FinTech Adoption Drivers & Challenges in Financial Services
advertisement

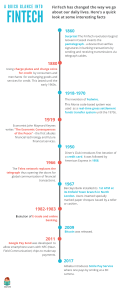
What are the key drivers and challenges of FinTech adoption in the financial services industry? INTRODUCTION FinTech is a portmanteau of "financial" and "technology". It refers to the use of technology to deliver financial services in a more efficient and convenient way. FinTech companies use a variety of technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Fig.1. Source: https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/ big data, to develop new products and services that can improve the way people manage their money. It encompasses any technical advancement in the financial industry, such as retail banking, investing, and even crypto-currencies [Decentralised Finance (DeFi)] that aims to improve financial literacy and education. FinTech services are a disruptive innovation that will transform the financial system. The financial institution makes significant investments. For example, global investment in FinTech increased dramatically in 2008, reaching around 930 million USD. Not to note that FinTech investment has more than tripled in five years, reaching 2.97 billion USD in 2013. FinTech introduces new technology that has the ability to cause a paradigm change in client lifestyles by giving a superior user experience of attaining rapid, seamless, anytime, and anywhere banking. Trends In Fintech Services Fintech services began to emerge in the 1950s, with the introduction of the automated teller machine (ATM) and credit card processing, followed by electronic stock trading and e-commerce. Each decade at the period saw the introduction of new technologies, which some took for granted. Now, the new generation of fintech services is based on near-universal internet access via internet banking, which has been followed by the emergence of mobile phone banking, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain, which helps to smoothen the banking business operation. FinTech service adoption has consistently increased, from 16% in 2015, the year EY's first FinTech Adoption Index was released, to 33% in 2017, to 64% in 2019. Even non adopters are becoming increasingly aware of FinTech. For example, 96% of customers worldwide are aware of at least one alternative FinTech service accessible to assist them transfer money and make payments. Emerging markets are leading the way, with 87% adoption rates in both China and India. Russia and South Africa are close behind, both having 82% adoption. The adoption rate is increasing quicker than expected. The actual worldwide adoption rate of 64% in 2019 surpasses the 52% future adoption rate anticipated by the 2017 study by 12 percentage points. FinTech has taken off globally, becoming the mainstream in all markets investigated. Among industrialized nations, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Ireland are at the forefront of adoption, reflecting the evolution of open banking in Europe. Fig.2. Source: https://assets.ey.com/ Types Of Fintech Services 1. Crowd funding: It is a set of services that enable networks of people to manage the development of new goods, media, and ideas while earning revenue for charity or venture capital. 2. Crypto currencies: These are digital or virtual forms of money that use cryptography for secure transactions and control of new units. They are decentralized and typically operate on a technology called blockchain, which is a distributed and transparent ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. 3. Cloud computing services: These refer to the delivery of various computing resources, including computing power, storage, databases, networking, software, and more, over the internet. These services are provided by cloud service providers (CSPs) and allow individuals, businesses, and organizations to access and utilize computing resources without the need for on-premises infrastructure. Cloud computing services are designed to be flexible, scalable, and cost-effective, enabling users to pay for only the resources they use. 4. Mobile banking: It refers to the use of mobile devices, such as smart phones and tablets, to conduct various banking and financial transactions remotely. It allows customers to access their bank accounts, manage finances, and perform banking tasks without the need to visit a physical bank branch. Mobile banking services are typically provided by banks and financial institutions through dedicated mobile apps or mobilefriendly websites. Adoption of Fintech in SMEs Fintech, or financial technology, is the use of technology to improve and automate financial services. Fintech companies are developing new and innovative products and services that are designed to meet the needs of SMEs. SMEs have become substantial consumers of FinTech internationally, with one in every four respondents claiming to have utilised services supplied by a FinTech in each of the following main categories: Banking and payments, financial management, financing, and insurance are all areas of expertise. Fig.3. Source: https://assets.ey.com/ This suggests that SMEs have made FinTech products and services an important element of their financial management. As with the consumer sector, this tendency was especially noticeable in China, where 61% of those polled agreed. The most popular FinTech service was in the banking and payments category, with 56% of customers claiming to have used it. China was once again a major outlier, with 92% of Chinese SMEs reporting having utilised FinTech banking and payments services. Key drivers of FinTech adoption in the financial services industry 1. The advancements in digital technologies The fast development of hardware and software, as well as the increasing convergence of information and communication technologies during the last two decades, has been critical to the growth of fintech firms. These advancements enable new business models and organisational structures to arise and disrupt sectors ranging from tourism and entertainment to finance. Furthermore, developing digital technologies such as 5G, the Internet of Things, blockchain, artificial intelligence, big data, and significant advancements in data storage and management are opening up new opportunities to change the way the financial sector operates. The exponential expansion of digital technology has enabled fintech businesses to supply financial services more quickly and cost-effectively than traditional banks, while also providing more comfortable digital banking experiences to their consumers. With the introduction of digital wallets, mobile banking, and other financial apps, the financial services business is already changing. Individuals may now use digital wallets to pay bills, buy real or digital goods, send money to family or friends, pay for parking or taxis, and create denotations. 2. The Evolving Landscape of Customer Expectations Customers' expectations for the financial services supplied by the traditional banking system have shifted as technology has advanced. Customers have grown increasingly self-sufficient in basic transactions and more demanding of banks' roles in complicated transactions. Furthermore, consumers have grown more connected, aware, empowered, and active as a result of new search and social media technologies. Consumers are increasingly making purchases online, and digital contact points have become critical in the customer journey, influencing both online and physical sales. Furthermore, the fintech age has provided 24/7 access to financial services rather than being confined to banking hours. As some banks throughout the world continue to deliver antiquated, expensive, and timeconsuming financial services, fintech startups are seizing the chance to supply some important operations of traditional banks while relying on technology and innovation to gain a competitive edge. Technology alone is not disruptive; rather, evolving customer behaviour and demand is the true disruptor. Changing consumer requirements are seen to be at the heart of the financial services sector's digital revolution. According to recent study performed in the United Kingdom and Germany, more than 90% of banking clients in the United Kingdom and more than 85% in Germany feel that a good technological offering is the most significant aspect when picking where to bank. Customers prefer other characteristics of fintech services, such as convenience, because most transactions are completed through online platforms rather than visiting a financial institution. Users may utilise mobile applications to execute various banking services such as bill payments, checking deposits, account balances, statements, and many more operations without visiting a bank. 3. The implications of COVID-19 The COVID-19 pandemic struck unexpectedly in a world unprepared for such a catastrophe, wreaking havoc on the worldwide economy. While worldwide markets have become used to economic shocks over the last century, the COVID-19 pandemic crisis was unique in one important way: it was the result of a global health catastrophe that immediately turned into an economic crisis. Due to a lack of physical presence in the normal places of business, the COVID-19 epidemic highlighted the necessity to hasten the digitization of many elements of people's everyday operations. Because of the spread of the corona virus, millions of individuals worldwide were compelled to work from home. When their operations were shut down due to the COVID-19 epidemic, several businesses were compelled to go online. As a result, customers switched to digital channels to complete their everyday transactions, and e-commerce has grown in popularity. The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a massive upgrade of people's digital knowledge across all age and social categories across the world. 4. Reduced obstacles to market entry Lower regulation for non-bank financial services was one of the factors that allowed fintech businesses to enter the financial services sector. Following the 2008 financial crisis, banks faced greater capital requirements and tougher lending conditions, making it difficult for small enterprises and people to acquire credit, resulting in an unmet demand for financial services. Banks have been busy dealing with laws, while fintech startups have been expanding their operations by employing technology to give novel financial services to clients at cheap cost. Furthermore, because they are less constrained by legal limitations and are ready to take on more risk than regulated banks, fintech businesses may unbundle financial service offerings using new technology. Because of the comparatively modest regulatory constraints, fintech businesses were able to adapt to a changing business and technological environment more easily than banks. The regulatory environment for innovative financial service providers appears to have been relaxed, lowering the hurdles to market access for fintech businesses. Furthermore, developments in technology, software, and cloud infrastructure have enabled the construction of sophisticated fintech platforms with small teams, allowing new entrants with fewer resources to compete in this market. As a result, established financial institutions today compete with incumbent competitors as well as a growing number of new financial and non-financial entities. 5. Increasing investments in the fintech industry during the previous decade Following the 2008 financial crisis, financial institutions and technology corporations appear to be boosting their investments in fintech advances. External investment for fintech advances has increased rapidly in recent years throughout the world. According to KPMG study, overall deal value has increased from $51.2 billion in 2014 to $210.1 billion in 2021. During the same time period, the number of transactions climbed from 1,628 to 5,684. Global venture capital investments in fintech startups increased from $1.89 billion in 2010 to $115 billion in 2021. Over the previous decade, increased investment in fintech businesses has resulted in an increase in the number of these firms and their activity in the financial services industry. Customers' increased need for e-commerce and mobile banking platforms that provide a more user-friendly environment for completing financial transactions is driving the worldwide fintech business. Some data related to Key Drives of Fintech in India 1. Awareness of various financial technology items The majority of responders (71.2%) are well-versed about digital wallets. The majority of respondents (55.0%) are aware of digital banking. The majority of responders (60.4%) are well-versed in mobile banking. The majority of responders (62.2%) are well-versed with mobile payments. The majority of responders (37.8%) are well-versed in digital lending. 2. Respondents' attitudes regarding fintech goods The majority of respondents (52.3%) have been utilising fintech for 2-3 years. The majority of respondents (71.2%) use mobile to access fintech services. The majority of respondents (40.5%) strongly believe that the rate of use of fintech products has grown after Covid-19. The majority (66.7%) of respondents strongly agreed that the most significant advantage acquired via fintech was speed. The majority (74.8%) of respondents strongly agreed that the most significant benefit acquired via fintech was convenience. The majority (66.7%) of respondents strongly agreed that the most significant advantage achieved through fintech is ease of access. 3. The respondents' degree of familiarity with various financial technology The majority (73.0%) of respondents frequently use Google Pay. The majority of responders (70.3%) always utilise phone pay. The majority of responders (68.5%) utilise razorpay on sometimes. The majority of responders (64.0%) always use paytm. The vast majority of responders (79.3%) never use mobikwik. The vast majority of responders (92.8%) never use coverfox. The vast majority of responders (98.2%) never use bankbazaar. All (100%) of those polled have never used zestmoney. The majority of responders (83.9%) never utilise early salary. The majority of respondents (78.4%) have used a digital wallet. The majority of respondents (83.8%) had used digital banking. All (100%) of those polled had used mobile banking. Challenges of FinTech adoption in the financial services industry 1. Data Security Data security has emerged as a big worry in the Internet world, whether it is related to mobile banking, payment applications, or Fintech in general. In 2021, there were 1,862 data breaches with an average cost of $4.24 million. This is a new all-time high, raising even more concerns about financial cybersecurity. Traditional banking systems, as we all know, rely on security guards, CCTVs, vaults, and massive bulletproof doors to keep their data safe and secure. However, when it comes to virtual security, things are not as simple as they appear. Vulnerabilities are far more subtle and possibly have a greater impact on consumers, as not only their money but also their personal data is at danger. 2. Regulatory Compliance One of the difficulties with fintech is that this high-risk business is plagued by government rules. Companies must comply with several regulations, including the GDPR, GLBA, Wiretap Act, Money Laundering Control Act, and others. As these firms become more popular and challenge traditional financial institutions, regulators have begun to scrutinise their operations to ensure they are in compliance with laws and regulations. These high regulatory and compliance standards can result in additional expenses and delays for fintech startups, making it harder for them to compete with conventional financial institutions. 3. Lack of tech and mobile expertise Some financial organisations or banks in the fintech industry lack adequate or convenient mobile banking services. Some banks, however, attempt to duplicate websites, but in this digital age, no one would prefer a mobile application. Every user desires a simple and straightforward method of operation. As a result, a lack of competence in fintech mobile app development services results in unfriendly apps that do not fully use mobile devices. Apps may not benefit from NFC chips, geolocation capabilities, fingerprint unlocking, and other features, for example. 4. AI- Integration and data Fig.2. Source: https://www.techtic.com/ According to Accenture, 82% of US bankers and 79% of worldwide bankers believe AI will transform the way banks gather data and engage with consumers. As we all know, big data and artificial intelligence have had an influence on every organisation. Organisations may gather personal information about consumers, from social status to financial behaviour, habits, and in-app activity, using big data. This information is critical for banks, especially when it comes to credit ratings and other high-risk banking services. AI automates the whole process of detecting fraud, doing risk analysis, and successfully managing transactions with the use of big data. 5. Market Saturation and competition Traditional financial institutions, which have adopted comparable technology and business models to remain competitive, are also fierce competitors for fintech firms. As a result, it is becoming increasingly difficult for fintech businesses to distinguish themselves in the competitive fintech sector in order to attract and recruit consumers. Traditional financial institutions have a large customer base and a well-established brand. This makes it difficult for fintech companies to acquire new customers. Traditional financial institutions have access to more capital than fintech companies. This gives them an advantage in terms of developing new products and services and acquiring new customers. Despite these challenges, fintech companies are still growing rapidly. They are able to attract customers with their innovative products and services, and they are forcing traditional financial institutions to innovate in order to compete. Works Cited Bureshaid, N., Lu, K. J., & Sarea, A. (2022). Adoption of FinTech Services in the Banking Industry. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358388507_Adoption_of_FinTech_Services_in _the_Banking_Industry Editorial Team. (2023). Top 8 challenges in fintech. anywhere.epam.com. https://anywhere.epam.com/business/fintech-challenges Elsaid, H. (2023). 5 factors driving the rise of fintech in the financial services industry. Trade Finance Global. https://www.tradefinanceglobal.com/posts/5-factors-driving-risefintech-financial-services-industry/ Hussain, M. (2023, January 28). The challenges faced by fintech companies in the current economic climate. Times of India Blog. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/voices/the-challenges-faced-by-fintechcompanies-in-the-current-economic-climate/ Hwa, G. (2019). EY Global FinTech Adoption Index 2019. In https://assets.ey.com. EY. Retrieved August 4, 2023, from https://assets.ey.com/content/dam/ey-sites/eycom/en_gl/topics/financial-services/ey-global-fintech-adoption-index-2019.pdf Hwa, G. (2020). Eight ways FinTech adoption remains on the rise. EY - Global. https://www.ey.com/en_gl/financial-services/eight-ways-fintech-adoption-remains-onthe-rise India, E. (2020). Can in-store digital experience transform the future of shopping? www.ey.com. https://www.ey.com/en_in/consulting/seven-key-trends-shaping-the-future-of-fintechindustry India’s growing FinTech market. (n.d.). Drishti IAS. https://www.drishtiias.com/dailyupdates/daily-news-editorials/india-s-growing-fintech-market Kagan, J. (2023). Financial Technology (Fintech): Its uses and impact on our lives. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fintech.asp Kanimozhi, V., Assistant Professor, Department of Management Sciences, Hindusthan College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, India., & K, D. R., MBA Student, Department of Management Sciences, Hindusthan College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, India. (2022). The Key Drives of Fintech in India; Study on Customer Adoption and Attitude. Quest Journals, Volume 10(7), 66–73. https://www.questjournals.org/jrbm/papers/vol10-issue7/Ser-1/H10076673.pdf Sharma, I. (2023). Fintech challenges and opportunities. Software and Technology Blog TatvaSoft. https://www.tatvasoft.com/outsourcing/2022/01/fintech-challenges-andopportunities.html Techtic Solutions, Inc. (n.d.). 8 Key Challenges Fintech Industry Faces and their Solutions. Techtic Solutions. https://www.techtic.com/blog/fintech-industry-challenges/ Wikipedia contributors. (2023). Mobile banking. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_banking