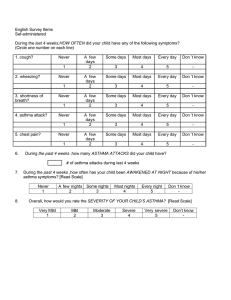
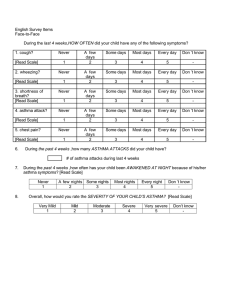
Patho Exam 2 Review 1) Herpes Simplex: If you have it, it stays with you for the rest of your life, it will be dormant, it is formed in trigeminal nerve and other ganglia. i)How many days does type 1 take to heal? Usually around 10 to 14 days ii) signs and symptoms of herpes simplex? Tingling, burning sensation and then pain and blisters. Once it is healed you will not have the blisters, but it can reappear due to mostly because of (A)Stress, (B) Hormonal Changes, (C) Cold 2) Herpes Zoster: is caused by reactivated chickenpox called Varicella While shingles we call it Herpes Zoster The first time you get Varicella it is called chickenpox when it is reactivated and reappears it is called herpes zosters (Shingles) 3) Who is at risk for Herpes Zoster (Shingles)? The Elderly. 4) What are the most common complications of Herpes Zoster Shingles? postherpetic neuralgia characterized by recurring pain at the site after rash; can persist for months to years and is most common in people > 50yrs. 5) We usually see Herpes Zoster (Shingles) on one side of the body 6) We name Superficial Fungal Infection by their location (i) if it on the scalp it is Tinea capitis) (ii) if it on the trunk it is Tinea Corporis and if it on the foot it is Tinea pedis Superficial infections mainly affects our nails and skin. 7) Candida Albicans in infants we call it Thrush 8) Intertrigo is when there is skin to skin friction, seen on children’s neck and obese patient 9) We see Mucocutaneous candidiasis in immunocompromised people 10) Impetigo is a Bacterial infection caused by staphylococci or streptococci. It is a highly contagious disease causes with Clinical Manifestations of vesicles, pustules, and yellowish crusts. 11) What causes Seborrheic Dermatitis? It is caused by high oil production What are the two types of Seborrheic Dermatitis? The two examples are cradle cap and dandruff 12) Psoriasis is a chronic inherited autoimmune disorder characterized by Silvery White Scales 13) What is the Pathogenesis of Acne Vulgaris? It is the obstruction of follicles due to cells and oils resulting in an inflamed lesion, which leads to sludging of sebaceous oils and deposition of loose epithelial cells, can be caused by Hormones, genetics, stress and some chemicals like cosmetics. 14) Atopic Dermatitis (Atopic means Allergy) What kind of Immune Globulin is mediated? IgE. Atopic dermatitis is genetically predisposed causing Purities (Itching) and eczema. 15) Atopic dermatitis what is the issue? It is the loss or defect of natural moisturizing factors (there is defect in the epidermal layer causing loss of normal moisturizing factors causing pruritis, inflammation, dermatitis, eczematous, rhinitis, allergic rhinitis; risk factor is history of asthma. 16) Contact Dermatitis, we have two types: Allergic and Irritant. 17) Rus dermatitis is exposure to three most important things; (a) poison ivy, (b)poison oak, (c) poison sumac, what is the characteristic of Rus dermatitis? Linear fashion with the rashes 18) What is the most important thing with, atopic dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and asthma? the most important thing is to know what caused it or the offending thing, you want to know the offending agent otherwise you will get asthma attack again and again. 19) Rock mounting spotted fever, what causes it? Infected tick bite that causes burrow under the skin, infected tick bites and burrows into the host and feeds releasing rickettsia into the blood stream; followed by a rash – within 4 to 8 days symptomatic, what is the causative agent? Infected tick bite. If not treated can be dangerous causing cranial nerve deficit. 20) What causes Scabies? Scabies is caused by eggs laid by Sarcoptic scabiei mite (called scabies) on the stratum corneum, eggs hatch into larvae, and in 3 to 4 days they grow to adulthood; usually contracted after close contact with infested Person causing severe scraping (itchiness). They burrow under skin like rocky mountain tick 21) Lyme disease is very dangerous if not treated, usually symptoms doesn’t start right away. We have 3 stages of Lyme disease Stage 1. Papules that itch and burn, after like month of no treatment neuromuscular functions will not show up. •Stage 2. Meningitis, cranial nerve palsies, and peripheral neuropathy •Stage 3. Oligoarticular arthritis What causes this disease? White tail deer transmit this disease 22) Lice and scabies are spread by person-to-person, lice is surface dwelling meaning it stays on hairs and clothing causing itchiness 23) We have two types of Sclerodermas: Systemic and Localized Localized means only involving the Skin, shrivel slowly and spontaneously especially around the scalp because of the hardening of the skin. Systemic meaning involving more than an organ Scleroderma is considered a benign disorder, it’s not malignant disorder, it’s not cancer. very likely an autoimmune in nature. They make the skin to become hard including esophagus and gastrointestinal tract Which become semirigid, lungs and heart fibrosis, bone resorbed, and overlying tissue calcifies 24) Scabies and Rocky Mountains burrow but lice and pediculosis don’t burrow. 25) Sunburn. The single most important factor for sunburn is excessive exposure to UV light on skin which increase the risk of cancer. Sunburn can cause redness, pain, tenderness, blisters, and edema 26) We have benign and malignant skin conditions. Examples of benign skin tumors arises from melanocyte or keratinocyte. 27) Kaposi sarcoma is seen in immunocompromised people, it could be an early symptom of HIV, it can be seen on people with comorbidities, those taking immunocompromised drugs cancer and cancer drugs, antarthritics drugs 28) Pressure ulcer, we say elderly people are at high risk for pressure ulcers because they lose subcutaneous tissue (Fat) causing the skin to be thin and fragile thereby causing it to easily sustain pressure ulcer 29) Who is at risk for skin cancers? Fair skin or light complexion. 30) How do viruses and bacteria cause infection? Bacteria attaches itself to the surface of the cell and send signals and cause a disease from the outside, Bacteria works from outside, they don’t enter inside the cell. Viruses, first, attach themselves to the surface of the cell and then they produce some enzymes, and these enzymes will let them inside the cell, once inside the cell they use whatever that is inside the cell (Host materials) to reproduce inside the cell 31) What do we mean by opportunistic diseases? These are diseases that take advantage of weak immune system like fungus which do not originally cause diseases but if someone’s immune is compromised they take advantage like in cancer patient, transplant patient, patient that are taking an immunosuppressant drugs and patient who have comorbidities 32) We have two major type of Asthma; (a) Atopic or allergic (extrinsic)allergic rhinitis, Mast cells and Eosinophils, More common in young children and adolescents (b) Non allergic, non-atopic Intrinsic basophils (cold, smoking, exercise, drugsAspirin, infection and occupational) poor prognosis affects Adults > 50yrs, exercises to avoids are running, jogging, tennis (Aerobic exercises) Aspirin and NSAID Induced Asthma is caused by inhibition of conversion of Arachtonic acid into prostaglandins which leads to severe very potent bronchoconstriction (Patient who have Asthma cannot take Aspirin, it is contraindicated) 33) In Exercise induced Asthma, there are types of sports and activities you don’t want them to do like Running, Jogging, Tennis especially in cold weather because it may induce Asthma attack. 34) In Asthma what do we see? 1. Narrowed Bronchos, 2.cells increase in size 3. The guplet cells (the epithelium are being replaced by guplet cell Metaplasia) they produce mucous. It is called Reactivity, constriction can be caused by varieties of stimuli like allergens, dust, mite, cat dander’s, dog dander’s. causing the smooth muscle to become narrowed and contracting which leads to bronchoconstriction 35) What are the common signs and symptoms of Asthma? Wheezing. Why do patient have Wheezing? Because of the narrowed airways causing a vibration (vibration and narrowed airways causes wheezing) wheezing are seen in Asthma but in Asthma Attack or Status Asthmaticus which is a life-threatening condition a severe form of Asthma, Patient may have minimal or absent sounds, Status Asthmaticus patient may have minimal or absent sound. 36) The causes of non-allergic asthma (cold, smoking, exercise, drugs, occupational, infection) IgE 37) Exercise induced Asthma we see IgE Basophils immunoglobulin , While in the other type of Asthma we see mast cell and Eosinophils 38) Most people who have Asthma have genetic predisposition and they already have small airways than other people. 39) Acute Asthma attack present with chest retraction, dyspnea, wheezing, nasal flaring (a compensatory mechanism) 40) When we do Chest x-ray on Asthma patient, we see Hyperinflated lungs 41) Occupational lung disease, the most important thing to remember is that, initially they have no symptoms at all, because no symptoms and inhalation of toxic gases and chemicals especially inorganic materials, for a long period of time, when they cause damage it is irreversible and pulmonary function test will show Hypoxemia and Hypercapnia. Early-no symptoms with normal x-ray result and then, late stage they will cause dyspnea and cough, hypoxemia and hypercapnia especially with activities and chest X-ray will show calcification of the lungs 42)