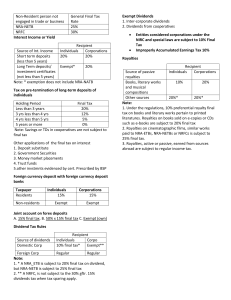
lOMoARcPSD|8787066 Chapter 5 final income taxation summary banggawan Income Taxation (University of the Philippines System) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 Chapter 5 Final Income Taxation FEATURES OF FINAL INCOME TAXATION (FITT) 1. 2. 3. 4. Final tax Tax withholding at source Territorial imposition Imposed on certain passive income and persons not engaged in business in the Philippines Final Withholding System (FWT) - Imposes upon the person making income payments the responsibility to withhold tax Tax will be deducted immediately to the income Taxpayer receives the income of net tax There would be no need for him to file an income tax to report the same Final Withholding System - Inherently territorial Applies only to certain passive income earned from sources within the Philippines Taxation is territorial - We can’t impose tax obligation against non-resident subjects of foreign sovereignty All items of income earned from sources abroad (passive/active) are subject to tax under Regular Income Tax Rationale of Final Income Taxation - FWT is built upon taxpayer and gov’t convenience For the gov’t, the FWT system is the most convenient and effective system in collecting taxes on income where there is high risk of non-compliance or tax evasion Passive Income - Items that are earned with very minimal involvement from the taxpayer and are generally irregular in timing and amount Not usually specifically monitored by taxpayers FW at source is the most favored scheme in taxing items of passive income Non-resident persons not engaged in business in the Philippines - NRP-NETBs, NRA-NETBs, NFRCs have high risk of non-compliance These taxpayers do not have offices or fixed places of business in the Philippines making compliance very unlikely due to their absence and distance in the Philippines The law subjects them to final income tax wherein Philippine residents paying them income (passive/active) are obligated to withhold the following final tax: Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 Non-resident person not engaged in trade or business NRA-NETBs NRFC General final tax rate 25% 30% PASSIVE INCOME SUBJECT TO FINAL TAX 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Interest or yield from bank deposits or deposit substitutes Domestic dividends, in general Dividend income from a Real Estate Investment Trust Share in the net income of a business partnership, taxable associations, joint ventures, joint accounts, or co-ownership Royalties, in general Prizes exceeding P10,000 Winnings Informer’s tax reward Interest income on tax-free corporate covenant bonds Interest Income or Yield - Interest income or yield from local currency bank deposits or deposit substitutes are subject to final tax as follows: Source of interest income Short term deposits Long-term deposits/ investment certificates *Exemption does not include NRA-NETB Recipient Individuals Corporations 20% 20% Exempt* 20% Short term deposits – those made for a period of less than five years Long-term deposits – not less than five years Tax on pre-termination of long-term deposits of individuals - If the deposits or investment placement of individual taxpayers is pre-terminated before 5 years, any previously untaxed or exempted interest income will be subjected to the ff. final taxes upon pre-termination: Holding period Final tax Less than 3 years 20% 3 years to less than 4 years 12% 4 years to less than 5 years 5% 5 years or more 0% Savings or time deposits with cooperatives are not subject to final tax Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 - Final tax is limited to banks and shall not be applied with time and savings account deposits maintained by members with cooperatives and by primary cooperatives with their federations Other applications of the final tax on interest 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Deposits substitutes Government securities Money market placements Trust funds Other investments evidenced by certificates prescribed by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas Foreign currency deposit with foreign currency depositary banks - Interest income from foreign currency deposits under foreign currency deposit system or expanded foreign currency deposit system by residents is subject to a final tax of 15% The old law imposed a rate of 7.5% until 2017 Taxpayer Residents Non-residents *NRA-NETBs and NRFCs are also exempt Individuals Corporations 15% 15% Exempt Exempt * There is no long-term or short-term classification of foreign currency deposits Joint accounts on forex deposits - If the bank account is jointly in the name of non-resident and a resident taxpayer, 50% of the interest shall be exempt while the other 50% shall be subject to the 15% final tax 50% of the deposited savings are exempt, while the remaining amount of 50% is subject to 15% final tax INTEREST INCOME SUBJECT TO REGULAR TAX 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lending activities, whether or not in the course of business Investment in bonds Promissory notes Foreign sources, whether bank or non-bank Penalty for legal delay or default Dividends - Any distribution made by a corporation to its shareholders out of its earnings or profits and payable to its shareholders, whether in money or property Types of dividends: 1. Cash dividends – paid in cash Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 2. 3. 4. 5. Property dividends – paid in non-cash properties Scrip dividends – paid in notes Stock dividends – paid in stocks Liquidating dividends – distribution of corporate net asset Stock dividend vs. Stock split - - Stock dividend Capitalization of earnings - May be taxable under certain conditions - Stock split Results in reduction in par value of stock and an increase in the number of shares of shareholders Will never be subject to income tax Dividend Tax Rules Recipient of dividends Individuals Corporations 10% final tax Exempt Regular tax Regular tax Source of dividends Domestic corporation Foreign corporation Historical dividend tax rates - Imposable final tax rates vary depending on the source of the dividends declared: Source Earnings before January 1, 1998 Earnings from 1998 Earnings from 1999 Earnings from 2000 and thereafter Final tax Exempt 6% 8% 10% Exempt Dividends 1. Inter-corporate dividends 2. Dividends from cooperatives Inter-corporate dividends - - Received by a domestics corporation and resident foreign corporation from a domestic corporation from a domestic corporation are exempted under NIRC to minimize double taxation When the dividend finally falls to an individual shareholder, the 10% final tax applies Exemption extends to dividends received by business partnerships from domestics corporation o Exemption doesn’t extend to dividends received by GPP, exempt joint ventures and exempt joint co-ownership Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 - Inter-corporate dividend doesn’t apply to the share of a corporation from the net income of a business partnership due to absence of express legal exemption. Exemption is restricted to dividend declaration only Dividend from cooperatives - Under RA 9520, distribution of dividends by an exempt cooperative shall not be subject to tax ENTITIES TAXABLE AS CORPORATIONS ARE SUBJECT TO 10% FINAL TAX 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Real Estate Investment Trusts Business partnerships Taxable associations Taxable joint ventures, joint accounts or consortia Taxable co-ownerships Royalties - Passive royalty income received from sources within the Philippines is subject to the ff. final tax rates: Source of passive royalties Books, literary works, and musical compositions (printed or hard copies) Other sources (e-copies) Recipient Individuals Corporations 10% final tax 20% final tax 20% final tax 20% final tax Passive vs. Active royalties Passive royalties Royalties of a passive nature are subject to 20% final tax Active royalties Royalties accrues from an undertaking where the taxpayer has active involvement, it is an active income subject to RIT Prizes - Prizes may be exempt from income tax or subject to either final tax or regular income tax Exempt prizes 1. Prizes received by a recipient without any effort on his part to join a contest 2. Prizes from sports competitions that are sanctioned by their respective Nat’l sport org. Requisite of exemption 1. Recipient was selected without any action on his part to enter the contest 2. Recipient is not required to render substantial future services as a condition to receiving he price or reward Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 Taxable prizes - For individual taxpayers, taxable prizes are subject to either final tax or regular tax depending on the amount of the prize There is no final tax imposition on corporate prizes under the NIRC, the same must be subject to RIT Recipient Amount of taxable price Individuals Corporations Prizes exceeding P10,000 20% final tax Regular tax Prizes not exceeding P10,000 Regular tax Regular tax *Final taxation does not apply to foreign passive income; hence prizes from foreign sources are subject to RIT Winnings - Winnings received from sources within the Philippines are subject to 20% final tax, except PCSO or lotto winnings amounting to P10,000 or less Winnings that are not subjected to final tax by the payor should be reported as part of the RIT Winnings from foreign sources are also subject to RIT Recipient Types of winnings Individuals Corporations PCSO/lotto winnings not exceeding P10,000 Exempt Exempt PCSO/lotto winnings exceeding P10,000 20% final tax 20% final tax Other winnings, in general 20% final tax Regular tax *PCSO/lotto winnings of NRA-NETB and NRFC, in any amount, are respectively subject to 25% and 30% final tax *Tax rules on PCSO or lotto winnings shall be applied on a per ticket basis Tax Informer’s Reward - Cash reward given to any person instrumental in the discovery of violations of the NURC or discovery of smuggled goods. It is subjected to 10% final tax Requisites of Tax Informer’s Reward: 1. Definite sworn information which is not yet in the possession of the BIR 2. The information furnished lead to the discovery of fraud upon internal revenue laws or provisions thereof 3. Enforcement results in recovery of revenues, surcharges, and fees and/or conviction of the guilty party or imposition of any fine or penalty Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 4. The informer must not be a : a. BIR official or employee b. Other public official or employee c. Relative within the 6th degree of consanguity of those officials or employee in a. and b. Amount of Cash Reward - - Whichever is the lower of the ff. per case: 1. 10% of revenues, surcharges, or fees recovered and or fine or penalty imposed and collected or 2. P1,000,000 – cash reward limit Amount of cash reward is subject to 10% fina withholding tax which shall be withheld by the gov’t. Example: Kunwari yung equivalent ng 10% sa na-recovered mo is mas mataas kesa sa 1M (i.e. 1.2M yung equivalent ng 10% sa na-recovered mo) ang makukuha mong reward is 1M kasi yun yung mababa. Kung ang equivalent naman ng 10% na na-recovered mo is mas mababa sa 1M (i.e. 900K yung equivalent ng 10% sa na-recovered mo) ang makukuha mong reward is yung 900K kasi yun yung mababa Tax-free Corporate Covenant Bonds - Interest income of individual taxpayer of the Phil on obligations of domestic or RFC with tax-free or tax reduction where the obligor shoulders in whole or in part any tax on the interest shall be subject to a 30% final withholding tax of 30% Tax on interest income on tax-free corporate covenant bonds Bond Investor Individuals Corporations 30% final tax Regular Income Tax EXCEPTIONS TO THE GENERAL FINAL TAX ON NON-RESIDENT PERSONS NOT ENGAGED IN TRADE OR BUSINESS (NRA-NETB) IN THE PHILIPPINES General Final Tax Rate Exceptions: 1. Capital gain on sale of domestic stocks directly to buyer NRA-NETB 25% NRFC 30% 15% Capital gains tax 15% Capital gains tax Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|8787066 2. Rentals on cinematographic films and similar works 3. Rental of vessels 4. Rentals of aircrafts, machineries, and other equipment 5. Interest income under the foreign currency deposit system 6. Interest on foreign loans 7. Dividend income 8. Tax on corporate bonds 25% of rentals 25% of rentals 25% of rentals 25% of rentals 4.5% of rentals 7.5% of rentals Exempt Exempt N/A 25% 20% 15% if tax sparing rule is applicable 30% 30% Capital gains tax - NRA-ETBs and NRFCs do not file income tax returns Exceptionally, they are required to file income tax returns to report their gain from dealing in domestic stocks directly to buyers The Tax Sparing Rule - NRFCs shall be subject to 15% final tax on dividend income instead of 30% if the country of domicile of the NRFC credits against the tax due of such NRFC taxes presumed to have been paid by such NRFC from the Philippines equivalent to 15% of the dividends Downloaded by John Eric Taguinod (taguinodjohn624@gmail.com)