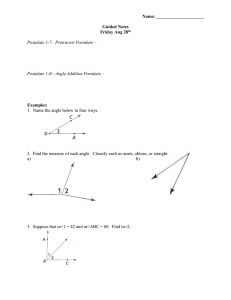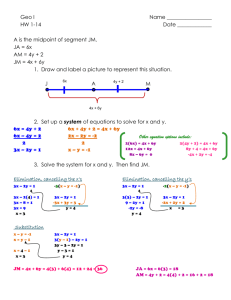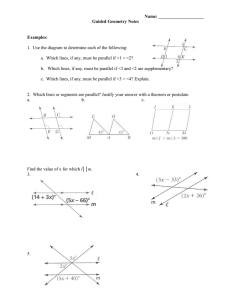
1.3/1.4 Postulates and Measuring Segments and Angles Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Postulates Are statements accepted as true without proof They are considered self-evident They are accepted on faith alone. Postulate 1-5 Ruler Postulate The distance between any two points is the absolute value of the difference of the corresponding numbers (on a number line or ruler) Congruent Segments: two segments with the same length Comparing Segment Lengths Postulate 1-6 Segment Addition Postulate If three points A, B, and C are collinear and B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC C B A Using the Segment Addition Postulate If DT = 60, find the value of x. Then find DS and ST. 2x - 8 D 3x - 12 S T Using the Segment Addition Postulate If EG = 100, find the value of x. Then find EF and FG. 4x - 20 E 2x + 30 F G Midpoint: a point that divides the segment into two equal parts A B B is the midpoint, so AB = BC C Finding Lengths C is the midpoint of AB. Find AC, CB, and AB. 3x – 4 2x + 1 A C B Z is the midpoint of XY, and XY = 27. Find XZ. 27 X Z Y Angle: formed by two rays with the same endpoint The endpoint is called the vertex Can be named by the vertex, by three letters with the vertex in the center, or by a number A B <ABC <CBA <B <1 1 C *Look at examples in your notes Postulate 1-7 Protractor Postulate You can use a protractor to measure an angle. *Look in book on page 28 Acute angle < 90° Right Angle = 90° Obtuse Angle > 90° but < 180° (90° < x < 180°) *Example 5 on pg 28 Straight Angle = 180° Postulate 1-8 Angle Addition Postulate If point B lies in the interior of <AOC, then m<AOB + m<BOC = m<AOC A B O C If <AOC is a straight angle, then m<AOB + m<BOC = 180 B A O C Using Angle Addition Postulate What is m<TSW if m<RST = 50 and m<RSW = 125? T x 50 R S W Using The Angle Addition Postulate If m<DEG = 145, find m<GEF. G 145 D x E F Congruent Angles: Angles with the same measure Homework Problems # 1-9 on worksheet #2 Segment and Angle Addition