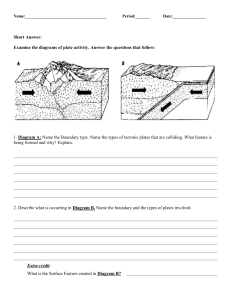
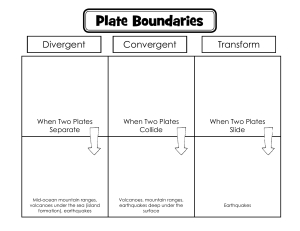
10 Science Quarter 1 – Module 1: Earth and Space Department of Education • Republic of the Philippines Science – Grade 10 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 1 – Module 1: Earth and Space First Edition, 2019 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this book are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education Secretary: Undersecretary: Assistant Secretary: Development Team of the Module Authors: Lesson 1 & 2 - Hellen M. Dizon Lesson 3 - Lilibeth B. Montemayor Lesson 4 - Patty M. Canyong Lesson 5 & 6 - Dulce S. Ortega Lesson 6 - Nilo Salazar Lesson 7 - Marygin T. Joson Lesson 8 - Helen Rose A. Ferrancullo / Shirlie G. Custodio Editor: Rebecca M. Roxas, EPS Reviewers: Arlene Gatpo, PSDS Illustrator: Layout Artist: Management Team: Malcolm S. Garma, Regional Director; Genia V. Santos, CLMD Chief; Dennis M. Mendoza, Regional EPS in Charge of LRMS and Regional ADM Coordinator; Maria Magdalena M. Lim, CESO V, Schools Division Superintendent; Aida H. Rondilla , CID Chief; Lucky S. Carpio, Division EPS in Charge of LRMS and Division ADM Coordinator Printed in the Philippines by ________________________ Department of Education – Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR) (Sample) Office Address: ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Telefax: E-mail Address: ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 10 Science Quarter 1 – Module 1: Earth and Space Department of Education • Republic of the Philippines Introductory Message An Alternative Delivery Mode is designed for the “New Normal” approach in teaching-learning process. This mode of learning materials helps the students as well as the teachers the teaching-learning process in a social distancing. In this module the learners must obtained the objectives of the lessons through his/her own learning process or he/she can be guided with his/her parents, elder siblings, any relatives, friends or with his/her guardians In answering the activities, pre-test and post-test in this module, the learners should write his/her answer in a separate sheet of paper. The answer sheet must be compiled in a short folder with corresponding name, grade and section. This module will be answered for three to four days. One lesson must be learned and understand. In this module each learners will develop their comprehension hence, the level of languages used is easy to understand. Learners should also enhance their reading ability. In reading and doing the activity in this module learners should learned that earthquake, volcanic eruption, mountain ranges formation, trench, plate tectonics are have interconnection with one another. What I Need to Know This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you master the Earth and Space. The scope of this module permits it to be used in many different learning situations. The language used recognizes the diverse vocabulary level of students. The lessons are arranged to follow the standard sequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be changed to correspond with the textbook you are now using. The module is divided into three lessons, namely: Lesson 1 – Describe the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters and major mountain belts; Lesson 2 – Infer the relationship of tectonic plates, earthquake epicenters and active volcanoes. Lesson 3 – Relate the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major mountain belts to Plate Tectonic Theory After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. Describe the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major mountain belts; 2. Enumerate the different geologic processes/events that occur from the different boundary; 3. Determine the scientific basis for dividing the Lithospheric plates. 4. Relate hot spot with plate tectonic. What I Know Multiple Choice: Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter on a separate sheet of paper. 1. The oceanic crust usually subduct beneath the continental crust when they collide because it is A. denser than continental crust B. thicker than continental crust C. less dense than continental crust D. thinner than continental crust 2. In which type of boundary do plates moves away from each other? A. convergent B. divergent C. transform D. strike-slip 3. Mountains are formed at A. convergent B. divergent C. transform D. strike-slip 4. Rift valley are formed at A. convergent B. divergent C. transform D. strike-slip 5. What is the cause of the volcanoes on Hawaii? A. convergent plate boundary B. divergent plate boundary C. hot spot D. rift zone Lesson 1 Earth and Space The Earth composed of air, water and land. These three composition of Earth are divided into different layers and materials. The water and air are taken already in grade 7 and grade 8. While in grade 9 mostly of the topic are related in space. In this lesson we are more dealing with the relationship of the layers of the earth, volcanoes, earthquakes, mountain ranges, and other geological processes. What’s In The Earth’s lithosphere are divided into several plates. Due to different geologic processes/events the earth surface have different types of land and water formation, these will cause by the movements of plate. There are three kinds of movement of plate: convergent plate, divergent plate and transform plate. Notes to the Teacher This module must be given to the learners a week before the students answer it in the exact given day of the lesson. And collect their answer before the second week of the lesson. And so on and so forth. This module will be your basis in rating or giving grades to your students. What’s New Earth and Space Defined Earth and Space is the interconnection of the land, oceans, atmosphere and the life of earth itself. It’s include all the cycles such as: water cycles, carbon cycles, rock cycles, and as well as the different movements on the earth surface. Every things happened on our planet can be explained and connected to earth and space. Observe the different pictures do you think they are connected with one another? Let’s us find out by reading and doing the activities in this module. Source: https://www.google.com/search?q=picture+of+earthquake&tbm=isch&ved=2ahUKEwjCm6PUlYbqAhUKJqYKHYluAoUQ 2cCegQIABAA&oq=picture+of+earthquake&gs_lcp=CgNpbWcQARgAMgIIADICCAAyAggAMgIIADICCAAyAggAMgIIADICCAAyAggAO gQIABAeOgQIABAYOgYIABAKEBg6BQgAELEDUNPvB1jfrQhgo78IaABwAHgAgAHdAYgBmRqSAQY5LjE4LjGYAQCgAQGqAQtnd3 Mtd2l6LWltZw&sclient=img&ei=qaToXoKjFIrMmAWJ3YmoCA&bih=657&biw=1366&hl=en#imgrc=0I4qkyAB82godM What is It Since you tackled already the three branches of earth and space in your previous grade level, in this module you will learned more about the solid part of the earth which is the lithosphere. Source: https://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/facts/media/plate-boundaries-800.jpg Crust and upper mantle is made up of Earth’s lithosphere. Earth lithosphere is made up of different tectonic plates, that’s move slowly over time. A divergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other. Along these boundaries, earthquakes are common and magma (molten rock) rises from the Earth’s mantle to the surface, solidifying to create new oceanic crust. When two plates come together, it is known as a convergent boundary. The impact of the colliding plates can cause the edges of one or both plates to buckle up into a mountain ranges or one of the plates may bend down into a deep seafloor trench. A chain of volcanoes often forms parallel to convergent plate boundaries and powerful earthquakes are common along these boundaries. Two plates sliding past each other forms a transform plate boundary. Natural or human-made structures that cross a transform boundary are offset—split into pieces and carried in opposite directions. Rocks that line the boundary are pulverized as the plates grind along, creating a linear fault valley or undersea canyon. Earthquakes are common along these faults. In contrast to convergent and divergent boundaries, crust is cracked and broken at transform margins, but is not created or destroyed. What’s More Places on earth where most of the earthquakes originated or some mountains and volcanoes were formed mark the boundaries of each lithospheric plate. Earthquake epicenters outline the plates. Mid-ocean ridges, trenches, and large faults mark the edges of the plates, and this is where earthquakes occur (Figure below). Source: https://www.ck12.org/book/ck-12-earth-science-for-high-school/section/6.4/ What I Have Learned According to the plate tectonics model, the entire lithosphere of the Earth is broken into numerous segments called plates. Plate boundary- a theory which suggests that Earth’s crust is made up of plates that interact in various ways, thus producing earthquakes, mountains, volcanoes, and other geologic features. • Each plate is slowly but continuously moving. • Three types of plate boundaries: 1. Divergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other. This types of boundary usually produced earthquakes and rift valley. 2. Convergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates come together. The plate which is denser will sink and form a trench and the other plate which is less dense will crumple and form a mountain ranges, an island arc, a volcanoes. It also cause a tremendous earthquakes that may produce a tsunami if the earthquakes happen under the ocean. 3. Transform plate boundary occurs when two tectonic plates sliding past each other. This type of boundary usually creating a linear fault valley or undersea canyon. Earthquakes are also produced along these faults. Hot spot- a concentration of heat in the mantle capable of creating magma Subduction- is a geological process that takes place at convergent boundaries of tectonic plates where one plate moves under another. • Trench a depression in the seafloor produced by subduction process. • Volcanic Island arc a chain of volcanoes that develop parallel to a trench. • • What I Can Do Activity 1 Let’s Match! Critical Thinking Communication Objectives: • Describe the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenter and mountain ranges. • Determine the different scientific basis for dividing the Lithospheric Plates. Materials: Fig. 15 Earth’s lithosphere that divided into majors plates Fig. 16 Mountain Ranges of the World Fig. 17 Locations of earthquakes Different colors of Marking Pen ( Red, Blue, Green ) Source:file:///C:/Users/WIN/Downloads/12%20STEM%205/2nd%20SEM!/BIOLOGY/Volcano,%20Earthquake,Fault.pdf Fig. 15 Earth’s lithosphere is divided into about 13 majors plates. Where plates collide, separate, and slip past one another at plate boundaries, interesting geological activity results. Source:file:///C:/Users/WIN/Downloads/12%20STEM%205/2nd%20SEM!/BIOLOGY/Volcano,%20Earthquake,Fault.pdf Fig. 17 Locations of earthquakes that have accurred between 1990 and 2000 are plotted above. Source: https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-a-mountain-range-definition-lesson-quiz.html Fig. 16 Mountain Ranges of the World Procedure: 1. Study Figure 15 showing the active volcanoes distribution around the world, Fig. 17 showing the earthquakes distribution and Fig. 16 Mountain Ranges of the World. 2. Using three different colors of marking pen (red, blue and green) Trace the approximate locations of several active volcanoes, earthquakes and mountain ranges on one plastic sheets. 3. Observe. Q1. What have you notice about the three different color of marking pen that trace on one plastic sheet? Q2. How are volcanoes, earthquakes and mountain ranges distributed on the map? Q3. Where are they located? Q4. Where are there no earthquakes? Q5. Based on the map, mention a country that is unlikely to experience volcanic eruption. Q5. How will you relate the distribution of mountain ranges with the distribution of earthquake epicenters and volcanoes? Q6. Can you make a conclusion regarding the location of volcanoes, earthquakes and mountain ranges. Source: Grade 10- Science – LM The Earth’s lithosphere, which includes the crust and upper mantle, is made up of a series of pieces, or tectonic plates, that move slowly over time. Source: https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/370491506826108033/visual-search/?cropSource=6&h=346&w=544&x=10&y=10 Figure 8. Map showing the relative motion of plates (Arrows indicate the direction of motion) Types of Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other. This types of boundary usually produced earthquakes and rift valley. Convergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates come together. The plate which is denser will sink and form a trench and the other plate which is less dense will crumple and form a mountain ranges, an island arc, a volcanoes. It also cause a tremendous earthquakes that may produce a tsunami if the earthquakes happen under the ocean. Transform plate boundary occurs when two tectonic plates sliding past each other. This type of boundary usually creating a linear fault valley or undersea canyon. Earthquakes are also produced along these faults. Image Source: https://slideplayer.com/slide/13123816/ Activity 2 Plate meets Plate! Objectives: • Explain the processes involves along convergent boundaries. • Determine the different geologic process that occur from the colliding of plates. Procedure: 1. Study Figure 10, Fig.11 and Fig. 12 showing a cross-sectional diagram of plates that are converging, and answer the questions in the table. Plate B Plate A Source:http://www.geosci.usyd.edu.au/users/prey/ACSGT/EReports/eR.2003/GroupD/Report1/web%20pages/ assignment_1.html Figure 10. Cross-sectional diagram of converging continental and oceanic plates Oceanic Plate A Oceanic Plate B Source:http://www.geosci.usyd.edu.au/users/prey/ACSGT/EReports/eR.2003/GroupD/Report1/web%20pages/ assignment_1.html Figure 11. Cross-sectional diagram of converging oceanic plates Plate A Plate B Source:http://www.geosci.usyd.edu.au/users/prey/ACSGT/EReports/eR.2003/GroupD/Report1/web%20pages/ assignment_1.html Figure 12. Cross-sectional diagram of converging tectonic plates Table: Questions 1. What type of plate is Plate A? - How about Plate B 2. Describe what happens to plate A as it collides with plate B. - Why it happens? 3. What are the geologic processes/events that will occur in this plate movement? Source: Grade 10- Science - LM Fig. 11 Fig. 12 Fig. 13 Additional Information: Examples of Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent is the Philippine Plate moving under Eurasian Plate created the Philippine Islands. Philippine and Pacific Plate moving under the Eurasian created Japan. Source: https://earthobservatory.sg/files/resources/large/philippines-block_diagram.png Critical Thinking Communication Activity 3 Let’s Separate! Objectives: • Explain the processes involves along divergent boundaries. • Determine the different geologic processes occurs if two plates are moving apart. Materials: picture of cracked boiled egg, Fig. 13 Development of a rift valley Procedure: 1. Study the picture below. Describe what have you observe on the cracked boiled egg shell. 2. Supposed the egg shell is a crust, do you think the crust can also separate with each other? 3. Study Fig. 13 Development of a rift valley and answer the guide questions below. Source:https://www.bonappetit.com/video/watch/every-way-to-cook-an-egg-59-methods Source: https://sites.google.com/site/tectonicswebsite/tectonic-processes Figure 13. Development of a rift valley Guide Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. In what direction the two plates move? What makes the two plate to move away from each other? Slowly what happen at the middle of the two separating plates? What geologic features form in this movement? If this event continues for millions of years, what do you think will be the effect on the crust? Critical Thinking Communication Activity 4 Strike, Slip, Slide Objective: determine the effect of transform-fault boundary on the Earth’s crust. Materials: images of transform boundary Procedure: 1. Study the images below and answer the guide questions. Source: https://www.ck12.org/assessment/tools/geometrytool/plix.html?eId=SCI.ESC.266&questionId=577d46ff9616aa26e7e6705e&artifactID=2776348&plix_redirect=1 Guide 1. 2. 3. Questions: How will you describe the movement of the two plates? What geologic event accompanied by the transform boundary? How can transform faults cause destruction even after the earthquake is over? Activity 5 It’s Hot, Hot, “Hot Spot” Critical Thinking Communication Objective: Relate hot spot with plate tectonics Materials: Images of Hot Spot Procedure: 1. Study the images below, analyze and answer the guide questions below. I 2 3 4 Guide Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the first volcano formed? What is the second volcano formed? What is the recent/last volcano formed? Which among the volcano is the oldest? youngest? Why it happens that there’s a series of volcano or chain of volcano in on place? What do you call this place where the chain of volcanoes are formed? Assessment Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Which plate boundary is formed between the Philippine plate and the Eurasian plate? A. convergent C. divergent B. reverse fault D. transform fault 2. In which type of boundary do plates moves away from each other? A. convergent C. transform B. divergent D. strike-slip For questions 3-4, refer to the diagram. Choose the letter of the correct answer. A B C 3. Which is the convergent boundary? 4. Which is the divergent boundary? 5. Refer to the picture below. Which of the following islands is the oldest? A. Hawaii C. Molokai B. Maui D. Kauai Additional Activities Open Discussion: One of the famous transform fault is the San Andres Fault found in California. This fault has a lots of recorded destructive earthquake. One of this days this fault is predicted to produce another tremendous and dangerous earthquake that can be called “The Big One”. Why this fault is so destructive and dangerous? How will you prepare for this kind of earthquake? Answer Key What 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. I Know A B A B C Assessment 1. A 2. B 3. B 4. A 5. D Activity 1: 1. They are located in the same place 2. Volcanoes, earthquakes and mountain ranges are distributed on the same place/location 3. Majority are found along the edges of some continents 4. Answer may vary. Some possible answer are: large part of the Pacific ocean, northernmost Asia, majority of Europe, eastern portion of North and South America and western Africa 5. Mountain ranges are found in places where volcanoes and earthquake epicenters are also located. 6. I therefore conclude that the earthquake epicenters, mountain ranges and volcanoes are in the same places because they are interconnected with one another. Activity 2: Questions 1. What type of plate is Plate A? - How about Plate B 2. Describe what happens to plate A as it collides with plate B. - Why it happens? 3. What are the geologic processes/events that will occur in this plate movement? Fig. 11 oceanic Fig. 12 oceanic Fig. 13 continental continental Plate A subduct or sink oceanic Plate A crumpled upward continental Plate A subduct or sink Plate A is denser than Plate B Trench, volcanoes, mountain ranges, earthquake Plate A is less dense than Plate B Trench, island arc, mountain ranges, volcanoes, earthquake, tsunami Plate A is denser than Plate B Mountain ranges, earthquake Activity 3: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. They move away from each other The releasing or the coming out of magma There’s a new sea floor form Mid-ocean ridge, rift valley, new sea floor Answer may vary, some possible answer: the sea floor become wider, the ocean become shallow, more rift valley were formed Activity 4: 1. They strike slip with each other 2. Earthquake 3. Can destroy roads, infrastructure, train track, rivers that may cause flood, other human properties and lives. Activity 5: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Kauai Oahu Hawaii Kauai/Hawaii There’s a source of high temperature or a magma chamber Hot spot References • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Science – Grade 10 Learner’s Manual First Edition 2015 https://www.edinformatics.com/math_science/seismic-waves-and-the-layers-of-theearth.html https://uh.edu/~jbutler/physical/chap18mult.html https://www.google.com/search?q=images+of+seismic+waves&source=lnms&tbm=isc h&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiUqr_t8rDpAhWMUt4KHYTlBlgQ_AUoAXoECBAQAw&biw=1 https://www.google.com/search?q=p+waves+images&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X& ved=2ahUKEwiS8Jud0LLpAhXRfd4KHZRaBW0Q_AUoAXoECA0QAw&biw=1366&bih= 657#imgrc=ndsRQjSDwhd7DM http://www.geo.mtu.edu/UPSeis/locating.html https://www.google.com/search?q=activity+on+seismic+waves&source=lnms&tbm=is ch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjvvp3a1rLpAhWrL6YKHVFAK4Q_AUoAXoECAwQAw&biw=1366&bih=657#imgrc=Tw6NPCJKrwFOeM&imgdii=4F MP76JZ1DOY1M https://www.google.com/search?ei=lRS9XpzCK5PWhwP7saLICQ&q=subduct&oq=sub duct&gs_lcp=CgZwc3ktYWIQARgGMgQIABBDMgQIABBDMgQIABBDMgQIABBDMgQIA BBDMgIIADICCAAyAggAMgIIADICCAA6BAgAEEc6BggAEA0QHjoFCAAQkQI6BQgAEIM BUIcYWLJJYNSgAWgAcAF4AIABngOIAeEVkgEJMC41LjIuMi4ymAEAoAEBqgEHZ3dzL Xdpeg&sclient=psy-ab https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/58a1cca5591412611058a6d8/types-of-plateboundaries https://www.google.com/search?q=image+of++type+of+plate+boundary&source=lnms &tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjo6L7_orPpAhVJVN4KHRH_BTYQ_AUoAXoECA0QAw &biw=1366&bih=657#imgrc=vN45BGQNEYTxUM https://www.ducksters.com/science/quiz/earthquakes_questions.php http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/visualgeology/geology101/Geology100Exams/Earthquakes. pdf https://www.maplesoft.com/support/help/Maple/view.aspx?path=MathApps/Epicen terOfEarthquakes https://www.kqed.org/quest/136760/how-to-find-the-epicenter-of-an-earthquake https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seismology https://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/facts/plate-boundaries.html https://slideplayer.com/slide/13123816/