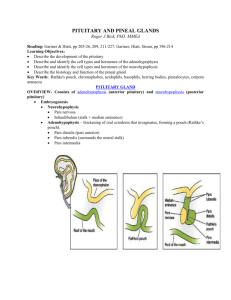
o Source of melanocytestimulating hormone (MSH) (regulates skin pigmentation) o In cattle, pigs, and rats, ACTH produces is cleaved into a-MSH and corticotropin-like intermediate lobe peptide or CLIP o In dog and horse significant source of ACTH o Tumors cab lead to spontaneous hyperadrenocorticism THE PITUITARY GLAND - Ptuo – spit Pituita – mucus Master gland of the body Controlled by chemical and electrochemical messengers Only the adrenal cortex can match the plethora of hormones produced by the pituitary gland MORPHOLOGY Anatomy - - - - Also called hypophysis o Hypo – under o Physis – growth Ventral to the brain in dorsal concavity of sphenoid bone called the sella turcica or hypophyseal fossa Covered by dura mater Pituitary stalk or infundibulum rises dorsally from the pituitary to connect with the hypothalamus Subdivided into adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis Three parts: Pars distalis o Five population of cells Thyrotropes Gonadotropes Lactotropes Corticotropes (tropic hormones) somatotropes - Pars tuberalis o Upward extension of the adenohypophysis, attached to infundibulum - Pars intermedia o Forms the junction between the pars distalis and pars nervosa Tropic hormones - Thyrotropin or TSH LH FSH Prolactin Adrenocorticotropin Growth hormone Somatotropin Neurohypophysis 2 parts: - Infundibulum or pituitary stalk - the pars nervors (posterior or neural lobe) - Nonapeptides - o Intramolecular disulfide bond 2 cysteine residues Oxytocin Arginine vasopressin Lysine vasopressin Arginine vasotocin Blood circulation - Receives both arterial and venous blood - Internal carotid arteries o Superior and inferior hypophyseal arteries o Venous blood enters the adenohypophysis from 2 capillary beds Median eminence of hypothalamus Lower infundibulum and neurohypophysis (READ THE BOOK) EMBRYOLOGY - Adenohypophysis arises from an evagination of the ectodermal roof of the oropharynx