Power Plant Engineering: Energy Sources & Transformation
advertisement

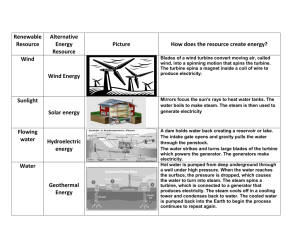
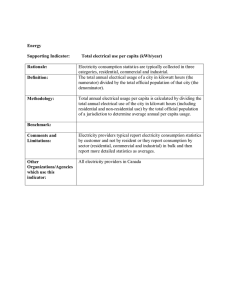
Objectives: 1. To familiarize with different types of energy sources 2. To familiarize with energy transformation 3. To familiarize with the different types of power plants Introduction to Power Plant Engineering Did you Know? There is a close relationship between the energy used per person and his standard of living. The greater the per capita consumption of energy in a country. The greater the demand in electricity What is energy per capita? Average power per capita was calculated according to the formula: Electric energy per capita [ in watt−hour] Total population electricity consumption [ in kW·h/yr ] ∗ 1,000 = 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 Energy exists in different forms in nature but the most important form is the electrical energy. Energy Transformation Chemical energy to light energy Chemical energy to kinetic energy Chemical energy to Light, Sound, Heat and chemical energy electricity to Light, Sound, Heat and chemical energy Electrical energy to mechanical energy Importance of Electrical Energy • a. Convenient form. It can be easily converted into other forms of energy. • Example. Convert electrical energy to heat by passing electrical current to high resistance wire Importance of Electrical Energy b. Easy control Example. Switch for lamp and motors, Variable speed control for motors Importance of Electrical Energy c. Greater flexibility Example. Ease of transporting electrical energy with the help of conductors Importance of Electrical Energy d. Cheapness Example. It is more economical to use electrical energy for domestic, commercial and industrial purposes Importance of Electrical Energy e. Cleanliness Example. Electricity is not associated with smoke, fumes or poisonous gases unlike automotive. Importance of Electrical Energy f. High transmission efficiency Example. Electricity can be transmitted conveniently and efficiently from the centers of generation to the consumers with the help of transmission lines. Generation of Electrical Energy Electrical energy is a manufactured commodity like clothing, furniture or tools. Just as the manufacture of a commodity involves the conversion of raw materials available in nature into the desired form, Generation of Electrical Energy similarly electrical energy is produced from the forms of energy available in nature. Generation of Electrical Energy However, electrical energy differs in one important aspect. Whereas other commodities may be produced at will and consumed as needed, the electrical energy must be produced and transmitted to the point of use at the instant it is needed. The entire process takes only a fraction of a second. The instantaneous production of electrical energy introduces technical and economic considerations unique to the electric power industry. Generation of Electrical Energy Sources of energy such as pressure head of water, chemical energy of fuels, nuclear energy of radioactive substances can be converted into electrical energy by the use of suitable arrangements. Generation of Electrical Energy The arrangement essentially employs an alternator coupled to a prime mover. The prime mover is the energy obtained from the various sources such as burning of fuel, pressure of water, force of wind etc. Generation of Electrical Energy Example Chemical energy of a fuel (e.g. coal) can be used to produce steam at high pressure. The steam is fed to prime mover which may be a steam engine or a steam turbine. The turbine converts the heat of steam into mechanical energy which is further converted into electrical energy by the alternator.