotes are single-celled, while only eukaryotic cells can be multicellular. What is the size range of most prokaryotes? Most prokaryotes are less than 1 mm in diameter. What is the structure of prokaryotic chromosomal DNA? Prokaryotic chromosomal DNA is single, circular, and double-stranded, found in the nucleoid region of the cell, and often have plasmids. What is the method of cell division for prokaryotes? Prokaryotes do binary fission. What is the method of genetic recombination for prokaryotes? Genetic recombination occurs through horizontal gene transfer, not sexual reproduction, and is not a form of reproduction. What is the internal compartmentalization of prokaryotes? Prokaryotes have no membrane-bounded organelles, no internal compartment, and ribosomes differ from eukaryotic form. What is the structure of flagella in prokaryotes? Flagella in prokaryotes are simple in structure and different from eukaryotic flagella. What are the types of metabolic diversity in prokaryotes? Prokaryotes have oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis and chemolithotrophic. What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella? Eukaryotic flagella are different in structure from prokaryotic flagella. What are the two types of photosynthesis that prokaryotes can perform? Prokaryotes can perform oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis. How do prokaryotes obtain energy from inorganic molecules? Prokaryotes can harness energy from inorganic molecules, such as water, through chemolithotrophy. What is the main characteristic of prokaryotic cells regarding internal compartments? Prokaryotes lack membrane-enclosed internal compartments. What is the main component of the cell wall in most prokaryotes? Most prokaryotes have a cell wall containing peptidoglycan. What is the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in terms of cell structure? Prokaryotes lack membrane-enclosed internal compartments, while eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles. Where is the chromosomal DNA located in a prokaryotic cell? The chromosomal DNA is localized in a nucleoid in a prokaryotic cell. What is the main component of the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells? The cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells consists of organelles suspended in gel-like cytosol plus the cytoskeleton. What percentage of the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells is water? 70-80% of the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells is water. What is the main component of the cytoplasm in prokaryotic cells? The cytoplasm in prokaryotic cells consists of ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and DNA. What is the cytosol? The fluid left after removing sub-cellular components from the cytoplasm. What is the function of the protein channel in the plasma membrane? It serves as a passage way. What is the nucleus? The control center of the cell that contains genetic material. What is the nuclear envelope? A double membrane that separates DNA from cytoplasm and transcription from translation. What are nuclear pores? Perforations in the nuclear envelope that connect nucleoplasm to cytoplasm and regulate flow of molecules back and forth. What is the nucleolus? A region inside the nucleus where ribosomes are assembled from RNA. What is a nuclear localization signal (NLS)? It is required by large molecules to pass through the nucleus. What is the nucleolus? It is a nonmembranous organelle inside the nucleus where ribosomes are assembled from RNA and proteins. What are ribosomes made of? They are made of two different-sized subunits, special RNA (rRNA), and proteins. What is the function of ribosomes during protein synthesis? They assemble amino acids into proteins. What is the mitochondrion? It is the site for the conversion of stored energy to a more useful form (ATP) and has an inner membrane that is folded into cristae. What is the endoplasmic reticulum? It is a network of interconnected membranous sacs and tubules that modifies proteins (rough ER) and synthesizes lipids (smooth ER). What is the lumen or cisternal space? It is the hollow portion of the ER tubules. What is the continuity between the ER and the nucleus? The membrane of the ER is continuous with the nuclear membrane. What is the name of the hollow portion of the ER tubules? Lumen or cisternal space. What is the ER membrane continuous with? Nuclear envelope. What is the function of ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic surface of rough ER? Manufacture proteins. Where are new proteins modified in the rough ER? Lumen of rough ER. What happens to modified proteins in the rough ER? They are either incorporated into cellular membrane or secreted from the cell. What is the function of smooth ER? Makes phospholipids for cellular membranes. What are peroxisomes? Small rounded organelles enclosed by a single membrane. What reactions occur in peroxisomes? Reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids. What is the function of the Golgi apparatus? Sort, package, and tag lipids or proteins within transport vesicles. What is the structure of the Golgi apparatus? A series of flattened membranes. What is the cytoskeleton? A network of protein fibers with several functions. What are the functions of the cytoskeleton? Helps maintain the shape of the cells and holds some organelles in specific positions. What are the functions of the cytoskeleton? The cytoskeleton helps maintain the shape of the cells, holds some organelles in specific positions, allows movement of the cytoplasm and vesicles within the cell, and enables cells within multicellular organisms to move. What are the three components of the cytoskeleton? The three components of the cytoskeleton are microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. What are the differences between animal and plant cells in terms of MTOCs and centrosomes? Both animal and plant cells have microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), but animal cells also have centrioles associated with MTOC, while plant cells do not have centrosomes. What are lysosomes, and what is their function? Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes and break down large biomolecules. What are microtubules made of, and what is their function? Microtubules are made of tubulin dimers and provide support to the cell. What are microfilaments, and what is their function? Microfilaments are involved in movement, determine and stabilize shape, and are made from actin monomers. What are cilia and flagella, and what is the difference between them? Cilia and flagella are ultrastructures that help with movement. Cilia are shorter and numerous, while flagella are longer and less numerous. What is the difference between cilia and flagella in terms of their length and abundance? Cilia are shorter and more numerous, while flagella are longer and less numerous (usually found in sperm cells). What is the main component of plant cell walls, and how does it differ from the cell walls of prokaryotes? The main component of plant cell walls is cellulose, which differs from the peptidoglycan that makes up the cell walls of prokaryotes. What is the function of chloroplasts, and what is the structure of a granum? Chloroplasts are organelles that carry out photosynthesis, and each stack of thylakoids within a chloroplast is called a granum. What is the purpose of intercellular junctions, and how do plants and animals differ in their methods of communication between cells? Intercellular junctions provide direct channels of communication between cells. Plants use plasmodesmata, while animals use tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. What are the four processes that regulate cell contents, and what is an example of simple diffusion? The four processes are diffusion, osmosis, dialysis, and surface tension. An example of simple diffusion is the spread of a smell throughout a room. What is osmosis, and what is the process illustrated in the figure provided in the text? Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The figure provided in the text illustrates osmosis. What is diffusion? The spread of smell or spread in general. What is osmosis? The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. What is the direction of water movement in osmosis? Water moves towards the area with a higher concentration of solute. What is osmotic pressure? The pressure required to prevent the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane due to differences in solute concentration. What happens to the volume of a solution with a higher solute concentration surrounded by water over time? The volume increases as water moves into the solution with a higher solute concentration. What is the purpose of applying force to an area in osmosis? To prevent or avoid the process of osmosis. What is isotonic? A solution where the concentration of solutes is equal inside and outside the cell. What is hypertonic? A solution where the concentration of solutes is higher outside the cell, causing water to move out of the cell and potentially causing it to shrink. What is hypotonic? A solution where the concentration of solutes is lower outside the cell, causing water to move into the cell and potentially causing it to swell and burst. What happens to plant cells in a hypotonic solution? They do not become disfigured. What is tonicity? Tonicity refers to the ability of a solution to cause a cell to swell or shrink. What is the difference between plant and animal cells in terms of tonicity? Plant cells are not easily disfigured by tonicity because of their cell wall, while animal cells can be disfigured because they lack a cell wall. What is the mechanism of action of a dialyzer in hemodialysis? A dialyzer is a machine that cleans the blood by removing waste products and excess fluids. What is surface tension? Surface tension is the force that causes the molecules on the surface of a liquid to be more tightly packed than those in the interior. What is the polar nature of water? Water is polar, meaning it can use either of its ends to interact with other molecules. What is the water content of the body's organs and tissues? The water content varies in different body organs and tissues. What is the role of water in cells? Water is the principal component of most cells and its solvent properties are largely determined by its polar nature. What is the effect of tonicity on cells? Tonicity can cause cells to swell or shrink depending on the concentration of solutes in the surrounding solution. What is the difference between protein and dialyzate in dialysis? Protein is too large to pass through the semi-permeable membrane of a dialyzer, while dialyzate is a solution that can pass through the membrane to remove waste products from the blood. What is the effect of tonicity on animal cells? Tonicity can cause animal cells to disfigure because they lack a cell wall to protect them. What is a polar molecule? A molecule that has a positive charge on one end and a negative charge on the other end. What is the interaction between Na and water? Na is positively charged and interacts with the negative part of water, which is surrounded by O atoms. What is the interaction between Cl and water? Cl is negatively charged and interacts with the positive part of water, which is surrounded by H atoms. What is the universal solvent? Water is called the universal solvent because it can use either of its ends to interact with other polar molecules. What is an ionic bond? An ionic bond is a type of bond formed between two ions with opposite charges. What is the electron configuration of sodium? Sodium has one electron in its outermost energy level. What is the electron configuration of chlorine? Chlorine has seven electrons in its outermost energy level. How does sodium become stable in an ionic bond with chlorine? Sodium transfers its outermost electron to chlorine, which results in a stable ionic bond. What is the charge of Na+? Na+ means that one electron has been lost, resulting in a positive charge. What is the maximum number of electrons that can be placed on a hydrogen atom? 2. What is the maximum number of electrons that can be placed on a chlorine atom? 8. How many electrons are in the outermost energy level of sodium? It is not specified in the given text. What is the charge on chlorine after receiving one electron from sodium? -1. What is the charge on sodium after transferring one electron to chlorine? +1. What is the difference between non-polar and polar covalent bonds? Non-polar covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons equally, while polar covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons unequally. What is the electron configuration of hydrogen gas? 1s1. What is the electron configuration of chlorine? 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5. Why do hydrogen and chlorine share electrons in a polar covalent bond? To complete the maximum capacity of electrons needed by both atoms. Why are the electrons pulled more towards the chlorine side in a polar covalent bond between hydrogen and chlorine? Chlorine has more protons in its nucleus, which attracts the shared electrons more strongly. What are the four types of non-covalent interactions? The four types of non-covalent interactions are hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals interactions. What is the difference between attraction and repulsion in ionic interactions? Attraction is possible when two opposite charges are present, while repulsion is possible when two same charges are present. What is the definition of hydrophobic interactions? Hydrophobic interactions can be seen only on hydrocarbons (hydrogen and carbons only), are non-polar, and can't interact with water. What is the mechanism of action of hydrogen bonds? Hydrogen bonds occur between neutral groups or between peptide bonds. What is the Arrhenius definition of an acid? According to the Arrhenius definition, an acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, releases hydronium ions. What is the Arrhenius definition of a base? According to the Arrhenius definition, a base is a substance that, when dissolved in water, releases hydroxide ions. What is the Arrhenius theory of acids and bases? Acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solutions, while bases are substances that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solutions. What is the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases? Acids are substances that donate protons (H+) in aqueous solutions, while bases are substances that accept protons (H+) in aqueous solutions. What is an amphoteric substance? An amphoteric substance is a substance that can act as both an acid and a base. What is the Lewis theory of acids and bases? The Lewis theory of acids and bases defines an acid as an electron pair acceptor and a base as an electron pair donor. What is the autoionization of water? The autoionization of water is the process by which water molecules dissociate into hydronium ions (H3O+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solutions. What is the equilibrium constant expression for the autoionization of water? Kw = [H3O+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10^-14 at 25°C. What is the ion product constant of water? The ion product constant of water (Kw) is the equilibrium constant for the autoionization of water and has a value of 1.0 x 10^-14 at 25°C. How does the Bronsted-Lowry theory explain the autoionization of water? The Bronsted-Lowry theory explains the autoionization of water as the transfer of a proton (H+) from one water molecule acting as an acid to another water molecule acting as a base. What is the Ion Product Constant of Water? The Ion Product Constant of Water has the value of 1.00 x 10-14. What is the definition of a buffer solution? A buffer solution resists drastic changes in pH upon addition of small to moderate amounts of strong acids or strong bases. What is the trend in the dissociation of weak acids? The first reaction Ka1 is much easier than the second one because that is the trend. What is the purpose of a titration curve? A titration curve shows the pH changes during a titration and can help identify the equivalence point and pKa. What is the mechanism of action of a buffer solution? A buffer solution works by maintaining a relatively constant pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. What is the difference between strong and weak acids? Strong acids completely dissociate in water, while weak acids only partially dissociate. What is the definition of a conjugate base? A conjugate base is the species that remains after a weak acid has donated a proton. What is the definition of a weak acid? A weak acid is an acid that only partially dissociates in water. What is the definition of pH? pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. What is the definition of pOH? pOH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration. What is a buffer solution? A combination of a weak acid (HA) and conjugate base (A-). What happens when a small amount of strong acid (OH-) is added to a buffer solution? It combines with the weak acid to form water (H2O) and conjugate base. What happens when a huge amount of strong acid (H+) is added to a buffer solution? It combines with the conjugate base to form the weak acid which is already present. What is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation used for? To calculate buffer solution, control pH for optimum reaction, prepare buffer solution, and calculate the degree of dissociation of weak acid-conjugate base pairs at a particular pH. What is buffering capacity? The ability of a buffer solution to resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. What is the difference between a virus and a bacterium? A virus is a non-living particle that requires a host cell to replicate, while a bacterium is a living organism that can replicate on its own. What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells, while meiosis is the process of cell division that results in four genetically diverse daughter cells. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon that can be tested, while a theory is a well-supported explanation for a phenomenon that has been extensively tested and confirmed. What is the difference between a renewable and non-renewable resource? A renewable resource is a resource that can be replenished over time, while a non-renewable resource is a resource that cannot be replenished once it is used up. What is the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell? A plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, while an animal cell does not have a cell wall, chloroplasts, or a large central vacuole. What is the difference between a herbivore and a carnivore? A herbivore is an animal that eats only plants, while a carnivore is an animal that eats only other animals. What is the difference between a solute and a solvent? A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent, while a solvent is a substance that dissolves a solute. What is the difference between a compound and a mixture? A compound is a substance made up of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together, while a mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded together. What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? A prokaryotic cell does not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, while a eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. What is the difference between weather and climate? Weather refers to the short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area, while climate refers to the long-term patterns of temperature, precipitation, and other weather variables in a region.