Biomolecules: Proteins, Carbs, Lipids, Nucleic Acids - Presentation
advertisement

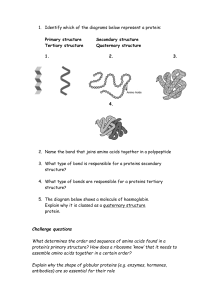
biomolecule Achievements per element Understanding Chemistry Participant educate capable observe , investigate and explain phenomenon daily in accordance rule Work scientific in explain draft chemistry in daily life ; apply operation mathematics in calculation chemistry ; learn properties , structure and interactions particle in form various compound including processing and application in daily life ; understand and explain aspect energy , speed and equilibrium reaction chemistry ; use draft acid-base in daily life ; use transformation energy chemistry in daily including thermochemistry and electrochemistry ; understand chemistry organic including its implementation in everyday life . Achievements per element Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Observe Questioning and predicting Plan and do investigation Processing , analyzing data and information Evaluate and reflect Communicate results Flow of Learning Objectives Proteins 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Explain structure and properties amino acids . Explain essential and non- essential Explain resulting protein structure exists inner hydrogen bonds protein molecules . Explain protein classification Designing test protein denaturation , do experiment , as well communicate through presentation . Observe reaction protein hydrolysis and communicating it through presentation . Designing protein recognition assay experiments , as well communicate it through results presentation . Flow of Learning Objectives Carbohydrate 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Explain grouping monosaccharides . Observe and draw structure open and structured cyclic from glucose and fructose Explain formation bond glycosidic disaccharides and polysaccharides . _ Explain hydrolysis disaccharides . Explain classification polysaccharides Designing recognition test experiment carbohydrates , as well communicate it through results presentation . Designing test produce ethanol from carbohydrates , as well communicate through presentation and produce product . Flow of Learning Objectives Fat 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Explain difference between fat and oil . Explain about saturated and unsaturated fatty acids bored . Explain number iodine in fats and oils . Design and perform reaction saponification , as well communicate results through presentation . Look for information from literature about phosphorid and make works ( klipping ) about phosphorid as well as communicate it through presentation . Look for information from literature about steroids and making works ( klipping ) about phospholipids as well as communicate it through presentation . Flow of Learning Objectives Sour Nucleate 1. 2. Explain about difference between DNA and RNA Look for information from literature about DNA and RNA and making works ( klipping ) about phosphorid as well as communicate it through presentation . biomolecules Key Concepts Difficulty Study Concept Pedagogical subject matter biomolecules proteins carbohydra lipid te s Sour nucleic proteins Amino acids Bond hydrogen amphoteric Protein structure Essential amino acids Primary structure Non- essential amino Structure secondary Bond peptide Structure tertiary Structure quaternary Enzyme Transport proteins Protein nutrient and storage Contractile Structural Defense Regulatory Hydrolysis Denaturation Ninhindrin Biuret test Xanthoproteic test Sulfur test Protein nutrient and carbohydrate Monosaccharide s Ketosa Aldos Triosa Tetrose Pentosa hexose Glucose Galactose Fructose 2-deoxyribose Ribose Structure Monosaccharide s Disaccharides Bond glycosides sucrose Maltose Lactose Polysaccharides Starch Glycogen Cellulose Reaction introduction carbohydrate lipids Fat Fatty acids Saturated Fatty acids do not fed up Number iodine Soaping Hydrolysis Hydrogenation Phospholipids Amphiphilic membrane cell Steroids Amphiphilic cholesterol A nucleic acid Nucleotides Nucleosides DNA RNA proteins monomers Amino characteristi c Amphoteric Active In molecule form Formed by Bond peptide Bond hydrogen Consists from Primary essentia l Non essential Structure tertiary Structure quaternary Reactio n Function biological Enzyme Transport Structure secondary Introduction with own Nutrients and storage Contractil e Structural proteins Defense Regulatory Ninhydrin experience Biuret Xanthoprotea te Sulfur Hydrolysis Denaturati on carbohydrat e Monosaccharid esConsists from Based on group Ketose Based on the number of C atoms Triosa Reaction introduction Bond glycosidic Produce Consists from Molisch test Disaccharid es Consists from sucrose Aldosa tested with Formed by Monomer Polysacchari des from Consists Amylum Tetrosa Pentose Maltose Lactose Hexose Glycogen Cellulose Reducing Starch test lipids Composed from Phospolipids Fat own own Formed by Fatty Number iodine Composed from Saturated Fatty acids do not fed up characteristic function experience Reaction Amphip hilic Hydrolysis Soaping Hydrogenatio n membran e cell Steroid characteristic Amphip hilic Example Cholester ol Sour nucleate monomer Nucleotides DNA RNAs Difficulty diagnosis Study No. Difficulty Study Solutions offered 1 2 Difficult explain structure amino acids . Difficult explain formation peptide bonds in proteins. 3 Difficult explain structure from protein. learning with e- module Virtual learning with application . Make work from molimod . 4 Difficult Understand structure monosaccharides , eg glucose , fructose , and ribose Difficult describe structure howart . Difficult explain difference starch , glycogen , and cellulose . Difficult explain structure of fats, oils , phospholipids , DNA and RNA 5 6 7 1 Student difficult differentiate recognition test For carbohydrates and proteins. Look for from literature about carbohydrate and protein tests as well do test Pedagogic subject matter Approach : scientific Media: Virtual Apps , molimod , tools practice Methods : Problem Base Learning and Project Base Learning thank you