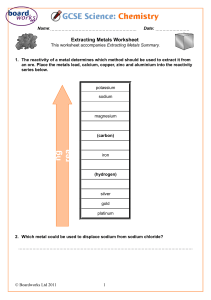
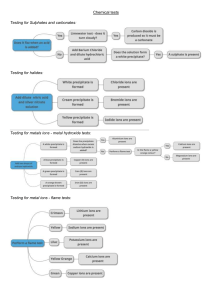
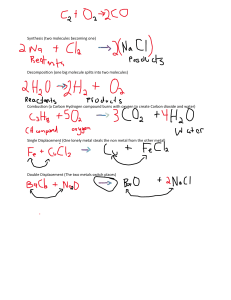
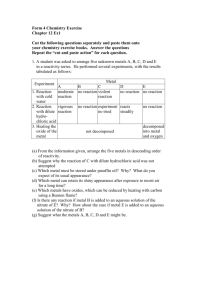
KS3 Chemistry 9E Metals and Metal Compounds 1 of 32 20 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Contents 9E Metals and Metal Compounds Metals and non-metals Metals and acids Metal compounds and acids Symbol equations Summary activities 1 of 32 20 2 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Metal or non-metal? Is this element a metal or a non-metal ? Hard to say! H Li Be Na Mg K Ca Sc Rb Sr Y Cs Ba La Fr Ra Ac 1 of 32 20 3 B C N O Al Si P S V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po Db Sg Bh Hs Mt ? ? ? iron antimony (Sb) iodine (I) (Fe) copper (Cu) phosphorus (P) sulfur (S) magnesium (Mg) Ti Zr Hf Rf F Cl Br I At He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Metals and non-metals in the periodic table The periodic table is a list of all the known elements which are arranged according to the similarities in their properties. Non-metals are Metals are on the mostly on the right. left and in the centre. Xe What type of elements are between metals and non-metals? 1 of 32 20 4 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Metals and non-metals in the periodic table 1 of 32 20 5 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Metal, non-metal or metalloid? francium krypton (Kr) (Fr) silicon(Co) (Si) scandium (Sc) cobalt Which side What are areare thethe nonmetalloids? metals on? H Li Be Na Mg K Ca Sc Rb Sr Y Cs Ba La Fr Ra Ac Ti Zr Hf Rf metalloid non-metal metal B C N O Al Si P S V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po Db Sg Bh Hs Mt ? ? ? F Cl Br I At He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Metals are on Metalloids sometimes Non-metals the left and in behave like metals and are mostly the centre. sometimes like non-metals. on the right. 1 of 32 20 6 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 What are the properties of metals? shiny malleable (easy to bend) sonorous (makes a sound) dense solid good conductor of electricity Properties of metals good conductor of heat high boiling point strong high melting point ductile (can be drawn into wires) Do all metals have these properties? 1 of 32 20 7 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Properties of metals and non-metals 1 of 32 20 8 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Metals and non-metals – true or false? 1 of 32 20 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Using metals Can all metals do the same job?. 1 ofof20 10 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Using metals activity 1 ofof20 11 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Contents 9E Metals and Metal Compounds Metals and non-metals Metals and acids Metal compounds and acids Symbol equations Summary activities 1 ofof20 12 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Reaction of metals with acids Many metals react with acids. When this happens the metal fizzes as bubbles are produced. What do the bubbles mean? A gas is produced. hydrogen burning splint magnesium + acid How can you test to find out if the gas produced is hydrogen? Place a burning splint next to the mouth of test tube. A ‘squeaky pop’ as the gas ignites shows that hydrogen is the gas produced in this reaction. 1 ofof20 13 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Reaction of metals with acids When a metal reacts with an acid, the products are a salt and hydrogen gas. metal hydrochloric sulfuric nitric acid acid acid metal salt chloride sulfate nitrate hydrogen The salt produced depends on the metal and type of acid involved in the reaction: When a metal reacts with hydrochloric acid, the salt produced is a metal chloride. When a metal reacts with sulfuric acid, the salt produced is a metal sulfate. When a metal reacts with nitric acid, the salt produced is a metal nitrate. 1 ofof20 14 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Complete the word equations Complete the word equations for metals reacting with acid: magnesium iron zinc lead ? 1 ofof20 15 32 nitric acid sulfuric acid hydrochloric acid sulfuric ? acid magnesium ? nitrate hydrogen iron ? sulfate hydrogen zinc ? chloride hydrogen lead sulfate hydrogen © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Reactivity of metals increasing reactivity Some metals react more vigorously with acids than others. Metals can be listed in order of how reactive they are. This list is called the reactivity series. 1 ofof20 16 32 potassium sodium calcium magnesium aluminium zinc iron lead (hydrogen) copper silver gold The more reactive the metal, the more vigorous the reaction. A metal that is below hydrogen will not react with dilute acids. © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Contents 9E Metals and Metal Compounds Metals and non-metals Metals and acids Metal compounds and acids Symbol equations Summary activities 1 ofof20 17 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Reaction of metal carbonates with acids When a metal carbonate reacts with an acid, it fizzes giving off carbon dioxide gas. Carbon dioxide can be tested for using the limewater test. When carbon dioxide gas is bubbled through limewater, it turns the limewater cloudy or milky white. Most metal carbonates are not very soluble and so the reactions may be slow. 1 ofof20 18 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Reaction of metal carbonates with acids When a metal carbonate reacts with an acid, the products are a salt, carbon dioxide and water. metal carbonate hydrochloric sulfuric nitric acid acid acid metal carbon salt chloride sulfate nitrate dioxide water The salt produced depends on the metal carbonate and type of acid involved in the reaction: When a metal carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, the salt produced is a metal chloride. When a metal carbonate reacts with sulfuric acid, the salt produced is a metal sulfate. When a metal carbonate reacts with nitric acid, the salt produced is a metal nitrate. 1 ofof20 19 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Complete the word equations metal carbonate acid salt carbon dioxide water Complete the word equation for each reaction between a metal carbonates and an acid: sodium carbonate nitric ? acid sodium nitrate carbon ? dioxide water calcium ? carbonate nitric acid calcium nitrate carbon dioxide water zinc carbonate sulfuric acid zinc ? sulfate carbon ? dioxide ? water 1 ofof20 20 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Reaction of metal oxides with acids When a metal oxide reacts with an acid, the products are a salt and water. metal oxide acid salt water A metal oxide is a type of chemical called a base. Bases are chemicals that react with an acid to produce a salt and water. A base that is soluble in water is called an alkali. Using the products as a clue, what is the reaction between a base (such as a metal oxide) and an acid called? neutralization 1 ofof20 21 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Complete the word equations metal oxide acid salt water Complete the word equation for each reaction between a metal oxide and an acid: magnesium oxide nitric acid magnesium ? nitrate water ? zinc oxide sulfuric acid zinc ? sulfate ? water iron oxide hydrochloric acid iron ? chloride water ? 1 ofof20 22 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Contents 9E Metals and Metal Compounds Metals and non-metals Metals and acids Metal compounds and acids Symbol equations Summary activities 1 ofof20 23 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Chemical formulae – what is the ratio of atoms? The name of a chemical can also be written as a formula. A formula uses chemical symbols and numbers to show the ratio of atoms of each element present in the chemical. Name of salt Formula Ratio of atoms in salt calcium chloride CaCl2 1 Ca 2 Cl sodium sulphate Na2SO4 2 Na 1 S 4 O 1 Mg 1 S 4 O magnesium sulphate MgSO4 magnesium nitrate Mg(NO3)2 1 Mg 2 N 6 O calcium sulphate CaSO4 1 1 S 4 O 1 ofof20 24 32 Ca © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 What is the ratio of atoms in each salt? What is the ratio of atoms in each salt? 1 ofof20 25 32 Name of salt Formula Ratio of atoms in salt sodium chloride NaCl 1 Na 1 Cl magnesium chloride MgCl2 1 Mg 2 Cl potassium nitrate KNO3 1K 1N 3O potassium sulphate K2SO4 2K 1S 4O calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2 1 Ca 2N 6O © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Writing equations using chemical formulae The names of chemicals in a word equation can be replaced with chemical formulae. When a chemical reaction is written using chemical formulae, the equation must be balanced. hydrochloric acid zinc Zn 1 Zn + 2 HCl 2 1 H, 2 1 Cl zinc chloride → ZnCl2 hydrogen + 1 Zn, 2 Cl H2 2H Write down the formula for each chemical. Count the number of atoms on each side of the equation. Where needed, adjust the numbers in front of the formula so that the numbers of atoms on each side are balanced. 1 ofof20 26 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Writing and balancing chemical equations Use chemical formulae to write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between lead and hydrochloric acid. lead hydrochloric acid Pb + 2 HCl lead chloride → PbCl2 + hydrogen H2 Use chemical formulae to write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between calcium oxide and hydrochloric acid. calcium Ca 1 ofof20 27 32 hydrochloric acid + 2 HCl calcium chloride hydrogen → CaCl2 + H2 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Balancing equations activity 1 ofof20 28 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Contents 9E Metals and Metal Compounds Metals and non-metals Metals and acids Metal compounds and acids Symbol equations Summary activities 1 ofof20 29 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Glossary alkali – A soluble base. base – A compound (such as a metal oxide) that reacts with an acid to produce a salt and water. conductor – A material that allows heat and electricity to travel through it easily. malleable – A material that can be hammered into shape. metal – An element found on the left of the periodic table which is usually hard, shiny and a good conductor. metal carbonate – A compound made of a metal, carbon and oxygen. It reacts with acid to produce a salt, carbon dioxide and water. metal oxide – A compound made of a metal and oxygen. It reacts with acid to produce a salt and water. property – A characteristic of a material. 1 ofof20 30 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Anagrams 1 ofof20 31 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004 Multiple-choice quiz 1 ofof20 32 32 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 2004