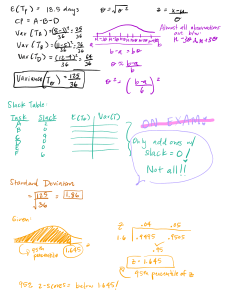
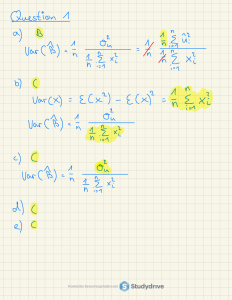Introduction to Econometrics Review of Necessary Maths 1 • n X Properties of Summation a = a + a + . . . + a = na i=1 • n X xi = x1 + x2 + x3 + . . . + xn i=1 • n X σi xi = σ1 x1 + σ2 x2 + . . . + σn xn i=1 3 3 3 X X X • (xi − yi ) = x1 − y1 + x2 − y2 + x3 − y3 = xi − yi i=1 2 i=1 i=1 Properties of the Expected Value • E(a) = a • E(aX) = aE(X) • E(aX + b) = E(aX) + E(b) = aE(X) + b • E(X + Y ) = E(X) + E(Y ) • E(x1 + x2 + ... + xn ) = E(x1 ) + . . . + E(xn ) ⇒ E n X i=1 ! xi = n X E(xi ) i=1 • E(aX + bY ) = E(aX) + E(bY ) = aE(X) + bE(Y ) • unless X and Y are independent: E(XY ) 6= E(X)E(Y ) University of Birmingham | Page 1 Introduction to Econometrics 3 Properties of the Variance • var(a) = 0 since constants have unchanging values Proof: var(a) = E[(a − E(a))2 ] = E[(a − a)2 ] = E(0) = 0 • var(X + b) = var(X) • var(aX) = a2 var(X) • var(aX + b) = a2 var(X) • var(X + Y ) = E[(X + Y − E(X) − E(Y ))2 ] = E[(X − µX )2 + (Y − µY )2 + 2(X − µX )(Y − µY )] = var(X) + var(Y ) + 2 cov(X, Y ) • var(X − Y ) = var(X) + var(Y ) − 2 cov(X, Y ) • var(aX + bY ) = a2 var(X) + b2 var(Y ) + 2 ab cov(X, Y ) • cov(X, Y ) = E[(X − µX )(Y − µY )] = E[XY − XµY − Y µX + µX µY ] = E(XY ) − µY E(X) − µX E(Y ) + µX µY = E(XY ) − µX µY If X and Y are independent: E(XY ) = E(X)E(Y ) = µX µY ⇒ cov(X, Y ) = 0 • If X and Y are independent so that cov(X, Y ) = 0, then var(aX + bY ) = a2 var(X) + b2 var(Y ) 4 Properties of the Covariance • cov(a + bX, c + dY ) = E[(a + bX − E(a + bX))(c + dY − E(c + dY ))] = E[(a + bX − a − bµX )(c + dY − c − dµY )] = E[b(X − µX ) d(Y − µY )] = bd cov(X, Y ) • cov(X, X) = E[(X − µX )(X − µX )] = var(X) University of Birmingham | Page 2