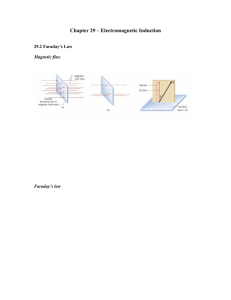
PHYSICS FORM 4 (NOTE) CHAPTER 7: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 7.2 FARADAY’S LAW OF INDUCTION Definition The faraday’s law of induction states that:The average EMF induced in a conducting coil of N loops is equal to the negative of the rate at which the magnetic flux through the coil is changing with time. N t The negative sign in the equation indicates that the direction of the induced emf is such that it opposes the change in flux. B. A Note; Where; is magnetic flux B is the strength of the magnetic field A is area perpendicular to magnetic field Real – life applications of Faraday’s Law 1. 2. 3. 4. Induction stoves Tape players Metal detector Transformers Example 7.3 Consider a flat square coil with 5 turns. The coil is 0.50 m on each side, and has a magnetic field of 0.5 T passing through it. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field; the field points out of the page. Use Page 1 of 2 Faraday’s Law to calculate the induced emf if the magnetic field is increased uniformly from 0.5 T to 1 T in 10 s. Solution N N N t f i t B f A Bi A NA t B f Bi t 1 0.5 50.52 10 0.0625V Page 2 of 2