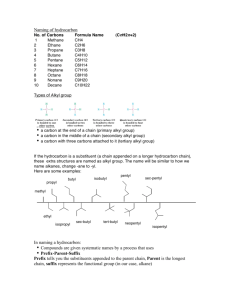
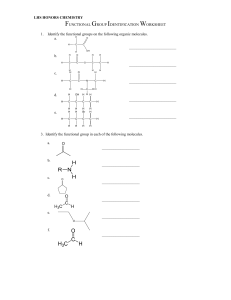
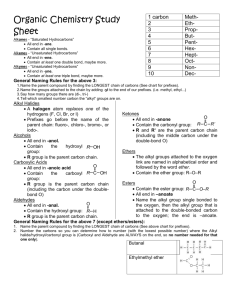
Properties of Organic Compounds - covalent bonds - low melting and boiling points - flammable and undergo combustion - not soluble in water Constitutional isomers - compounds with same molecular formula but different structural formulas - Structural formulas give more info than molecular formula - # of isomers increases with # of carbons Stereoisomers - 3-dimensional shape of a molecule - Conformations are shapes that a molecule - can take because of bond rotations Properties of Carbon - Small size enables close approach - Strong bonds to itself and other elements - Can have long chains, cyclic arrangements or both Hydrocarbons Name Definition Hydrocarbon hydrogen + carbon Hydrocarbon derivative carbon and hydrogen + O, N, S, P, F, Cl, Br Alkanes Single bonds tetrahedral 109.5° Alkenes Double bond Naming 1. Find longest continuous chain of carbon atoms and number from end nearest to first alkyl group 2. Identify alkyl groups and where they are attached 3. Use prefixes di, tri, tetra, etc. when have two 4. or more identical substituents 5. Alphabetize alkyl groups and specify position 6. Iso and cyclo prefixes considered in the alphabetizing. 7. End with the name of the parent chain + “ane” + “ene” + “yne” trigonal planar 120° Alkynes Triple bond linear 180° Cycloalkane One or more carbon rings with single C-C bonds + “Cyclo” at the beginning Number substituents with lowest number alphabetical order Cycloalkene One or more carbon rings with double C-C bonds Aromatic hydrocarbon/ring Cyclic ring with alternating single and double bonds 1. “benzene” as parent ring 2. If one substituent, location not indicated 3. If multiple substituents, ring is numbered to give the lowest possible numbers • ortho (o) - 1,2 relationship • meta (m) - 1,3-relationship • para (p) - 1,4-relationship (benzene) Alcohols Name Definition Naming Alcohols -OH attached to alkane Number from end nearest -OH Replace “e” with “ol” Specify OH location for carbon chains longer than 2 Identify alkyl groups as usual R-OH Classified according to the # of carbons attached to the carbon directly attached to the -OH Phenols -OH and aromatic ring The carbon bearing the OH in the phenol is always C-1 Ethers Name Definition Naming Ethers Carbon - oxygen - carbon Name the groups attached to the O as alkyl groups and add “ether,” using prefix based on number of repeat groups as applicable (example to the left is dimethyl ether) Name Definition Naming Thiols Contain an –SH attached to alkane Number from end nearest -SH Alkane name + “thiol” (example to left is ethanethiol) Specify SH location for carbon chains longer than 2 Identify alkyl groups as usual Name Definition Naming Aldehydes carbonyl (C=O) attached to one H and either a second H or a C The parent chain must include the carbonyl group Parent numbered from end nearest the carbonyl C-O-C Thiols RSH Aldehydes Aldehyde carbonyls are always C-1 and not indicated in the name Aldehyde: drop “e” and add “al” Ketones Name Definition Naming Ketones carbonyl (C=O) attached to two other Cs The parent chain must include the carbonyl group Parent numbered from end nearest the carbonyl Ketone: drop “e” and add “one” Carboxylic Acids Name Definition Naming Carboxylic acids Carboxyl -OH attached to a caronyl (C=O) Parent chain is longest continuous carbon chain that includes the carboxyl group • Numbering begins at the carboxyl group • Alkyl groups are identified by name, position and number of appearances • For IUPAC names, drop “e” on the name of the corresponding hydrocarbon and add “oic acid” Carboxylic acid salts Carboxylate ion Replace “ic acid” with “ate” Esters Name Definition Naming Esters C-O-C One of the carbons is a carbonyl Esters are named in two parts • First: the alkyl group in the alcohol residue • Second: change the ending on the name of the carboxylic acid residue from “ic acid” to “ate” Name Definition Naming Amines Classified by the number of carbon atoms directly attached to the N • primary (1°): 1 C secondary (2°): 2 C • tertiary (3°): 3 C • quaternary (4°): 4 C N atom carries a +1 formal charge The parent chain of amines is the longest chain of carbon atoms attached to the amine. • Named as alkylamines • List the names of the alkyl groups bonded to the N atom in alphabetical order in front of the word amine • Use prefixes to identify duplicate alkyl substituents Amines Aromatic amines Amine of benzene is aniline Alkyl groups on the N use the prefix N- with the alkyl name Amides Name Definition Amides General structure: Naming Amide names are based on the parent carboxylic acid: A nitrogen group (-NH2) replaces the hydroxyl/alcohol (-OH) group on carboxylic acids • For simple amides containing an -NH2, change “oic acid” to “amide”: Propanamide Stars are either H or C groups. • When amine residue is present, substituents attached to the nitrogen are identified and “N” is used to identify location N-ethyl-3,3-dimethylbutanamide