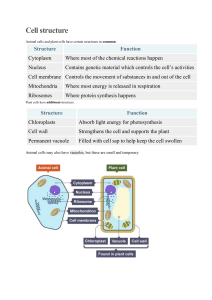
Biology Chap 1: Cells: The Building Blocks Of Life. Cells are referred to as the building blocks of life. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently. There are 2 types of Cells 1) Eukaryotes and 2) Prokaryotes. . Eukaryotes consists of 2 cellular structures, Animal and Plant Cell, whereas Prokaryotes consists of 1 type of cellular structure which is Bacteria cell. “Similar Subcellular structures in Plant and Animal Cells” 1. Cell Membrane: Controls which substances can pass in and out of the cell 2. Nucleus: Contains the genetic material / DNA and so controls the cell’ss acitivities/ 3. Cytoplasm: A watery and jelly type substance present in both cells, it’s where all chemical reactions take place. 4. Mitochondria: These are known as the powerhouses of a cell because they provide cells the energy they need to function. They get their energy through breaking down sugars like glucose through Aerobic respiration. (Mitochondria are the site of aerobic respiration, so they release energy for the cell) 5. Ribosomes: The ribosomes are where proteins are made. We sometimes call them the site of protein synthesis. “Subcellular structures that are only available in Plant cells” 1. Rigid Cell Wall (Cellulose): Supports the plant, prevents cells from bursting incase if too much water enters the cell.made of cellulose. This makes it strong and allows it to maintain the shape of the cell. 2. Vacuole :The vacuole is a large sac in the middle of the cell that contains a watery solution of sugars and salts (cell sap). It helps maintain the structure and shape of the cell. 3. Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts carry out the process of photosynthesis, which involves using light energy from the sun to make glucose. 4. Chlorophyll: Absorbs the light energy for photosynthesis and contains green pigment that makes the plant green. “Bacterial Cells”. These are prokaryotic cells They consist of singular prokaryotic cell so we can call them UniCellular A bacterial cell only contains Ribosomes, Cell membrane, Cell wall, Cytoplasm. Instead of a Nucleus they contains a cellular stand of DNA which contains all the genes They need to survive + reproduce, it's also referred to as ‘Circular chromosome’ / ‘Nucleoid’ They contain Plasmids which are extra genes which carry antibiotic resistance. Some bacterial cells also consist of Flagella, it's a thread like structure which allows the bacteria To move around. Cells, Tissues Organs AND Organ Systems: Organelles: Subcellular structures which make up a cell for e.g. Nucleus, ribosomes and mitochondria. Each organelle has its role to play. Cells: They come in various shapes and sizes and contain different combinations and numbers of organelles. These types of cells are called Specialized cells some examples are Muscle and Epithelial cells. Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to carry out a particular function. Organs: A group of different tissues that work together to perform a particular function. Organ systems: A group of organs that work together to perform a particular function. Organisms: Multiple organ systems working together to form an organism.