Guía de Enseñanza de Matemáticas Generales para Secundaria
advertisement

Commission on Higher Education
in collaboration with the Philippine Normal University
TEACHING GUIDE FOR SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL
General Mathematics
CORE SUBJECT
This Teaching Guide was collaboratively developed and reviewed by educators from public
and private schools, colleges, and universities. We encourage teachers and other education
stakeholders to email their feedback, comments, and recommendations to the Commission on
Higher Education, K to 12 Transition Program Management Unit - Senior High School
Support Team at k12@ched.gov.ph. We value your feedback and recommendations.
Published by the Commission on Higher Education, 2016
Chairperson: Patricia B. Licuanan, Ph.D.
Commission on Higher Education
K to 12 Transition Program Management Unit
Office Address: 4th Floor, Commission on Higher Education,
C.P. Garcia Ave., Diliman, Quezon City
Telefax: (02) 441-1143 / E-mail Address: k12@ched.gov.ph
DEVELOPMENT TEAM
Team Leader: Debbie Marie B. Verzosa, Ph.D.
Writers: Leo Andrei A. Crisologo, Lester C. Hao,
Eden Delight P. Miro, Ph.D., Shirlee R. Ocampo,
Emellie G. Palomo, Ph.D., Regina M. Tresvalles,
Technical Editors: Mark L. Loyola, Ph.D.,
Christian Chan O. Shio, Ph.D.
Copy Reader: Sheena I. Fe
Typesetters: Juan Carlo F. Mallari, Regina Paz S. Onglao
Illustrator: Ma. Daniella Louise F. Borrero
Cover Artists: Paolo Kurtis N. Tan, Renan U. Ortiz
CONSULTANTS
THIS PROJECT WAS DEVELOPED WITH THE PHILIPPINE NORMAL UNIVERSITY.
University President: Ester B. Ogena, Ph.D.
VP for Academics: Ma. Antoinette C. Montealegre, Ph.D.
VP for University Relations & Advancement: Rosemarievic V. Diaz, Ph.D.
Ma. Cynthia Rose B. Bautista, Ph.D., CHED
Bienvenido F. Nebres, S.J., Ph.D., Ateneo de Manila University
Carmela C. Oracion, Ph.D., Ateneo de Manila University
Minella C. Alarcon, Ph.D., CHED
Gareth Price, Sheffield Hallam University
Stuart Bevins, Ph.D., Sheffield Hallam University
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL SUPPORT TEAM
CHED K TO 12 TRANSITION PROGRAM MANAGEMENT UNIT
Program Director: Karol Mark R. Yee
Lead for Senior High School Support: Gerson M. Abesamis
Lead for Policy Advocacy and Communications: Averill M. Pizarro
Course Development Officers:
Danie Son D. Gonzalvo, John Carlo P. Fernando
Teacher Training Officers:
Ma. Theresa C. Carlos, Mylene E. Dones
Monitoring and Evaluation Officer: Robert Adrian N. Daulat
Administrative Officers: Ma. Leana Paula B. Bato,
Kevin Ross D. Nera, Allison A. Danao, Ayhen Loisse B. Dalena
This Teaching Guide by the
Commission on Higher Education
is licensed under a Creative
Commons AttributionNonCommercial-ShareAlike
4.0 International License. This
means you are free to:
Share
the material in any medium or
format
Adapt
build upon the material.
The licensor, CHED, cannot
revoke these freedoms as long as
you follow the license terms.
However, under the following
terms:
Attribution
appropriate credit, provide a link
to the license, and indicate if
changes were made. You may do
so in any reasonable manner, but
not in any way that suggests the
licensor endorses you or your use.
NonCommercial
not use the material for
commercial purposes.
ShareAlike
transform, or build upon the
material, you must distribute
your contributions under the
same license as the original.
Printed in the Philippines by EC-TEC
Commercial, No. 32 St. Louis
Compound 7, Baesa, Quezon City,
ectec_com@yahoo.com
Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . i
DepEd General Mathematics Curriculum Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Chapter 1 Functions
Lesson 1: Functions as Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
Lesson 2: Evaluating Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11
Lesson 3: Operations on Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Chapter 2 Rational Functions
Lesson 4: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Rational Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23
Lesson 5: Rational Functions, Equations, and Inequalities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
28
Lesson 6: Solving Rational Equations and Inequalities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
31
Lesson 7: Representations of Rational Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
42
Lesson 8: Graphing Rational Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Chapter 3 One-to-One and Inverse Functions
Lesson 9: One-to-One Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Lesson 10: Inverse of One-to-One Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
70
Lesson 11: Graphs of Inverse Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
76
Chapter 4 Exponential Functions
Lesson 12: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Exponential Functions . . . . . . . . . .
88
Lesson 13: Exponential Functions, Equations, and Inequalities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
94
Lesson 14: Solving Exponential Equations and Inequalities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
96
Lesson 15: Graphing Exponential Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Lesson 16: Graphing Transformations of Exponential Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
107
Chapter 5 Logarithmic Functions
Lesson 17: Introduction to Logarithms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
114
Lesson 18: Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and Inequalities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
125
Lesson 19: Basic Properties of Logarithms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
128
Lesson 20: Laws of Logarithms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
130
Lesson 21: Solving Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
136
Lesson 22: The Logarithmic Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
147
Chapter 6 Simple and Compound Interest
Lesson 23: Illustrating Simple and Compound Interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
156
Lesson 24: Simple Interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
158
Lesson 25: Compound Interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
166
Lesson 26: Compounding More than Once a Year . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Lesson 27: Finding Interest Rate and Time in Compound Interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
185
Chapter 7 Annuities
Lesson 28: Simple Annuity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
196
Lesson 29: General Annuity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
210
Lesson 30: Deferred Annuity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
224
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Stocks and Bonds
Lesson 31: Stocks and Bonds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
234
Lesson 32: Market Indices for Stocks and Bonds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
241
Lesson 33: Theory of Efficient Markets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
245
Chapter 9 Basic Concepts of Loans
Lesson 34: Business Loans and Consumer Loans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
249
Lesson 35: Solving Problems on Business and Consumer Loans (Amortization and
Mortgage) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Chapter 10 Logic
Lesson 36: Propositions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
Lesson 37: Logical Operators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
268
Lesson 38: Constructing Truth Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
Lesson 39: Logical Equivalence and Forms of Conditional Propositions . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
285
Lesson 40: Valid Arguments and Fallacies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
292
Lesson 41: Methods of Proof . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
306
Biographical Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
319
Introduction
As the Commission supports DepEd’s implementation of Senior High School (SHS), it upholds the vision
and mission of the K to 12 program, stated in Section 2 of Republic Act 10533, or the Enhanced Basic
Education Act of 2013, that “every graduate of basic education be an empowered individual, through a
program rooted on...the competence to engage in work and be productive, the ability to coexist in fruitful
harmony with local and global communities, the capability to engage in creative and critical thinking,
and the capacity and willingness to transform others and oneself.”
To accomplish this, the Commission partnered with the Philippine Normal University (PNU), the
National Center for Teacher Education, to develop Teaching Guides for Courses of SHS. Together with
PNU, this Teaching Guide was studied and reviewed by education and pedagogy experts, and was
enhanced with appropriate methodologies and strategies.
Furthermore, the Commission believes that teachers are the most important partners in attaining this
goal. Incorporated in this Teaching Guide is a framework that will guide them in creating lessons and
assessment tools, support them in facilitating activities and questions, and assist them towards deeper
content areas and competencies. Thus, the introduction of the SHS for SHS Framework.
The SHS for SHS Framework
The SHS for SHS Framework, which stands for “Saysay-Husay-Sarili for Senior High School,” is at the
core of this book. The lessons, which combine high-quality content with flexible elements to
accommodate diversity of teachers and environments, promote these three fundamental concepts:
SAYSAY: MEANING
HUSAY: MASTERY
SARILI: OWNERSHIP
Why is this important?
How will I deeply understand this?
What can I do with this?
Through this Teaching Guide,
teachers will be able to
facilitate an understanding of
the value of the lessons, for
each learner to fully engage in
the content on both the
cognitive and affective levels.
Given that developing mastery
goes beyond memorization,
teachers should also aim for deep
understanding of the subject
matter where they lead learners
to analyze and synthesize
knowledge.
When teachers empower
learners to take ownership of
their learning, they develop
independence and selfdirection, learning about both
the subject matter and
themselves.
i
The Parts of the Teaching Guide
This Teaching Guide is mapped and aligned to the DepEd SHS Curriculum, designed to be highly usable
for teachers. It contains classroom activities and pedagogical notes, and integrated with innovative
pedagogies. All of these elements are presented in the following parts:
1. INTRODUCTION
•
Highlight key concepts and identify the essential questions
•
Show the big picture
•
Connect and/or review prerequisite knowledge
•
Clearly communicate learning competencies and objectives
•
Motivate through applications and connections to real-life
2. MOTIVATION
•
Give local examples and applications
•
Engage in a game or movement activity
•
Provide a hands-on/laboratory activity
•
Connect to a real-life problem
3. INSTRUCTION/DELIVERY
•
Give a demonstration/lecture/simulation/hands-on activity
•
Show step-by-step solutions to sample problems
•
Give applications of the theory
•
Connect to a real-life problem if applicable
4. PRACTICE
•
Provide easy-medium-hard questions
•
Give time for hands-on unguided classroom work and discovery
•
Use formative assessment to give feedback
5. ENRICHMENT
•
Provide additional examples and applications
•
Introduce extensions or generalisations of concepts
•
Engage in reflection questions
•
Encourage analysis through higher order thinking prompts
•
Allow pair/small group discussions
•
Summarize and synthesize the learnings
6. EVALUATION
•
Supply a diverse question bank for written work and exercises
•
Provide alternative formats for student work: written homework, journal, portfolio, group/
individual projects, student-directed research project
ii
On DepEd Functional Skills and CHED’s College Readiness Standards
As Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) welcome the graduates of the Senior High School program, it is
of paramount importance to align Functional Skills set by DepEd with the College Readiness Standards
stated by CHED.
The DepEd articulated a set of 21st century skills that should be embedded in the SHS curriculum across
various subjects and tracks. These skills are desired outcomes that K to 12 graduates should possess in
order to proceed to either higher education, employment, entrepreneurship, or middle-level skills
development.
On the other hand, the Commission declared the College Readiness Standards that consist of the
combination of knowledge, skills, and reflective thinking necessary to participate and succeed - without
remediation - in entry-level undergraduate courses in college.
The alignment of both standards, shown below, is also presented in this Teaching Guide - prepares
Senior High School graduates to the revised college curriculum which will initially be implemented by
AY 2018-2019.
College Readiness Standards Foundational Skills
DepEd Functional Skills
Produce all forms of texts (written, oral, visual, digital) based on:
1. Solid grounding on Philippine experience and culture;
2. An understanding of the self, community, and nation;
3. Application of critical and creative thinking and doing processes;
4. Competency in formulating ideas/arguments logically, scientifically,
and creatively; and
5. Clear appreciation of one’s responsibility as a citizen of a multicultural
Philippines and a diverse world;
Visual and information literacies
Media literacy
Critical thinking and problem solving skills
Creativity
Initiative and self-direction
Systematically apply knowledge, understanding, theory, and skills
for the development of the self, local, and global communities using
prior learning, inquiry, and experimentation
Global awareness
Scientific and economic literacy
Curiosity
Critical thinking and problem solving skills
Risk taking
Flexibility and adaptability
Initiative and self-direction
Work comfortably with relevant technologies and develop
adaptations and innovations for significant use in local and global
communities;
Global awareness
Media literacy
Technological literacy
Creativity
Flexibility and adaptability
Productivity and accountability
Communicate with local and global communities with proficiency,
orally, in writing, and through new technologies of communication;
Global awareness
Multicultural literacy
Collaboration and interpersonal skills
Social and cross-cultural skills
Leadership and responsibility
Interact meaningfully in a social setting and contribute to the
fulfilment of individual and shared goals, respecting the
fundamental humanity of all persons and the diversity of groups
and communities
Media literacy
Multicultural literacy
Global awareness
Collaboration and interpersonal skills
Social and cross-cultural skills
Leadership and responsibility
Ethical, moral, and spiritual values
iii
The General Mathematics
Teaching Guide
Implementing a new curriculum is always subject to a new set of challenges.
References are not always available, and training may be too short to cover all the
required topics. Under these circumstances, providing teachers with quality resource
materials aligned with the curricular competencies may be the best strategy for
delivering the expected learning outcomes. Such is the rationale for creating a series of
teaching guides for several Grade 11 and 12 subjects. The intention is to provide
teachers a complete resource that addresses all expected learning competencies, as
stated in the Department of Education’s offi︎cial curriculum guide.
This resource is a teaching guide for General Mathematics. The structure is quite
unique, re︎flective of the wide scope of General Mathematics: functions, business
mathematics, and logic. Each lesson begins with an introductory or motivational
activity. The main part of the lesson presents important ideas and provides several
solved examples. Explanations to basic properties, the rationale for mathematical
procedures, and the derivation of important formulas are also provided. The goal is to
enable teachers to move learners away from regurgitating information and towards an
authentic understanding of, and appreciation for, the subject matter.
The chapters on functions are an extension of the functions learned in Junior High
School, where the focus was primarily on linear, quadratic, and polynomial functions.
In Grade 11, learners will be exposed to other types of functions such as piecewise,
rational, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Related topics such as solving
equations and inequalities, as well as identifying the domain, range, intercepts, and
asymptotes are also included.
iv
The chapters on business mathematics in Grade 11 may be learners' ︎first opportunity
to be exposed to topics related to ︎financial literacy. Here, they learn about simple and
compound interest, annuities, loans, stocks, and bonds. These lessons can hopefully
prepare learners to analyze business-related problems and make sound ︎financial
decisions.
The ︎final chapter on logic exposes learners to symbolic forms of propositions (or
statements) and arguments. Through the use of symbolic logic, learners should be able
to recognize equivalent propositions, identify fallacies, and judge the validity of
arguments. The culminating lesson is an application of the rules of symbolic logic, as
learners are taught to write their own justifications to mathematical and real-life
statements.
This Teaching Guide is intended to be a practical resource for teachers. It includes
activities, explanations, and assessment tools. While the beginning teacher may use
this Teaching Guide as a “script,” more experienced teachers can use this resource as a
starting point for writing their own lesson plans. In any case, it is hoped that this
resource, together with the Teaching Guide for other subjects, can support teachers in
achieving the vision of the K to 12 Program.
v
First Quarter
Hour 1
Hour 2
Hour 3
Hour 4
Week a
Lesson 1
Lesson 1, 2
Lesson 3
Lesson 3
Week b
Lesson 4
Lesson 5, 6
Lesson 6
Lesson 7
Week c
Lesson 7
Lesson 8
Lesson 8
Review/Exam
Week d
Lesson 9
Lesson 10
Lesson 10
Lesson 11
Week e
Lesson 11
Review/Exam
Lesson 12
Lesson 12, 13
Week f
Lesson 14
Lesson 14
Lesson 15
Lesson 15
Week g
Lesson 16
Lesson 16
Review/Exam
Review/Exam
Week h
Lesson 17
Lesson 17
Lesson 18, 19
Lesson 19, 20
Week i
Lesson 20
Lesson 21
Lesson 21
Lesson 21
Week j
Lesson 22
Lesson 22
Review/Exam
Review/Exam
Second Quarter
Hour 1
Hour 2
Hour 3
Hour 4
Week a
Lesson 23
Lesson 24
Lesson 25
Lesson 25, 26
Week b
Lesson 26
Lesson 27
Lesson 27 / Review
Review/Exam
Week c
Lesson 28
Lesson 28
Lesson 29
Lesson 29
Week d
Lesson 29
Lesson 30
Lesson 30
Review/Exam
Week e
Lesson 31
Lesson 31
Lesson 32
Lesson 33
Week f
Lesson 34
Lesson 35
Lesson 35
Review/Exam
Week g
Lesson 36
Lesson 36
Lesson 37
Lesson 37
Week h
Lesson 38
Lesson 39
Lesson 39
Lesson 39
Week i
Lesson 40
Lesson 40
Lesson 40
Lesson 41
Week j
Lesson 41
Lesson 41
Review/Exam
Review/Exam
vi
Grade: 11
Core Subject Title: General Mathematics
CONTENT STANDARDS
The learner demonstrates
understanding of...
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL – CORE SUBJECT
1. accurately construct
mathematical models to
represent real-life
situations using
functions.
The learner is able to...
PERFORMANCE
STANDARDS
Semester: First Semester
No. of Hours/Semester: 80 hours/semester
Prerequisite (if needed):
LEARNING COMPETENCIES
CODE
2. evaluates a function.
M11GM-Ia-3
M11GM-Ia-2
M11GM-Ia-1
3. performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, division,
and composition of functions
Page 1 of 5
M11GM-Ic-3
M11GM-Ic-2
M11GM-Ic-1
M11GM-Ib-5
M11GM-Ib-4
M11GM-Ib-3
M11GM-Ib-2
M11GM-Ib-1
M11GM-Ia-4
5. represents real-life situations using rational functions.
6. distinguishes rational function, rational equation, and
rational inequality.
7. solves rational equations and inequalities.
8. represents a rational function through its: (a) table of
values, (b) graph, and (c) equation.
9. finds the domain and range of a rational function.
10.
determines the:
(a) intercepts
(b) zeroes; and
(c) asymptotes of rational functions
11.
graphs rational functions.
12.
solves problems involving rational functions,
equations, and inequalities.
4. solves problems involving functions.
1. represents real-life situations using functions, including
piece-wise functions.
The learner...
Core Subject Description: At the end of the course, the students must know how to solve problems involving rational, exponential and logarithmic functions; to solve
business-related problems; and to apply logic to real-life situations.
CONTENT
Functions and
Their Graphs
1. key concepts of
functions.
2. key concepts of rational
functions.
2. accurately formulate and
solve real-life problems
involving rational
functions.
K to 12 Senior High School Core Curriculum – General Mathematics December 2013
CONTENT
CONTENT STANDARDS
3. key concepts of inverse
functions, exponential
functions, and
logarithmic functions.
1. represents real-life situations using
one-to one functions.
2. determines the inverse of a one-to-one function.
3. represents an inverse function through its: (a) table of
values, and (b) graph.
4. finds the domain and range of an inverse function.
5. graphs inverse functions.
6. solves problems involving inverse functions.
7. represents real-life situations using exponential
functions.
8. distinguishes between exponential function, exponential
equation, and exponential inequality.
9. solves exponential equations and inequalities.
10. represents an exponential function through its: (a) table
of values, (b) graph, and (c) equation.
11. finds the domain and range of an exponential function.
12. determines the intercepts, zeroes, and asymptotes of
an exponential function.
13. graphs exponential functions.
14. solves problems involving exponential functions,
equations, and inequalities.
15. represents real-life situations using logarithmic
functions.
16. distinguishes logarithmic function, logarithmic equation,
and logarithmic inequality.
17. illustrates the laws of logarithms.
18. solves logarithmic equations and inequalities.
19. represents a logarithmic function through its: (a) table
of values, (b) graph, and (c) equation.
20. finds the domain and range of a logarithmic function.
21. determines the intercepts, zeroes, and asymptotes of
logarithmic functions.
22. graphs logarithmic functions.
23. solves problems involving logarithmic functions,
equations, and inequalities.
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL – CORE SUBJECT
PERFORMANCE
LEARNING COMPETENCIES
STANDARDS
3. apply the concepts of
inverse functions,
exponential functions,
and logarithmic functions
to formulate and solve
real-life problems with
precision and accuracy.
K to 12 Senior High School Core Curriculum – General Mathematics December 2013
CODE
M11GM-Id-1
M11GM-Id-2
M11GM-Id-3
M11GM-Id-4
M11GM-Ie-1
M11GM-Ie-2
M11GM-Ie-3
M11GM-Ie-4
M11GM-Ie-f-1
M11GM-If-2
M11GM-If-3
M11GM-If-4
M11GM-Ig-1
M11GM-Ig-2
M11GM-Ih-1
M11GM-Ih-2
M11GM-Ih-3
M11GM-Ih-i-1
M11GM-Ii-2
M11GM-Ii-3
M11GM-Ii-4
M11GM-Ij-1
M11GM-Ij-2
Page 2 of 5
CONTENT
Basic Business
Mathematics
Logic
CONTENT STANDARDS
The learner demonstrates
understanding of...
1. key concepts of simple
and compound interests,
and simple and general
annuities.
2. basic concepts of stocks
and bonds.
3. basic concepts of
business and
consumer loans.
The learner demonstrates
understanding of...
1.
key concepts of
propositional logic;
syllogisms and
fallacies.
41. illustrates a proposition.
42. symbolizes propositions.
43. distinguishes between simple and compound
propositions.
44. performs the different types of operations on
propositions.
45. determines the truth values of propositions.
46. illustrates the different forms of conditional
propositions.
47. illustrates different types of tautologies and fallacies.
40. solves problems involving business and consumer loans
(amortization, mortgage).
39. distinguishes between business and consumer loans.
24. illustrates simple and compound interests.
25. distinguishes between simple and compound interests.
26. computes interest, maturity value, future value, and
present value in simple interest and compound interest
environment.
27. solves problems involving simple and compound
interests.
28. illustrates simple and general annuities.
29. distinguishes between simple and general annuities.
30. finds the future value and present value of both simple
annuities and general annuities.
31. calculates the fair market value of a cash flow stream
that includes an annuity.
32. calculates the present value and period of deferral of a
deferred annuity.
33. illustrate stocks and bonds.
34. distinguishes between stocks and bonds.
35. describes the different markets for stocks and bonds.
36. analyzes the different market indices for stocks and
bonds.
37. interprets the theory of efficient markets.
38. illustrates business and consumer loans.
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL – CORE SUBJECT
PERFORMANCE
LEARNING COMPETENCIES
STANDARDS
The learner is able to...
1. investigate, analyze and
solve problems involving
simple and compound
interests and simple and
general annuities using
appropriate business and
financial instruments.
2. use appropriate financial
instruments involving
stocks and bonds in
formulating conclusions
and making decisions.
3. decide wisely on the
appropriateness of
business or consumer
loan and its proper
utilization.
The learner is able to...
1. judiciously apply logic
in real-life arguments.
K to 12 Senior High School Core Curriculum – General Mathematics December 2013
CODE
M11GM-IIa-1
M11GM-IIa-2
M11GM-IIa-b-1
M11GM-IIb-2
M11GM-IIc-1
M11GM-IIc-2
M11GM-IIc-d-1
M11GM-IId-2
M11GM-IId-3
M11GM-IIe-1
M11GM-IIe-2
M11GM-IIe-3
M11GM-IIe-4
M11GM-IIe-5
M11GM-IIf-1
M11GM-IIf-2
M11GM-IIf-3
M11GM-IIg-1
M11GM-IIg-2
M11GM-IIg-3
M11GM-IIg-4
M11GM-IIh-1
M11GM-IIh-2
Page 3 of 5
M11GM-IIi-1
CONTENT
CONTENT STANDARDS
2. key methods of proof
and disproof.
48. determines the validity of categorical syllogisms.
49. establishes the validity and falsity of real-life arguments
using logical propositions, syllogisms, and fallacies.
50. illustrates the different methods of proof (direct and
indirect) and disproof (indirect and by
counterexample).
51. justifies mathematical and real-life statements using
the different methods of proof and disproof.
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL – CORE SUBJECT
PERFORMANCE
LEARNING COMPETENCIES
STANDARDS
2. appropriately apply a
method of proof and
disproof in real-life
situations.
K to 12 Senior High School Core Curriculum – General Mathematics December 2013
CODE
M11GM-IIi-2
M11GM-IIi-3
M11GM-IIj-1
M11GM-IIj-2
Page 4 of 5
(x, y)
x
(x, y)
y
f = {(1, 2), (2, 2), (3, 5), (4, 5)}
g = {(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 7)}
h = {(1, 3), (2, 6), (3, 9), . . . , (n, 3n), . . .}
f
g
y
x
h
x
(1, 3)
(1, 4)
y
f
g
h
f
x2X
g
h
y
y = 17
x=7
X
y = 11
19
x = a
(a, b)
y
(a, c)
x=a
y 2Y
13
x=2
(a) (b) (c)
(d)
x
y
x
x
y
y = 2x + 1
y = x2
2x + 2
x2 + y 2 = 1
p
y = x+1
2x + 1
y=
x 1
(e)
y = bxc + 1
bxc
x
y
x=0
y
+1
1
x
R
[ 1, +1)
R
( 1, 1) [ (1, +1)
R
[ 1, 1]
y
f (x)
y
x
f
f (x) = 2x + 1
q(x) = x2 2x + 2
p
g(x) = x + 1
2x + 1
r(x) =
x 1
F (x) = bxc + 1
bxc
C
x
40
40
C(x) = 40x
A
x
A = xy
x + 2y = 100
A(x) = x(50
0.5x) = 50x
x
y = (100
0.5x2
300
1
m
t(m)
t(m) =
(
300
300 + m
8.00
1.50
d
0 < m 100
m > 100
x)/2 = 50
0.5x
F (d)
F (d) =
bdc
•
(
8
8 + 1.5bdc
0<d4
d>4
d
b4.1c = b4.9c = 4
d
25
•
0
•
0
•
100
•
100
•
100
T (x)
T (x)
15
1, 000
400
f (x) =
8
<1000
:1000 + 400dx
0x3
3e
x>3
700
f (x) = 700d x4 e x 2 N
150
130
110
100
f (x) =
8
>
>
150x
>
>
>
>
<130x
>
>
110x
>
>
>
>
:100x
0 x 20
21 x 50
51 x 100
x > 100
x2N
x
f
a
f
f (a)
x = 1.5
f (x) = 2x + 1
q(x) = x2 2x + 2
p
g(x) = x + 1
2x + 1
r(x) =
x 1
F (x) = bxc + 1
bxc
1.5
x
f (1.5) = 2(1.5) + 1 = 4
q(1.5) = (1.5)2 2(1.5) + 2 = 2.25
p
p
g(1.5) = 1.5 + 1 = 2.5
r(1.5) =
3 + 2 = 1.25
2x + 1
2(1.5) + 1
3+1
=
=
=8
x 1
(1.5) 1
0.5
F (1.5) = bxc + 1 = b1.5c + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
g( 4)
r(1)
g
r
4
g(x)
r(x)
f
f (3x
1)
q
q(2x + 3)
a
f (3x
1)
f (3x
x
1) = 2(3x
q(3x + 3)
x
q(2x + 3) = (2x + 3)2
f (x) = 2x + 1
1) + 1 = 6x
q(x) = x2
2 + 1 = 6x
2x + 2
2(2x + 3) + 2 = (4x2 + 12x + 9)
f (x) = x
(3x
1)
1
(2x + 3)
4x
6 + 2 = 4x2 + 8x + 5
2
f (0)
2
f (⇡)
⇡
2
f (3)
f (x + 1)
x
1
f ( 1)
f (3x)
3x
2
f (x) =
4
x
f (1)
4
f (2)
2
f ( 1)
p
f ( 2)
2 2
f (1/x)
4x
f (2x)
2/x
p
f (x) =
p
x
4
3
f (3)
0
f (4)
1
f (12)
f (x 3)
✓
◆
1
f
1 x
f (x2 + 4x + 7)
3
p
p
x 6
3x 2
1 x
x2 + 4x + 4
|x + 2|
200
25
C(x) = 25x + 200
x
C(x)
2700
t
s(t) =
g = 10m/s2
5t2 + 100
3950
1
3
2
5
1 2
5
6
5+6
+ =
+
=
3 5
15 15
15
11
=
15
1
x
2
3
x
5
(x
1
x
3
+
2
x
5
=
x
x2
10
21
3)(x
5)
(x2
8x + 15)
5
2(x 3)
x 5 + 2x 6
+ 2
= 2
8x + 15 x
8x + 15
x
8x + 15
3x 11
= 2
x
8x + 15
15
8
10 15
2·5
3·5
6 2 · 5· 6 3 · 5
25
·
=
·
=
=
21 8
3·7 2·2·2
6 3 · 7· 6 2 · 2 · 2
28
x2
x2
x2
x2
f
4x 5 x2
·
3x + 2 x2
4x 5
3x + 2
x2
x2
5x + 6
3x 10
5x + 6
(x + 1)(x 5) (x 2)(x 3)
=
·
3x 10
(x 2)(x 1) (x 5)(x + 2)
⇠(x⇠⇠
⇠
(x + 1)⇠
(x⇠⇠5)
⇠ 2)(x 3)
=
⇠
⇠ + 2)
(x⇠⇠2)(x
1)⇠
(x⇠⇠5)(x
⇠
(x + 1)(x 3)
x2 2x 3
=
= 2
(x 1)(x + 2)
x +x 2
g
f +g
(f + g)(x) = f (x) + g(x)
f
g
(f
g)(x) = f (x)
g(x)
f ·g
x
f /g
g(x) = 0
(f · g)(x) = f (x) · g(x)
(f /g)(x) = f (x)/g(x)
• g(x) = x2 + 2x
x+7
• h(x) =
2 x
x 2
• t(x) =
x+3
• f (x) = x + 3
• p(x) = 2x
7
• v(x) = x2 + 5x + 4
(v + g)(x)
(f + h)(x)
(f · p)(x)
(p
7) = 2x2
(v/g)(x)
f )(x)
(v + g)(x) = x2 + 5x + 4 + x2 + 2x
(f · p)(x) = (x + 3) (2x
8
x
8 = 2x2 + 7x
4
21
x+7
2 x x+7
(x + 3)(2 x) + (x + 7)
= (x + 3) ·
+
=
=
2 x
2 x 2 x
2 x
6 x x2 + x + 7
13 x2
13 x2
1
x2 13
=
=
=
·
=
2 x
2 x
2 x
1
x 2
f )(x) = (2x 7) (x + 3) = 2x 7 x 3 = x 10
(f + h)(x) = (x + 3) +
(p
(v/g)(x) = (x2 + 5x + 4) ÷ (x2 + 2x
• f (x) = 2x + 1
8) =
x2 + 5x + 4
x2 + 2x 8
• q(x) = x2
2x + 2
• r(x) =
f1 (x) = x2 + 3
q(x)
x2
+3
q(x) + f (x) = (x2
2x + 2) + (2x + 1)
= x2 + 3
= f1 (x)
f1 (x) = q(x) + f (x)
f2 (x) = x2
4x + 1
f (x)
2x + 1
x 1
q(x)
f (x) = (x2
q(x)
=x
2
2x + 2)
f (x)
(2x + 1)
4x + 1
= f2 (x)
f2 (x) = q(x)
f (x)
f3 (x) =
2x2 + x
x 1
x
2x2 + x
x 1
1
r(x) =
f (x)
r(x)
2x + 1
f (x) + r(x) = 2x + 1 +
x 1
(2x + 1)(x 1) 2x + 1
=
+
x 1
x 1
(2x + 1)(x 1) + (2x + 1)
=
x 1
(2x2 x 1) + (2x + 1)
=
x 1
2x2 + x
=
x 1
= f3 (x)
(f + g)(x) = f (x) + g(x)
f1 (x) = q(x) + f (x) = (q + f )(x)
f2 (x) = q(x)
f (x) = (q
f )(x)
f3 (x) = f (x) + r(x) = (f + r)(x)
g1 (x) = 2x3
3x2 + 2x + 2
2x + 1
x 1
x2
4x + 1
2x3
3x2 + 2x + 2
f (x)
f (x) · q(x) = (2x + 1)(x2
= (2x)(x2
= (2x3
= 2x
3
2x + 2)
2x + 2) + (x2
4x2 + 4x) + (x2
2x + 2)
2x + 2)
2
3x + 2x + 2
= g1 (x)
g1 (x) = f (x) · q(x)
g2 (x) = x
r(x) =
f (x)
r(x)
2x + 1
x 1
x
1
1
2x + 1
f (x)
2x + 1
= (2x + 1) ÷
r(x)
x 1
x 1
= (2x + 1) ·
2x + 1
2x + 1
=
· (x 1)
2x + 1
=x 1
= g2 (x)
g2 (x) =
f (x)
r(x)
g3 (x) =
g3 (x) =
2x + 1
1
x
1
r(x)
r(x) =
f (x) = 2x + 1
r(x)
2x + 1
=
÷ (2x + 1)
f (x)
x 1
2x + 1
1
=
·
x 1 2x + 1
1
=
x 1
= g3 (x)
g3 (x) =
r(x)
f (x)
2x + 1
x 1
1
x
1
q(x)
q(x) =
f
x2
(2x + 1)2
2x + 2
f (x) = 2x + 1
2(2x + 1) + 2
g
(f
(f
g)(x) = f (g(x)).
p
• f (x) = 2x + 1
• g(x) =
2x + 2
2x + 1
• r(x) =
x 1
• F (x) = bxc + 1
• q(x) =
x2
x+1
(g f )(x)
(g f )(x) = g(f (x))
p
= f (x) + 1
p
= (2x + 1) + 1
p
= 2x + 2
(q f )(x)
(f
q)(x)
g)
(q f )(x) = q(f (x))
= [f (x)]2
= (2x + 1)
2 [f (x)] + 2
2
2(2x + 1) + 2
= (4x2 + 4x + 1)
(4x + 2) + 2
= 4x2 + 1
(f
q)(x) = f (q(x))
= 2(x2
= 2x2
(q f )(x)
(f
2x + 2) + 1
4x + 5
q)(x)
(f
r)(x)
(f
r)(x) = f (r(x))
= 2r(x) + 1
2x + 1
=2
+1
x 1
4x + 2
=
+1
x 1
(4x + 2) + (x 1)
=
x 1
5x + 1
=
x 1
(F
(F
r)(5)
r)(5) = F (r(5))
= br(5)c + 1
⌫
2(5) + 1
=
+1
5 1
⌫
11
=
+1=2+1=3
4
f
g
f +g f
g
f · g f /g g/f
f (x) = x + 2 g(x) = x2
x2 + x
f (x) =
f (x) =
f (x) =
f (x) =
f
p
4
x2 + x + 6 x3 + 2x2
2
x 1 g(x) = x2 + 4
p
p
x 1 + x2 + 4 x
x 2
1
g(x) =
x+2
x
x 2 1 x 2
+
x+2 x x+2
1
g g f f
g(x) =
p
x
p
1
1
+ x 2
x2
x
f (x) = x2 + 3x
f g g
p
4
p
x
8
1
x
1(x2
2
x
+ 4)
2
p
x
x2
1
x
+4
2
1
x 2
x(x 2)
x+2
x x(x + 2)
x+2
x(x 2)
1
x 2
g(x) =
x+2
x
1
x 2
1
+
x+2
x
x+2
1
x2
x2
4x
x
x
2
x
x 2
x
x(x + 2) (x + 2)(x
(x + 2)(x
2)
x
2)
p
p
x
1
p x2 x
x2 x2 x
g(x) = x
2
x2
x
2 x2 + 3x
2 x4 + 6x3 + 12x2 + 9x x
(f
(g f ) = x
f (x) = 3x 2 g(x) = 13 (x + 2)
x
2x
f (x) =
g(x) =
2 x
x 1
p
3
f (x) = (x 1) + 2 g(x) = 3 x
2+1
g) = x
4
p(x) = an xn + an
a0 , a1 , . . . , an 2 R an 6= 0
1x
n 1
+ an
2x
n 2
+ · · · + a1 x + a0
n
a 0 , a1 , a2 , . . . , a n
an xn
an
a0
100, 000
y
x
y=
100, 000
x
x
y
750
g(x)
g(x) =
x
y
100, 000
+ 750
x
f (x) =
f (x)
q(x)
q(x) 6= 0
x
p(x)
p(x)
q(x)
q(x) 6⌘ 0
v
q(x)
v(t)
t
v
t
t
v
v(t) =
10
t
v
c(t) =
t
t = 1, 2, 5, 10
t
c(t)
5t
t2 + 1
t
c(t)
•
•
•
•
• a
• b
• c
• x
• y
x
y
y =
x
a
x
b
+c
P (x)
P (x) =
b(t) =
t
b(t)
t = 1, 2, 5, 10, 15, 20
50t
t+1
0 t 20
2x2 + 800
x
x2 + 3x + 2
x+4
1
3x2
x2 + 4x
2
3
p
x+1
x3 1
1
x+2
x 2
1
(x + 2)(x
2)
p(x)
q(x)
q(x)
q(x)
f (x) =
p(x)
2
x
3
1
=
2x
5
5
x
3
2
x
x2 + 2x + 3
x+1
x2 + 2x + 3
y=
x+1
f (x) =
x
x
y
p
15
x 1
y = 5x3 2x + 1
8
x
8=
x
2x 1
p
x 2=4
x 1
= x3
x+1
p
7x3 4 x + 1
y=
x2 + 3
5
6x
0
x+3
5x4
6x7 + 1
x3
5
x
x+1
= 10
2x
x+1
10
2x
x
2
x
3
1
=
2x
5
10x
10x
✓ ◆
2
10x
x
10x
✓
3
2x
20
◆
✓ ◆
1
= 10x
5
15 = 2x
5 = 2x
5
x=
2
x
x
x+2
1
x
2
x
x+2
=
8
x2
4
1
x
2
=
(x
8
2)(x + 2)
(x 2)(x+2)
(x
x
2)(x + 2) ·
x+2
2)(x + 2) ·
(x
(x
x2
1
x
2
2)x
(x + 2) = 8
x2
3x
3x
10 = 0
(x + 2)(x
5) = 0
x=
2)(x + 2)]
(x
8
2)(x + 2)
10 = 0
x+2=0
x=2
= [(x
✓
x
2
5=0
x=5
x=5
◆
x
x
12 + x
25 + x
12 + x
= 0.6
25 + x
25 + x
12 + x
= 0.6
25 + x
12 + x = 0.6(25 + x)
12 + x = 0.6(25) + 0.6x
x
0.6x = 15
12
0.4x = 3
x = 7.5
x
60%
v=
v=
v
d
t
t=
d
t
d
v
5
v
v + 10
5
v+10
4
3
5
5
4
+
=
v v + 10
3
3v(v + 10)
5
5
4
+
=
v v + 10
3
3v(v + 10) ·
5
5
4
+ 3v(v + 10) ·
= 3v(v + 10) ·
v
v + 10
3
15(v + 10) + 15v = 4v(v + 10)
30v + 150 = 4v 2 + 40v
4v 2 + 10v
150 = 0
2
2v + 5v
75 = 0
(2v + 15)(v
15
v=
2
5) = 0
v=5
v
(a, b)
{x|a < x < b}
a
b
[a, b]
{x|a x b}
a
b
[a, b)
{x|a x < b}
a
b
(a, b]
{x|a < x b}
a
b
(a, 1)
{x|a < x}
a
[a, 1)
{x|a x}
a
( 1, b)
{x|x < b}
b
( 1, b]
{x|x b}
b
( 1, 1)
R
x
•
•
2x
x+1
1
2x
1
x+1
2x (x + 1)
x+1
x 1
x+1
x=1
0
0
0
x= 1
x=1
x=
1
1
1
x 1
x+1
x
x<
1
x=
2
x=0
1
+
x
+
1
1
( 1, 1) [ [1, 1)
3
x
2
<
1
x
1}
1
x
3
1
x 2 x
3x (x 2)
x(x 2)
2x + 2
x(x 2)
2(x + 1)
x(x 2)
x =
1
x=2
+
+
1
{x 2 R|x <
x>1
+
x+1
x 1
x+1
x<
1<x<1
1
1
<0
<0
<0
<0
0
x<
x=
1
1<x<0
2
x=
2(x + 1)
0<x<2
x>2
x=1
x=3
+
+
+
+
1
2
+
x
x 2
2(x + 1)
x(x 2)
+
+
{x 2 R|x <
+
1
0 < x < 2}
x
h
x
h
8 = x2 h
h
x
h=
8
x2
h>x
8
>x
x2
h
x
8
>x
x2
(2
8
x>0
x2
8 x3
>0
x2
x)(x2 + 2x + 4)
>0
x2
x = 16
x = 28
x=0
4
x<0
x=
2
x2
x
+ 2x + 4
1
0<x<2
x>2
x=1
x=3
+
+
+
+
+
x2
+
+
+
(2 x)(x2 +2x+4)
x2
+
+
0<x<2
x<0
x
x
x=4
1120
x
1600
x+4
1600
x+4
1120
x
10
1600
1120
x+4
x
160
112
x+4
x
160
112
1
x+4
x
160x 112(x + 4) (x2 + 4x)
x(x + 4)
160x 112x 448 x2 4x
x(x + 4)
10
1
0
0
0
x2
44x + 448
0
x(x + 4)
(x 16)(x 28)
0
x(x + 4)
x
16
x
28
x = 16
x = 28
0 < x < 16
16 < x < 28
x > 28
x = 10
x = 20
x = 30
+
+
x<
4
4<x<0
x=
5
x=
+
x
x+4
(x 16)(x 28)
x(x + 4)
1
x=0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
x=4
4<x<0
x = 16
16 < x < 28
x = 28
3
2
=
x+1
x 3
2x
5
+
=2
x + 1 2x
x2
x
10
=
1
x2
x
4x
14
=
2
x
(x + 3)(x
(x + 2)(x
5
14 5x
x 1
9x
2
7
0
( 1, 3] [ [2, 1)
2)
1)
(x + 4)(x 3)
(x 2)(x2 + 2)
x+1
2
x+3
x
x2
x
0
[ 4, 2) [ [3, 1)
( 1, 5] [ ( 3, 1)
2
3x
4, 1
10
<0
( 1, 2) [ (2, 5)
3+x
6+x
t
f (x) =
f (x)
x
q(x)
q(x) 6= 0
p(x)
p(x)
q(x)
q(x) 6⌘ 0
s=
s=
100
t
d
t
q(x)
x
s(x)
s(x) =
100
x
s=
d
t
x
x
s(x)
x
s(x)
s(x) =
100
x
s(x) =
100
x
x
f (x) =
x
x
x
f (x)
10
8
6
4
x 1
x+1
10
10
2
1
1
E
F
f (x) =
x 1
x+1
E
x 1
x+1
x = 1
f (x) =
E
x=
F
1
E
x
1
F
F
f (x) =
x2
3x
x
10
x
x=0
6 x 10 x 6= 0
x
5
4
3
f (x)
6
4.5
2.67
x
f (x)
3
4
3.33
1.5
5
f
2
6
1
12
7
8
6
9
10
x
x=
2
1
x=5
x
x
x=0
x
1
x
p
p(x) =
12 + x
25 + x
p(x)
x
p(x)
25 + x
60(t + 1)
P (t) =
t+6
P
t
⌫
b·c
t=5
⌫
60(5 + 1)
P (5) =
= b32.726c = 32
5+6
P (x)
t
P (t)
t
I
V
R
I=
V
R
R
I
f (x) =
x
x
6
5
4
f (x)
3
2
1
6
2.5
1.33
f
f (x) =
0.75
x 3
x+4
0.4
6x2 x
0.167
x=
4
x2 + x 6
x2 + x 20
x = 4, 5
6x2
x
x
f (x)
6
5
4
0.75
3
2
1
0.22
0.3
0.3
0.22
0
x=
3, 2
x
f (x)
x
x
y
x=0
x
x
y
f (x) =
x 2
x+2
{x 2 R | x 6=
f (x)
2}
x=
f (x)
2
x=
x
x
f (x)
y
1
x
x
2
x
2
x=2
x=2
f (x)
x
y
f (0)
f (0) =
2
2
=
1
f (x)
x
x
x=
x<
2
2
x
x
3
2.5
2
x
x
2
2
x>
2
2
2.1
2.01
2.001
2.0001
f (x)
x
2
f (x)
x
f (x) ! +1
2
x!
2
f (x)
2+
x
x
1
1.5
1.9
1.99
1.999
1.9999
f (x)
3
7
39
399
3999
39999
x
f (x)
2+
2+
x
f (x) !
2
x
x= 2
1
x!
2+
f (x)
2
x=a
x
a
x=a
f
a
f
x
f (x)
f (x)
x ! +1
x
x ! +1
x
f (x)
f (x)
f (x)
x
5
f (x)
x! 1
10
100
x ! +1
x!
x
1000
10000
f (x)
f (x)
x
1
x!
1
1+
f (x)
y=1
y = b
b
x ! +1
x
y=b
b
x!
f
1
f (x)
1
x
x ! +1
x!
2
1
x
x=
x=2
x
x<
2
x=
3
2<x<2
x=0
+
+
+
+
+
x
x
x
x
x=2
y
f (x) < 1
(2, 0)
f (x)
x!
x=3
2
x+2
x 2
x+2
2+
x>2
x ! +1
x!
f (x) > 1
x!
2
1
f (x)
f (x)
2
y=
y=1
x 2
x+2
f (x)
f (x)
( 1, 1) [ (1, +1)
f (x) =
4x2 + 4x + 1
x2 + 3x + 2
x x!
x
x = 1000
4, 000, 000
4x2
4x2 + 4x + 1
x
4x2
f (x)
x2
x
f (x) =
x ! +1
4, 004, 001
x2 + 3x + 2
x
1
x2
= 4
f (x)
y=4
2x2 5
3x2 + x 7
2x2 5
3x2 + x 7
2x2
2
=
2
3x
3
x
y=
f (x) =
3x + 4
+ 3x + 1
2x2
3x + 4
+ 3x + 1
3
x
2x
2x2
3x
3
=
2
2x
2x
0
x
y=0
f (x) =
4x3 1
3x2 + 2x 5
x
x
y
2
3
4x
3
4x3 1
3x2 + 2x 5
4x3
4x
=
2
3x
3
x
n
m
•
n<m
y=0
•
n=m
y =
•
n>m
a
b
a
b
x
y
y
y
x=0
x
x
x
f (x) =
3x2 8x
2x2 + 7x
3
4
x
( 1, 4) [ ( 4, 12 ) [ ( 12 , +1)
f (x)
f (x)
f (x) =
• y
• x
f (0) =
3x2 8x
2x2 + 7x
0 0 3
3
=
0+0 4
4
3x + 1 = 0 ) x =
3
(3x + 1)(x 3)
=
4
(2x 1)(x + 4)
1
3
x
3=0)x=3
•
2x
1=0)x=
1
2
x+4=0)x=
4
•
y=
3
2
f (x)
x
4,
x< 4
x = 10
3x + 1
x 3
2x 1
x+4
(3x + 1)(x 3)
(2x 1)(x + 4)
4<x<
x= 2
+
+
x
1 1
3, 2
1
3
3
1
3
<x<
x=0
+
+
1
2
1
2
<x<3
x=1
+
+
+
+
x
x
x>3
x = 10
+
+
+
+
+
x
x
y
x
R
x
x
y
f (x) =
2
x+1
f (x) =
(5x
(3x
f (x) =
2
x2 + 2x + 1
f (x) =
x2
x2
x+6
6x + 8
f (x) =
3x
x+3
f (x) =
x2
4x 5
x 4
f (x) =
2x + 3
4x 7
f (x) =
x
x3
f (x) =
(4x 3)(x 1)
(2x + 1)(x + 1)
f (x) =
x2 9
x2 + 4
N (t)
2)(x 2)
4)(x + 2)
1
4x
t
N (t) =
75t
t+5
t
0.
N
N (t)
t!1
t ! 1 N (t) ! 75
c
t
c(t) =
20t
+2
t2
t
0.
c(t)
c(t)
t ! 1 c(t) ! 0
x = 3
x =
5
9
f (x) =
3
(x 5)2 (x2 + 1)
(x + 3)(x 3)(x2 + 5)
y = 1
x
5
t!1
y
p =
5125000V 2 449000V + 19307
125V 2 (1000V 43)
p
p
V =0
p=0
p
V
V = 0.043
V
V
V = 43/1000
T
C
T
F
F
C
5
= (T F 32)
9
9
= T C + 32
5
200 F
93.33 C
120 C
f
x1 x2
y
•
•
•
•
f
x
2
248 F
f (x1 ) 6= f (x2 )
•
d
F (d) =
(
8.00
(8.00 + 1.50 bdc)
bdc
0<d4
d>4
d
F (3) = 8
F (3) = F (2) = F (3.5) = 8
y
F
x
y
x
2
y = x2
4
y = 2x
x
4
3
2
1
y
9
7
5
3
1
y
x
x
y
x
9
7
5
3
y
4
3
2
1
1
x
y
1
x
4
3
2
1
y
1
1
1
1
0
y
x
y=1
x
x = 1, 2, 3, 4
y
x
1
1
1
1
y
4
3
2
1
0
x=1
•
x
•
x
y
y
f
A
1
f
f (x) = y
y
B
y
B
x
y
B
A
f
f
1 (y)
=x
y
x
y = f (x)
x
y
y
x
f (x) = 3x + 1
x
y
y
x
y = 3x + 1
x = 3y + 1
x = 3y + 1
x
x
3
f (x) = 3x + 1
f (f
1 (x))
f
1 = 3y
1
x
= y =) y =
f
1 (x)
1 (f (x))
=
x
1
3
1
3
f (x)
f
=x
x
f
1 (f (x))
=x
x
f
g(x) = x3
x
y
1 (x)
f (x)
1 (x))
f (f
f
1 (x)
f
2
y = x3
x = y3 2
y
x
1
2
x = y3
p
3
g(x) = x3
2
g
x + 2 = y =) y =
1 (x)
=
p
3
p
3
x + 2 = y3
x+2
x+2
f (x) =
y=
x
y
y
x=
x
x=
2
2y + 1
3y 4
2x + 1
3x 4
2x + 1
3x 4
2y + 1
3y 4
x(3y
4) = 2y + 1
3xy
4x = 2y + 1
3xy
2y = 4x + 1
y
y
y(3x
2) = 4x + 1
4x + 1
y=
3x 2
f (x)
f
1 (x)
=
4x + 1
3x 2
f (x) = x2 + 4x
y = x2 + 4x
x
y
2
x = y 2 + 4y
y
x
2
x = y 2 + 4y
2
2
x + 2 = y 2 + 4y
x + 2 + 4 = y 2 + 4y + 4
x + 6 = (y + 2)2
p
± x+6=y+2
p
± x+6
p
y = ± x+6
f (x) =
x2
+ 4x
p
2 = y =) y = ± x + 6
2
2
x
y
x = 3 y
2
f (x) = |3x|
y = |3x|
1
5
f
f (1) = f ( 1) = 3
x
y
1
f
x
1
y
f
y = |4x|
y x = |4y|
x
x = |4y|
p
x = (4y)2
|x| =
x2 = 4y 2
p
x2
x2
= y2
4
r
r
x2
x2
±
= y =) y = ±
4
4
x = 2
f (x) = |3x|
y = 1
y =
y = ±
1
q
x2
4
k(t) = 59 (t 32) + 273.15
t
k = 59 (t
k
32) + 273.15
t
t
k
9
(k
5
9
(k
5
5
k = (t
9
5
273.15 = (t
9
273.15) = t
k
32) + 273.15
32)
32
9
273.15) + 32 = t =) t = (k
5
t(k) = 95 (k
273.15)
k
273.15)
1
f (x) = x + 4
2
f (x) = (x + 3)3
3
f (x) =
x 4
x+3
f (x) =
x 3
2x + 1
f (x) =
4x 1
f
f
f
f
f
f (x) = |x
1|
1 (x)
= 2x 8
3
1 (x) = p
x 3
4x
+3
1 (x) =
x
3x
+3
1 (x) =
x 1
1 (x) = x + 1
4x 2
y=x
y = x
y=x
y=x
y=x
•
•
y=x
x
f
f
y
1
f
y
f (x)
1 (f (x))
=x
x
x
f (x)
!y
f
1 (y)
!x
y=x
y = f
{x | 2 x 1.5 }
1 (x)
y = f (x) = 2x + 1
f (x)
f
1 (x)
y = 2x + 1
{y 2 R |
y=x
3 y 4}
f
f
1
(x) = [ 3, 4]
f
1
(x) = [ 2, 1.5]
1 (x)
=
x
1
2
f (x)
1
x
1 (x)
[ 2, 1.5]
[ 3, 4]
[ 3, 4]
[ 2, 1.5]
f (x) =
f (x) =
f
1
x
y =x
y=x
f (x)
f
1 (x)
= f (x)
f
1 (x)
= f (x) =
1
x
f (x) =
f (x)
y=x
p
3
x+1
f (x) =
f
1 (x)
=
x3
1
p
3
x+1
y = x3
1
f (x) =
5x 1
x+2
f (x) = ( 1, 2) [ (2, 1)
f (x) = ( 1, 5) [ ( 5, 1)
x=2
y= 5
y=x
x
y
y=x
x= 5
y=2
f (x)
( 1, 2) [ (2, 1)
( 1, 5) [ ( 5, 1)
f
1 (x)
( 1, 5) [ ( 5, 1)
( 1, 2) [ (2, 1)
y=x
y=x
f
1
1
(x) = f (x)
f (x) = (x + 2)2 · 3 ÷ 2 =
3(x + 2)2
2
x
x
x
y
y
x
0
3(y + 2)2
x=
,y
2
0
0
x=
3(y + 2)2
2
2x
= (y + 2)2
3
r
2x
=y+2
y 2
3
r
r
2x
2x
2 = y =) y =
2
3
3
r
x = 54
f
1
(54) =
r
2(54)
3
2=
r
108
3
2=
p
36
2=6
t
d
t(d) =
t=
d
✓
✓
12.5
d
12.5
d
◆3
◆3
d
t
✓
12.5
t=
d
p
12.5
3
t=
d
12.5
d= p
3
t
◆3
12.5
d(t) = p
3
t
22.5
t = 6.5 d(6.5) = p
= 12.06
3
6.5
12.06
t
2=4
2x
3
f (x) = x2 + 1
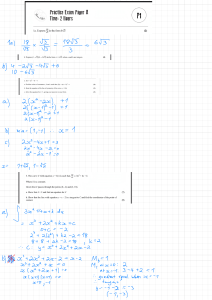
{0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3}
f
f
x
1
1.25
2
3.25
5
7.25
10
1 (x)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
x
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
f (x)
1
1.25
2
3.25
5
7.25
10
A = {( 4, 4), ( 3, 2), ( 2, 1), (0, 1), (1, 3), (2, 5)}
A
1
= {(4, 4), (2, 3), (1, 2), ( 1, 0), ( 3, 1), ( 5, 2)}
p
f (x) = 2 x
2+3
[2, 1)
f (x) =
[3, 1)
3x + 2
x 4
[2, 1)
( 1, 3) [ (3, 1)
( 1, 4) [ (4, 1)
x=a
f
1 (a)
=0
1/2
w
w = (3.24 ⇥ 10
l
l=
0
p
w/(3.4 ⇥ 10
3)
3 )l2
l
n
s
n=
2s
f (x) = bx
b
b > 0 b 6= 1
x = 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2
y=
1 x
3
y=
10x
y=
(0.8)x
3
y = bx
x
y=
3
2
1
1
3
1 x
3
1
1000
y = 10x
1
100
1
9
1
27
1
10
y = (0.8)x
f (x) = 3x
f (2) f ( 2) f
1
2
f (0.4)
f (⇡)
f (2) = 32 = 9
f ( 2) = 3
2
=
1
1
=
2
3
9
✓ ◆
p
1
= 31/2 = 3
2
p
p
5
5
f (0.4) = 30.4 = 32/5 = 32 = 9
f
3⇡
⇡ ⇡ 3.14159
f (⇡) = 3⇡
33.14
3⇡
⇡
3⇡
b
b
g(x) = a · bx
a c
d
c
+d
33.14159
t
t=0
t
t=0
t = 100
20(2)
t = 200
= 20(2)2
t = 300
= 20(2)3
t = 400
= 20(2)4
y = 20(2)t/100
y
y
t
T
y0
y = y0
t
t=0
t = 10
t = 20
t = 30
(2)t/T
y = 10
1 t/10
2
100, 000
6%
t
t=0
= 100, 000
t=1
= 100, 000(1.06) = 106, 000
t=2
= 106, 000(1.06) = 112, 360
t=3
= 112, 360(1.06) ⇡ 119, 101.60
= 119, 101.60(1.06) ⇡ 126, 247.70
t=4
= 26, 247.70(1.06) ⇡ 133, 822.56
t=5
y = 100, 000(1.06)t
P
t
r
A = P (1 +
r)t
y = 100000(1.06)t
t = 8
179, 084.77
y =
100, 000(1.06)8 ⇡
159, 384.81
t
t = 10
200, 000
t
y =
100, 000(1.06)10 ⇡
e ⇡ 2.71828
e
e
e
f (x) = ex
T
T =
t
170165e0.006t
t
t
T
50, 000
t = 18
A = 50, 000(1.044)t
t
18
A = 50, 000(1.044) ⇡ 108, 537.29
t = 10, A =
32, 577.89
A = 20, 000(1.05)t
t
10
20, 000(1.05) ⇡ 32, 577.89
100, 000
x/250
y = 100 12
x = 500
y = 100
x=0
= 100
1 500/250
2
1 2
2
= 25
y = 1, 000(3)x/80
x=0
100/80
x = 100
y = 1, 000(3)
= 3, 948.22 ⇡ 3, 948
10, 000
A = 10, 000(1.02)t
A = 10, 000(1.02)12 = 12, 682.42
12, 682.42
t
4x
1
y = 2x
= 16x
2x
a · bx
b 6= 1
72x
x2
=
1
343
52x
f (x) = 2x3
f (x) = 2x
y = ex
22 (5x+1 ) = 500
625
5x+8
y
+d
b > 0
f (x) = bx
b 6= 1
b>0
f (x) = (1.8)x
(1.8)x
5x+1 0
x
x
c
26
y =
a 6= 0
a0 = 1
a
n
=
1
an
r
s
r
s
a a = ar+s
ar
= ar s
asr s
(a ) = ars
(ab)r = ar br
⇣ a ⌘r
ar
= r
b
b
49 = 7x+1
7 = 2x + 3
3x = 32x 1
5x 1 = 125
x1 6= x2
8x = x2 9
x2 = 3x3 + 2x 1
2x + 3 > x 1
2x 2 > 8
bx1 6= bx2
b x1 = b x2
4x
1
= 16
4x
1
= 16
4x
1
= 42
x
1=2
x=2+1
x=3
4x
1
= 16
(22 )x
1
= 24
22(x
1)
= 24
2(x
2x
1) = 4
2=4
2x = 6
x=3
x1 = x2
43
x=3
16
125x
1
= 25x+3
125x
1
= 25x+3
(53 )x
1
= (52 )x+3
53(x
1)
= 52(x+3)
3(x
1) = 2(x + 3)
3x
3 = 2x + 6
x=9
2
9x = 3x+3
2
(32 )x = 3x+3
2
32x = 3x+3
2x2 = x + 3
2x2
(2x
x
3=0
3)(x + 1) = 0
2x
3=0
3
x=
2
x+1=0
x=1
1
= 42 =
y = bx
b>1
x
b < by
x
x<y
y = bx
0<b<1
bx > by
x
x<y
bm < bn
m<n
3x < 9x
m>n
b
2
3x < (32 )x
3x < 32(x
3x < 32x
2
2)
4
3>1
x < 2x
4
4 < 2x
x
4<x
(4, +1]
x=5
✓
1
100
=
1 2
10
1
10
◆x+5
✓
1
10
✓
1
10
✓
1
10
✓
◆x+5
◆x+5
◆x+5
1
100
✓
✓
x=4
◆3x
1
100
◆3x
◆
1 3x
102
✓ ◆6x
1
10
1
10
1
10
<1
x + 5 6x
5 6x
x
5 5x
1x
[1, +1)
x=1
x=0
y0
1
256
y = y0
1 t/2.45
2
y0
✓ ◆t/2.45
1
1
=
2
256
✓ ◆t/2.45 ✓ ◆8
1
1
=
2
2
t
=8
2.45
t = 19.6
t=0
(0.6)x
3
> (0.36)
x 1
1 t/2.45
2
t
=
1
256 y0
1
(0.6)x
3
> (0.36)
x 1
(0.6)x
3
> (0.36)
x 1
(0.6)x
3
> (0.62 )
x 1
(0.6)x
3
> (0.62 )
x 1
(0.6)x
3
> (0.6)2(
(0.6)x
3
> (0.6)2(
(0.6)x
3
> (0.6)
(0.6)x
3
> (0.6)
x
3>
2x
x 1)
2x 2
2
x
3x > 1
1
x>
3
(0.6)x
x > 13
3<
2x
x 1)
2x 2
2
3x < 1
1
x<
3
3
> (0.6)
2x 2
x
3>
2x
2
x
162x 3 = 4x+2
✓ ◆2x
1
= 23 x
2
42x+7
✓ ◆5x
2
5
x=
1
2
2
1
x=
322x 3
1
25
4
25
4
✓ ◆
2
5
2
8
3
3
◆
29
, +1
6
( 1,
1
5]
x
7x+4 = 492x
1
4x+2 = 82x
✓ ◆5x+2 ✓ ◆2x
2
3
=
3
2
x=2
✓
x=1
◆
2
, +1
7
f (x) = bx
b>1
f (x) = bx
0<b<1
f (x) = 2x
f (x)
x
f (x)
4
1
16
3
1
8
2
1
4
1
1
2
f (x) = 2x
f (x) = 2x
x
y
x
y=0
✓ ◆x
1
g(x) =
2
g(x)
x
f (x)
3
2
1
1
2
1
4
1
8
1
16
g(x) =
✓ ◆x
1
2
g(x) =
✓ ◆x
1
2
x
x
y=0
b > 1
b>1
0 < b < 1
f (x) = bx
0<b<1
f (x) = bx
b 6= 1
b>0
R
(0, +1)
y
x
y=0
x
f (x) = 2x
x
4
3
2
g(x) = 3x
1
f (x)
g(x)
x
f (x)
4
y
1
g(x)
y
✓ ◆x
1
f (x) =
2
x
4
3
2
✓ ◆x
1
g(x) =
3
1
f (x)
g(x)
x
f (x)
g(x)
4
y
1
y
5
x
f (x) = 5✓ x◆
1
1 x
= x =
5
5
y
•
•
x
3
x
4
y
1
y = 2x
•
y = 2x
y = 2x
y = 3 · 2x
y = 25 · 2x
y = 2x + 1
y = 2x 1
y = 2x+1
y = 2x 1
x
3
2
1
0.125
.25
.5
y = 2x
y = 2x
2x
y=
1
2
4
8
y
y = 3 · 2x
y=
2
5
y
1
y
2/5
· 2x
y = 2x + 1
y = 2x
1
0.875
0.75
0.5
y = 2x+1
y = 2x
1
y = 2x
y=
2x
y=2
x
y
x
y=
3
2
1
0.125
0.25
0.5
2x
y=
y=2
2x
1
2
4
8
x
y = 2x
y = 2x
y
y=
2x
y
y = 2x
x
y=2
x
x
y = 2x
y = 2x
y
x
y=2
x
y=
f (x)
x
y = f (x)
y = f ( x)
y
y = f (x)
y = 2x
y = 3(2x )
y = 0.4(2x )
y
x
3
2
1
y = 2x
y = 3(2x )
y = 0.4(2x )
y = 3(2x )
y
y=
y
2x
y
y = 0.4(2x )
y
y = 2x
R
y
y = 3(2x )
y
y = 0.4(2x )
y
y=0
(0, +1)
a>0
y = af (x)
y = f (x)
0<a<1
a>1
y
a
y = f (x)
y = 2x
y = 2x
y
x
y=
3
2
1
2.875
2.75
2.5
2x
y = 2x
3
y = 2x + 1
2
1
3
y = 2x + 1
R
y = 2x + 1
y = 2x
(1, +1)
3
( 3, +1)
y
y
y=
y=
2x
+1
y= 3
d
d>0
2x
y = 2x
y=1
d
y = 2x
y
y=0
y = 2x
y = f (x) + d
d<0
d
y = f (x)
y = 2x
2
y = 2x+4
3
x
3
2
1
y = 2x
y = 2x
2
y = 2x+4
R
(0, +1)
y
y = 2x+4
24
= 16
y
y=
x=0
22 = 0.25
y
2x 2
y=0
c
c>0
y = f (x)
y = f (x
c
c)
c
c<0
f (x) = a · bx
•
c
+d
b
•
b>1
0<b<1
|a|
•
a
x
d
•
d>0
c
d
d<0
c>0
c
c<0
y = bx
y
y = 3x 4
✓ ◆x
1
y=
+2
2
y = 2x
5
y = (0.8)x+1
✓ ◆x
1
3
y = 0.25(3x )
y=2
y = 2x 3 + 1
✓ ◆x 1
1
y=
3
2
x
24 = x
43 = x
1 1
5 4
5
1
=x
16
1
2
=x
5x = 625
1
3x =
9
7x = 0
10x = 100, 000
x
x
log3 81 = 4
x
log2 32 = 5
34
b
= 81
logb x
b
25 = 32
log5 1 = 0
50 = 1
✓ ◆
1
log6
= ( 1)
6
6
1
=
1
6
log2 32
log5 5
log7 1
log9 729
log 1 16
1
log5 p
5
2
4
1
p
5
1/2
a
b
b 6= 1
b
logb a
b
a
blogb a = a
logb a
a
log2 32 = 5
25 = 32
log9 729 = 3
93 = 729
log5 5 = 1
51 = 5
log1/2 16 =
p1
5
1
2
=
= 16
70 = 1
log7 1 = 0
log5
4
1
2
4
5
1/2
=
p1
5
logb a = c
bc = a
•
b
•
c
•
c = logb a
logb a a
•
log2 ( 8)
logb x
log5
1
=
125
log x
log10 x
e
e
ln
ln x
3
loge x
5
3
=
1
125
53 = 125
1
7 2=
49
102 = 100
✓ ◆2
2
4
=
3
9
(0.1)
4
= 10, 000
40 = 1
7b = 21
e2 = x
( 2)2 = 4
log5 125 = 3
1
log7
= 2
49
log 100 = 2
✓ ◆
4
log 2
=2
3
9
log0.1 10, 000 =
4
log4 1 = 0
log7 21 = b
b=3
73 6= 21
b
71 .5645
ln x = 2
log m = n
log3 81 = 4
logp5 5 = 2
64
log 3
= 3
4 27
1
2
log10 0.001 =
log4 2 =
ln 8 = a
3
10n = m
41/2 = 2
34 = 81
p
( 5)2 = 5
✓ ◆ 3
3
64
=
4
27
10
3
= 0.001
10
3
=
1
1, 000
ea = 8
log 1031
R=
2
E
log 4.40
3
10
104.40
E
1012
1031
= 31
2
1012
2
log 4.40 = log 107.6
3
10
3
log107.6 = 7.6
log 107.6 = 7.6
2
R = (7.6) ⇡ 5.1
3
E = 1012
107.6
R=
1012 /104.40 = 107.6 ⇡ 39810717
D = 10 log
I
2
I
10 12
10
12
106
2
60
85
90
100
10
D = log
10
10
6
12
= 10 log 106
106
log 106
log 106 = 6
D = 10(6) = 60
10
10
6
12
= 106 = 100, 000
6
m2
[H + ]
pH =
log[H + ]
pH = log
10
1
[H + ]
5
10
log 10
5
=
( 5) = 5
5
log 10 5
log 10 5 =
log 10
5
5
log3 243
✓
◆
1
log6
216
log0.25 16
5
3
2
49x = 7
log49 7 = x
1
6 3=
216
102 = 100
✓
4
log 11
2
121
ln 3 = y
log 0.001 =
log6 216 =
3
log 100 = 2
◆
=
3
2
✓
11
2
◆
10
2
4
121
y
e =3
=
3
= 0.001
log3 (x
2) = 5
ln x
9
logx 2 = 4
ln x2 > (ln x)2
x
y=
g(x) = log3 x
log 1 x
2
x
• logx 2 = 4
• log2 x =
4
• log2 4 = x
•
logx 2 = 4
•
log2 x =
•
x
4
log2 4 = x
log
2x
=4
4
x
y
f (x) = 3x
x
f (x)
4
1
g(x) = log3 x
x
x
g(x)
1
81
1
3
log2 x = 4
logx 16 = 2
log 1000 =
log2 x = 4
24 = x
x = 16
logx 16 = 2
x2 = 16
x2 16 = 0
(x + 4)(x 4) = 0
x = 4, +4
x=4
log 1000 =
x
x
log 1000
3= x
x= 3
log3 81
34 = 81
log4 1
log4 3 = 0
log3 3 = 1
log4 42 = 2
log3 3
40 = 1
31 = 3
42 = 42
log4 42
b
x
b 6= 1
b>0
logb 1 = 0
logb bx = x
blogb x = x
x>0
logb 1
b? = 1
b
logb bx
b
bx
x
logb x
b
x
b
x
log2 14
23 = 8
24 = 16
23.8074 ⇡ 14.000
2log2 14 = 14
logb 1 = 0 logb bx = x
blogb x = x
✓
log 10
log5
ln e3
5log5 2
log4 64
log 1
log 10 = log10 101 = 1
ln e3 = loge e3 = 3
log4 64 = log4 43 = 3
✓
◆
1
log5
= log5 5
125
3
=
3
1
125
◆
5log5 2=2
log 1 = 0
10
D
D
D
D
D
✓
◆
I
= 10 log
✓ I0 2 ◆
10
= 10 log
10 12
= 10 log 1010
= 10 · 10
= 100
pH = log[H + ]
3.0 = log[H + ]
3.0 = log[H + ]
+
10 3.0 = 10log H
10 3.0 = [H+]
10
log7 49
log27 3
ln e
1
3
3.0
2
m2
log7 73 · 78
✓ ◆
49
log7
7
log7 73 + log7 78
log7 49
log7 75
5 · log7 7
✓ 4◆
2
log2
log2 24
210
log3 (27 · 81)
log7 7
log2 210
6
log3 27 + log3 81
b > 0, b 6= 1
n2R
logb (uv) = logb u + logb v
⇣u⌘
logb
= logb u logb v
v
logb (un ) = n logb u
u > 0, v > 0
log7 73 · 78 = log7 73 + log7 78
✓ ◆
49
log7
= log7 49 log7 7
✓ 74 ◆
2
log2
= log2 24 log2 210
210
log7 75 = 5 · log7 7
log3 (27 · 81) = log3 27 + log3 81
logb (uv) = logb u + logb v
logb
⇣u⌘
v
= logb u
logb v
logb (un ) = n logb u
r = logb u
s = logb v
u = br
v = bs
logb (uv) = logb (br bs )
) logb (uv) = logb br+s
) logb (uv) = r + s
) logb (uv) = logb u = logb v
r = logb u
u = br
un = brn
un = brn
) logb (un ) = logb (brn )
) logb (un ) = rn
) logb (un ) = n logb u
logb un
u
(logb u)n
n
n
logb u
log2 (5 + 2) 6= log2 5 + log2 2
log2 (5 + 2) 6= (log2 5)(log2 2)
2) 6= log2 5 log2 2
log2 5
log2 (5 2) 6=
log2 2
2
log2 (5 · 2) 6= 2 log2 (5 · 2)
log2 (5
log(ab2 )
✓ ◆3
3
log3
x
ln[x(x
log(ab2 ) = log a + log b2 = log a + 2 log b
✓ ◆3
✓ ◆
3
3
log3
= 3 log3
= 3(log3 3 log3 x) = 3(1
x
x
ln[x(x 5)] = ln x + ln(x 5)
log3 x) = 3
log 2 + log 3
log5 (x2 )
2 ln x
ln y
2
2 ln x
log 2 + log 3 = log(2 · 3) = log 6
✓ 2◆
x
2
ln y = ln(x ) ln y = ln
y
log5 (x2 )
2
3 log5 x = log5 (x2 )
log5 (x3 ) = log5
log 5
2 = 2(1)
= 2(log 10)
= log 102
= log 100
1 = logb b
n logb u = logb un
2
100
5
log 5 = log 100 = log
✓
◆
= log 20
✓
x2
x3
5)]
3 log3 x
3 log5 x
log 5
◆
= log5
✓ ◆
1
= log5 (x
x
1)
=
log5 x
log3 729
6
log9 729
3
log27 729
2
log1/27 729
2
log729 729
1
log81 729
3/2
log81 729
811/4 = 3
816/4 = 813/2 = 729
log81 729 =
log3n 729 =
3
2
6
n
a 6= 1, b 6= 1
a b
x
loga x
logb x =
loga b
log3n 729 =
6
n
log3n 729 =
log8 32
1
27
1
p
5
log243
log25
log3 729
6
= .
n
log3 3
n
36 = 729
(811/4 )6 = 729
log8 32 =
log243
1
27
1
log25 p
5
log2 32
5
=
log2 8
3
1
log3
27 = 3
=
log3 243
5
1
log5 p
1/2
5
=
=
=
log5 25
2
1
4
log6 4
log 1 2
e
2
log2 4
2
=
log2 6
log2 6
ln 2
ln 2
ln 2
ln 2
log 1 2 = ✓ ◆ =
=
=
=
2
1
ln 1 ln 2
0 ln 2
ln 2
ln
2
log6 4 =
log
✓
x3
2
ln(2e)2
◆
3 log x
log(x + 2) + log(x
log 2
(2e)2 = 4e3
log4 (16a)
1
2 ln 2 + 2
2 + log4 a
2)
2 log3 5 + 1
✓ ◆
3
2 ln
ln 4
2
(log3 2)(log3 4) = log3 8
(log3 2)(log3 4) = log3 6
log(x2
4)
log3 75
✓ ◆
9
ln
16
log 22 = (log 2)2
log4 x
log4 (x 4) =
log4 4
2
3 log9 x = 6 log9 x
3(log9 x)2 = 6 log9 x
log3 2x2 = log3 2 + 2 log3 x
log3 2x2 = 2 log3 2x
log5 ✓
2 ⇡ ◆0.431
p
1
log5 8, log5
, log5 2, log25 2
log25 8
16
1.2920, 1.7227, 0.2153, 0.2153, 0.6460
log 6 ⇡ 0.778
log 4 ⇡ 0.602✓ ◆
✓ ◆
2
3
log6 4, log 24, log4 6, log
log
3
2
0.7737, 1.3802, 1.2925, 0.1761, 0.1761
b
x
logb x
• b
• x
•
logb x
•
•
•
f (x) = logb x
ab = 0
logb u = logb v
a=0
u=v
b=0
x
log4 (2x) = log4 10
log2 (x + 1) + log2 (x
log3 (2x
log x2 = 2
1) = 2
logx 16 = 2
log4 (2x) = log4 10
2x = 10
x=5
(log x)2 + 2 log x
1) = 3
3=0
log4 (2 · 5) = log4 (10)
log3 (2x 1) = 2
2x 1 = 32
2x 1 = 9
2x = 10
x=5
log3 (2 · (5)1) = log3 (9) = 2
logx 16 = 2
x2 = 16
x2 16 = 0
(x + 4)(x 4) = 0
x = 4, 4
a2
log4 (16) = 2
log2 (x + 1) + log2 (x 1) = 3
log2 [(x + 1)(x 1)] = 3
(x + 1)(x 1) = 23
x2 1 = 8
x2 9 = 0
(x + 3)(x 3) = 0
x = 3, 3
3
x=3
log x2 = 2
log x2 = 2
x2 = 102
x2 = 100
b2 = (a + b)(a
b)
4
log
logb u + logb v = logb (uv)
a2
b2 = (a + b)(a
log2 (3 + 1)
log2 (31
log2 (3 + 1) = log2 (2)
b)
4 (16)
x2 100 = 0
(x + 10)(x 10) = 0
x = 10, 10
log(10)2 = 2
log x2 = 2
log x2 = log 102
x2 = 102
x2 100 = 0
(x + 10)(x 10) = 0
x = 10, 10
log(10)2 = 2
2 = 2(1) = 2(log 10) = log 102
log(10)2 = 2
log(10)2 = 2
logb un = n logb u
log x2 = 2
2 log x = 2
log x = 1
x = 10
log x2 = 2 log x
(log x)2 + 2 log x
x>0
3=0
log x = A
A2 + 2A 3 = 0
(A + 3)(A 1) = 0
A= 3
A=1
log x =
x = 10
3
3
log x = 1
1
x = 10
=
1000
log
✓
1
1000
◆
log 10
x
2x = 3
2x = 3
log 2x = log 3
x log 2 = log 3
log 3
x=
⇡ 1.58496
log 2
x
logb un = n logb u
log 1 x
x
2
1
8
1
8
1
4
1
4
1
2
1
2
x
log 1 x
x
2
log2 x
log2 x
1
8
1
8
3
1
4
1
4
2
1
2
1
2
1
1
2
3
1
2
log 1 x
x
log 1 x
log2 x
x
log2 x
2
2
logb x
0<b<1
b>1
x 1 < x2
x 1 < x2
logb x1 > logb x2
logb x1 < logb x2
•
<
•
>
b
x
log3 (2x
1) > log3 (x + 2)
log0.2 >
3
2 < log x < 2
log3 (2x
2x
1) > log3 (x + 2)
2x 1 > 0
1>0
x+2>0
x > 12
x+2>0
x>
log3 (2x
2x 1 > x + 2
x>3
)x>3
1) > log3 (x + 2)
x
(3, +1)
log0.2 >
3
x>0
1
2
x> 2
x > 12
x
2
1
5
3
5
✓ ◆
1
log 1 x > log 1
5
5
5
0.2 =
x
1
5
✓ ◆
1
log 1 x > log 1
5
5
5
✓ ◆
1
5
3 = log 1
3
3
✓ ◆ 3
1
x<
= 125
5
0 < x < 125
3
(0, 125)
2 < log x < 2
x>0
2
log 10
log 10
log 10
2
2
< log x < log 102
< log x
10
2
<x
log x < log 102
x < 102
1
< x < 100
✓100
◆
1
, 100
100
EB
EN
EB
EN
7.2 =
2
EB
log 4.4
3
10
6.7 =
2
EN
log 4.4
3
10
2
log 102
✓ ◆
3
EB
= log 4.4
2
10
EB
10.8 = log 4.4
10
EB
10.8
10
= 4.4
10
EB = 1010.8 · 104.4 = 1015.2
EB 7.2
✓ ◆
3
EN
= log 4.4
2
10
EN
10.05 = log 4.4
10
EN
10.05
10
= 4.4
10
EB = 1010.05 · 104.4 = 1014.45
1015.2
= 14.45 = 100.75 ⇡ 5.62
10
EN 6.7
EB
EN
n
n+1
E1
E2
n=
E1
E2
n
E2
E1
2
E1
log 4.4
3
10
3
E1
n = log 4.4
2
10
E1
3n/2
10
= 4.4
10
3n
E1 = 103n/2 · 104.4 = 10 2 +4.4
3
E2
(n + 1) = log 4.4
2
10
E2
3(n+1)/2
10
= 4.4
10
3(n+1)
3(n+1)/2
E2 = 10
· 104.4 = 10 2 +4.4
3(n+1)
3
E2
10 2 +4.4
=
= 10 2 ⇡ 31.6
3n
+4.4
E1
10 2
n+1=
2
E2
log 4.4
3
10
n+1
P
A = P (1 + r)n
r
A
n
A = 2P r = 2.5% = 0.025
r)n
A = P (1 +
2P = P (1 + 0.025)n
2 = (1.025)n
log 2 = log(1.025)n
log 2 = n log(1.025)
log 2
n=
⇡ 28.07
log 1.025
log
ln
ln 2
ln 1.025
P (x) = 20, 000, 000 · e0.0251x
x
P (x) = 200, 000, 000
200, 000, 000 = 20, 000, 000 · e0.0251x
10 = e0.0251x
ln 10 = ln e0.0251x
ln 10 = 0.0251x(ln e)
ln 10 = 0.0251x
ln 10
x=
⇡ 91
0.0251
x=0
f (t) = Aekt
t
f (0) =
Aek(0)
f (0) = 5, 000
= A = 5, 000
A
f (90) = 12, 000
12
5
12
12
= ln
) 90k = ln
) k ⇡ 0.00973
5
5
f (90) = 5, 000ek(90) = 12, 000 ) e90k =
ln e90k
f (t) = 5, 000 · e0.00973t
f (180) = 5, 000 · e0.00973(180) ⇡ 28, 813
y=
y=4
k
ex + e
2
x
4=
8 = ex + e x
1
8 = ex + x
e
8ex = e2x + 1
e2x 8ex + 1 = 0
u = ex
u2 = e2x
u = ex
x
log5 (x
ex + e
2
x
8 = ex + e
x
u2 8u + 1 = 0
p
u = 4 ± 15
p
p
4 + 15 = ex
4
15 = ex
p
p
ln(4 + 15) = x
ln(4
15) = x
y=4
p
p
ln(4 + 15) ln(4
15) ⇡ 4.13
1) + log5 (x + 3)
1=0
log3 x + log3 (x + 2) = 1
1
ln x > 1
log 3
⇡ 1.0959
log 3
e ⇡ 2.7183
3x+1 = 10
(e, +1)
log0.5 (4x + 1) < log0.5 (1
4x)
(0, 1/4)
log2 [log3 (log4 x)] = 0
f (x) = bx
f (x) = bx
y = f (x) = bx
y = bx
x = by
y = logb x
f 1 (x) = logb x
x
y
y = log2 x
y = log2 x
x
y
1
16
1
8
4
3
1
4
2
1
2
1
y = log2 x
y = log2 x
x>0
x
x=0
y = 2x
y = log2 x
y = x
y = log 1 x
2
y = log 1 x
2
x
1
16
1
8
1
4
1
2
y
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
y = log 12 x
y = log 12 x
x>0
x
x=0
y = log2 x
y = logb x
y = log 1 x
2
b
y = logb x(b > 1)
y = logb x b > 1
y = logb x(0 < b < 1)
0<b<1
{x 2 R|x > 0}
logb x
x
x
y
x=0
y
y=x
y = bx
y = bx
y = logb x(b > 1)
y=
y = logb x(0 < b < 1)
log2 x
y = log 1 x
2
y = 2 log2 x
x
y = 2 log2 x
y
y = 2 log2 x
1
16
x
1
8
1
4
1
2
log2 x
4
3
2
1
y = 2 log2 x
8
6
4
2
{x|x 2 R, x > 0}
{y|y 2 R}
x=0
x
y = log3 x
1
y = log3 x
>
1
y = log3 x
(1, 0), (3, 1)
(1, 1), (3, 0)
(9, 2)
(9, 1)
{x|x 2 R, x > 0}
{y|y 2 R}
x=0
x
x
x
y=0
0 = log3 x 1
log3 x = 1
x = 31 = 3
y = log0.25 (x + 2)
y = log0.25 [x
y = log0.25 x
( 2)]
0 < 0.25 < 1
2
y = log0.25 x
(1, 0), (4, 1),
( 1, 0), (2, 1),
(0.25, 1)
( 1.75, 1)
{x|x 2 R, x >
x+2
2}
log0.25 (x + 2)
x
2
{y|y 2 R}
x
x=
2
1
f (x) = a · logb (x
•
b
•
•
c) + d
b>1
0<b<1
a
a
x
f (x) = a · logb x
d<0
c<0
d
c
d>0
c>0
d
c
y = logb x
y
y = logx (x + 3)
y = (log0.1 x)
y = log 1 (x
y = log 2 (x
1)
3
5
y = (log5 x) + 6
2
4) + 2
y = log6 (x + 1) + 5
log 2 ⇡ 0.3010
log 3 ⇡ 0.4771
log 5 ⇡ 0.6990
log 7 ⇡ 0.8451
21/3
51/4
21/3
51/4
21/3
n = 1/4
5
log n
log n =
1
log n ⇡ (0.3010)
3
n
0.0744
log n ⇡
n ⇡ 10
0.0744
1
(0.6990) ⇡
4
1
log 2
3
0.0744
n
0.0744
1
log 5
4
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
t
P
r
I
Is
Ic
F
t
r
t
t
P
r
t
t
t
Is = P rt
Is
P
r
t
P = 1, 000, 000
r = 0.25% = 0.0025
t=1
Is
Is = P rt
Is = (1, 000, 000)(0.0025)(1)
Is = 2, 500
P = 50, 000
r = 10% = 0.10
9
t=
12
Is
M
Is = P rt
Is = (50, 000)(0.10)
t=
✓
9
12
◆
Is = (50, 000)(0.10)(0.75)
Is = 3, 750
M
12
P
Is
1, 500
=
rt
(0.025)(4)
P = 15, 000
P =
Is
4, 860
=
Pt
(36, 000)(1.5)
r = 0.09 = 9%
r=
Is
275
=
Pr
(250, 000)(0.005)
t = 0.22
t=
Is = P rt = (500, 000)(0.125)(10)
Is = 625, 000
r
t
r = 7% = 0.07
t=2
IS = 11, 200
P
P =
Is
11, 200
=
rt
(0.07)(2)
P = 80, 000
P = 500, 000
Is = 157, 500
t=3
r
r=
Is
157, 500
=
Pt
(500, 000)(3)
r = 0.105 = 10.5%
P
r = 5% = 0.05
1
Is = P = 0.5P
2
t
t=
Is
0.5P
=
Pr
(P )(0.05)
t = 10
t
r
F
F = P + Is
F
P
Is
Is
P rt
F = P + P rt
F = P (1 + rt)
F = P (1 + rt)
F
P
r
t
P = 1, 000, 000, r = 0.25% = 0.0025
F
F
Is
F = P (1 + rt)
t=1
Is = P rt
Is = (1, 000, 000)(0.0025)(1)
Is = 2, 500
F = P + Is
F = 1, 000, 000 + 2, 500
F = 1, 002, 500
F
F = P (1 + rt)
F = (1, 000, 000)(1 + 0.0025(1))
F = 1, 002, 500
t=5
Is = P rt
Is = (1, 000, 000)(0.0025)(5)
Is = 12, 500
F = P + Is
F = 1, 000, 000 + 12, 500
F = 1, 012, 500
F = P (1 + rt)
F = (1, 000, 000)(1 + 0.0025(5))
F = 1, 012, 500
P
F = P + Is .
P
P
r
r
t
t
I
I
1
2
I
F
I
I = 9, 500
F
P = 300, 000
P
t=5
F
I = 16, 250
r = 9.5%
F = 1, 016, 250
1
4
P
r
P
r
100, 000 · 1.05 = 105, 000
P (1 + r) = P (1 + r)
P (1 + r)(1 + r) = P (1 +
P (1 +
r)2 (1
P (1 +
r)3 (1
r)2
+ r) = P (1 +
+ r) == P (1 +
(1 + r)
105, 000·, 1.05 = 110, 250
r)3
r)4
110, 250 · 1.05 = 121, 550.63
121, 550.63 · 1.05 = 127, 628.16
1+r
r
F = P (1 + r)t
P
F
r
t
Ic
Ic = F
P
P = 10, 000
r = 2% = 0.02
t=5
F
Ic
F = P (1 + r)t
F = (10, 000)(1 + 0.02)5
F = 11, 040.081
Ic = F P
Ic = 11, 040.81
Ic = 1, 040.81
10, 000
F
P = 50, 000
r = 5% = 0.05
t=8
F
Ic
F = P (1 + r)t
F = (50, 000)(1 + 0.05)8
F = 73, 872.77
Ic = F P
Ic = 73, 872.77
Ic = 23, 872.77
50, 000
F
P = 10, 000
r = 0.5% = 0.005
t = 12
F
F
F = P (1 + r)t
F = (10, 000)(1 + 0.005)12
F = 10, 616.78
F
F = P (1 +
t
r
r)t
P
P (1 + r)t = F
P (1 + r)t
F
=
(1 + r)t
(1 + r)t
F
P =
(1 + r)t
P = F (1 + r)
P
P =
P
F
r
t
F
= F (1 + r)
(1 + r)t
t
t
F = 50, 000
r = 10% = 0.1
t=7
P
P
F
(1 + r)t
50, 000
P =
(1 + 0.1)7
P =
P = 25, 657.91
F = 200, 000
r = 1.1% = 0.011
t=6
P
P
F
(1 + r)t
200, 000
P =
(1 + 0.011)6
P =
P = 187, 293.65
P
r
t
Ic
P
r
t
Ic
F
Fc = 23, 820.32 Ic = 3, 820.32
Fc = 25, 250.94 Ic = 250.94
Fc = 90, 673.22 Ic = 2, 673.22
P = 89, 632.37
t
t
r
Ic
t
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
•
•
•
•
m
i(m)
j
j=
•
i(m)
=
m
n
n = tm =
⇥
r, i(m) , j
r
i(m)
i(m)
= 0.02
0.02
= 0.02 = 2%
1
i(2) = 0.02
0.02
= 0.01 = 1%
2
i(3)
0.02
= 0.005 = 0.5%
4
i(1)
= 0.02
i(12)
0.02
= 0.0016 = 0.16%
12
= 0.02
i(365)
0.02
365
= 0.02
F = P (1 + j)t
•
•
j=
t
mt
i(m)
m
j
F =P
i(m)
1+
m
!mt
F =
P =
i(m) =
m=
t=
F = P (1 + j)t
F =P
j
t
i(m)
m
mt
i(m)
1+
m
!mt
P = 10, 000
i(4) = 0.02
t=5
m=4
F
P
j=
i(4)
0.02
=
= 0.005
m
4
n = mt = (4)(5) = 20
.
F = P (1 + j)n
= (10, 000)(1 + 0.005)20
F = 11, 048.96
Ic = F
P = 10, 000
i(12) = 0.02
t=5
m = 12
F
P
P = 11, 048.96
10, 000 = 1, 048.96
j=
i(12)
0.02
=
= 0.0016
m
12
n = mt = (12)(5) = 60
.
F = P (1 + j)n
= (10, 000)(1 + 0.0016)60
F = 11, 050.79
Ic = F
P = 50, 000
i(12) = 0.12
t=6
m = 12
F
P = 11, 050.79
10, 000 = 1, 050.79
!tm
i(12)
F =P 1+
m
✓
◆
0.12 (6)(12)
F = (50, 000) 1 +
12
F = (50, 000)(1.01)72
F = 102, 354.97
P =
F
i(m)
1+
m
!mt
F =
P =
i(m) =
m=
t=
F = 50, 000
t=4
i(2) = 0.12
P
j=
i(2)
0.12
=
= 0.06
m
2
n = tm = (4)(2) = 8
P =
P =
F
(1 + j)n
50, 000
50, 000
=
= 31, 370.62
8
(1 + 0.06)
(1.06)8
F = 25, 000
1
t=2
2
i(4) = 0.10
P
j=
i(4)
0.10
=
= 0.025
m
4
1
n = tm = (2 )(4) = 10
2
P =
P =
F
(1 + j)n
25, 000
25, 000
=
= 19, 529.96
(1 + 0.025)10
(1.025)10
i(m)
F
F
3%
1
m
x = = (m)
j
i
m
x = (m) ! 1
i
i(m)
m!1
x=
m = x(i(m) )
m
m
i(m)
!mt
i(m)
F =P 1+
m
✓
◆ (m)
1 xi t
F =P 1+
x
✓
◆ i(m) t
1 x
F =P
1+
x
x
x ! 1
✓
1+
1
x
◆x
✓
1
1+
x
◆x
e
i(m)
P
F
t
F = P ei
(m) t
P = 20, 000
i(m) = 0.03
t=6
F
F = P ei
F = P ei
(m) t
(m) t
= 20, 000e(0.03)(6) = 20, 000e0.18 = 23, 944.35
P = 3, 000
F = 3, 500
i(12) = 0.25% = 0.0025
m = 12
j=
i(12)
0.0025
=
m
12
t
F = P (1 + j)n
✓
0.0025
3, 500 = 3, 000 1 +
12
✓
◆
3, 500
0.0025 n
= 1+
3, 000
12
◆n
n
✓
◆
0.0025 n
log
= log 1 +
12
✓
◆
0.0025
log(1.166667) = n log 1 +
12
3, 500
3, 000
◆
✓
n = 740.00
t=
1, 000
n
m
300
F = 1, 300
m=2
i(2) = 0.12
j=
n
i(2)
0.12
=
= 0.06
2
2
t
F = P (1 + j)n
1, 300 = 1, 000(1 + 0.06)n
1.3 = (1.06)n
log(1.3) = log(1.06)n
log(1.3) = n log(1.06)
n=
log 1.3
= 4.503
log(1.06)
300
n=5
t=
n
m
=
5
2
= 2.5
1, 000
300
=
740
12
= 61.67
12%
n
n=5
n = 4.503
F = 15, 000
P = 10, 000
t = 10
m=2
n = mt = (2)(10) = 20
i(2)
F = P (1 + j)n
15, 000 = 10, 000(1 + j)20
15, 000
= (1 + j)20
10, 000
1.5 = (1 + j)20
1
(1.5) 20 = 1 + j
1
(1.5) 20
1=j
j = 0.0205
i(m)
m
i(2)
0.0205 =
2
(2)
i = (0.0205)(2)
j=
i(2) = 0.0410
4.10%
t
F = 2P
t = 10
s
m=4
n = mt = (4)(10) = 40
i(4)
F = P (1 + j)n
2P = P (1 + j)n
2 = (1 + i)40
(2)1/40 = 1 + j
(2)1/40
1=j
j = 0.0175
1.75%
i(4)
m
i(4)
0.0175 =
4
(4)
i = (0.0175)(4)
j=
i(4) = 0.070
•
7.00%
•
•
i(1)
i(4) = 0.10
m=4
i(1)
F1 = F2
P (1 + i(1) )t = P
i(4)
1+
m
!mt
P
(1 + i(1) )t =
i(4)
1+
m
!mt
1
t
(i)
(1 + i ) =
i
(i)
=
✓
✓
0.10
1+
4
0.10
1+
4
◆4
◆4
1 = 0.103813
10.38%
j
j = (1.025)4
F1 = F 2
P
t
t=1
t
i(12) = 0.12
i(1) =
m = 12
m=1
P
P
t
t
F1
F2
P
F1 = F2
!(1)t
!12t
i(12)
=P 1+
12
! ✓
◆
i(1)
0.12 12
1+
= 1+
1
12
i(1)
1+
1
i(1) = (1.01)12
1
i(1) = 0.126825%
i(2) = 0.08
i(4) =
m=2
m=4
P
P
t
t
1
F1
F2
P
F1 = F 2
!(4)t
!(2)t
i(2)
=P 1+
2
!4 ✓
◆
i(4)
0.08 2
1+
= 1+
4
2
!4
i(4)
1+
= (1.04)2
4
i(4)
1+
4
i(4)
4
(4)
i
1+
4
i(4)
1+
4
i(4)
4
(4)
i
4
i(4)
1+
= [(1.04)2 ](1/4)
= (1.04)1/2
= 1.019804
= 1.019804
1
= 0.019804
= (0.019804)(4)
i(4) = 0.079216%
i(12) = 0.12
i(2) =
F1
m = 12
m=2
P
P
t
t
F2
P
F1 = F2
!(2)t
!(12)t
i(12)
=P 1+
12
!2 ✓
◆
i(2)
0.12 12
1+
= 1+
2
12
!2
i(2)
1+
= (1.01)12
2
i(2)
1+
2
i(2)
42
i(2)
1+
2
(2)
i
1+
2
(2)
i
2
i(2)
2
i(2)
1+
i
F = 2, 000, P = 1, 750, m = 2, t =
j
(2)
= [(1.01)12 ](1/2)
= (1.01)6
= 1.061520
= 1.061520
1
= 0.061520
= (0.061520)(2)
= 0.12304
12.304%
i(m)
j = 0.016831504
1.68%, i(m) = 0.033663008
i(m)
F = 100, 000, P = 10, 000, t =
j = 0.024275
F = 30, 000, P = 10, 000, i(m) = 16%
2.43%, i(m)
j
n
j
= 0.2913
,t = 7
j
j = 0.06, n = 7
29.13%
t
j = 0.04, n = 28
F = 18, 000, P = 12, 000, i(m) = 12%
3.37%
n
t
, t = 3.48
j
j
j
P
•
•
•
•
t
R
•
•
F
P
•
•
P
0
R
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
5
F
R
···
···
n
P
0
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
F
3, 000
1
2
3
4
5
6
6
R = 3, 000
t=6
=1
P
0
R
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
5
•
F
R
···
···
n
•
R = 3, 000
t=6
i(12) = 0.09
m = 12
0.09
j=
= 0.0075
12
F
0
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
1
2
3
4
5
6
t=6
0
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
1
2
3
4
5
6
3, 000
3, 000(1 + 0.0075)
3, 000(1 + 0.0075)2
3, 000(1 + 0.0075)3
3, 000(1 + 0.0075)4
3, 000(1 + 0.0075)5
3, 000
= 3, 000
(3, 000)(1 + 0.0075) = 3, 022.5
(3, 000)(1 + 0.0075)2 = 3, 045.169
(3, 000)(1 + 0.0075)3 = 3, 068.008
(3, 000)(1 + 0.0075)4 = 3, 091.018
(3, 000)(1 + 0.0075)5 = 3, 114.20
F = 18, 340.89
t=1
t=2
t=3
3, 000 ⇥ 6 = 18, 000
t=1
t=2
F
0
R
R
1
2
···
···
F
R
R
n
1
n
R
R(1 + j)
R(1 + j)n
2
R(1 + j)n
1
F = R + R(1 + j) + R(1 + j)2 + · · · + R(1 + j)n
2
+ R(1 + j)n
1
1+j
F (1 + j) = R(1 + j) + R(1 + j)2 + R(1 + j)3 + · · · + R(1 + j)n
F (1 + j)
F = R(1 + j)n
R
F [(1 + j)
1] = R[(1 + j)n
1]
F (j) = R[(1 + j)n
1]
F =R
(1 + j)n
j
j
sn
R
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
5
F = Rsn = R
+ R(1 + j)n
1
1
0
R
j
n
(1 +
j)n
1
(1 + j)n
j
···
···
1
,
s
R
n
n
(1 + j)n 1
j
(1 + 0.0075)6
= 3, 000
0.0075
= 18, 340.89
F =R
1
F
R = 200
m = 12
i(12) = 0.250% = 0.0025
0.0025
j=
= 0.0002083
12
t=6
n = tm = 6(12) = 72
F
(1 + j)n 1
j
(1 + 0.0002083)72
= 200
0.0002083
= 14, 507.02
F =R
1
R = 3, 000
t=6
i(12) = 0.09
m = 12
0.09
j=
= 0.0075
12
P
F
P =
1+
0
3, 000(1.0075)
1
3, 000(1.0075)
2
3, 000(1.0075)
3
3, 000(1.0075)
4
3, 000(1.0075)
5
3, 000(1.0075)
6
i(m)
m
!mt =
3, 000
= 3, 000(1.0075) t .
1.0075t
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
3, 000
1
2
3
4
5
6
(3, 000)(1.0075)
1
= 2, 977.667
(3, 000)(1.0075)
2
= 2, 955.501
(3, 000)(1.0075)
3
= 2, 933.50
(3, 000)(1.0075)
4
= 2, 911.663
(3, 000)(1.0075)
5
= 2, 889.988
(3, 000)(1.0075)
6
= 2, 868.474
P = 17, 536.79
P =
F
=
(1 + j)n
F
18, 340.89
!tm = ✓
◆ = 17, 536.79.
.09 6
i(m)
1+
1+
12
m
F = P (1 + j)n
P =
F
(1 + j)n
P
P =
0
R(1 + j)
1
R(1 + j)
2
R(1 + j)
F
= F (1 + j)
(1 + j)n
R
R
1
2
···
···
n
R
n
.
R
1
n
(n 1)
R(1 + j)
n
P = R(1 + j) 1 + R(1 + j) 2 + · · · + R(1 + j) (n 1) + R(1 + j) n
R
R
R
R
R
P =
+
+
+ ··· +
+
(1 + j)1 (1 + j)2 (1 + j)3
(1 + j)n 1 (1 + j)n
1
1+j
P
R
R
R
R
=
+
+ ··· +
+
2
3
n
1+j
(1 + j)
(1 + j)
(1 + j)
(1 + j)n+1
1
R
R
=
1+j
1 + j (1 + j)n
◆
✓
◆
1
R
1
=
1
1+j
1+j
(1 + j)n
✓
◆
1+j 1
R
=P
=
1
1+j
1+j
✓
◆
j
R
P
=
1 (1 + j) n
1+j
1+j
P
✓
P 1
P
Pj = R 1
P =R
1
(1 + j)
j
1
n
n
(1 + j)
(1 + j)
j
(1 + j)
n
n
an
a
P
P = Ran = R
F =R
1
(1 + j)
j
(1 + j)n
j
1
n
.
.
P =
F
(1 + j)n
n
R (1+j)j 1
F
(1 + j)n
P =
=
=R
n
n
(1 + j)
(1 + j)
j
1
(1 + j)
n
=R
1
(1 + j)
j
n
.
n
0
R
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
5
P = Rn = R
1
(1 + j)
j
···
···
n
,
R
j
n
P
(1 + j) n
j
1 (1 + 0.0075)
= 3, 000
0.0075
= 17, 536.79
P =R
= 200, 000
R = 16, 200
i(12) = 0.105
0.105
j=
= 0.00875
12
t=5
n = mt = 12(5) = 60
1
6
R
n
P =?
16, 200
16, 200
16, 200
1
2
3
0
16, 200
···
(1 + j) n
j
1 (1 + 0.00875)
= 16, 200
0.00875
= 753, 702.20
P =R
···
60
1
=
60
+
= 200, 000 + 753, 702.20
= 953, 702.20
P = 100, 000
i(1) = 0.08
m=1
j = 0.08
t=3
n = mt = 1(3) = 3
R
P = 10, 000
0
R =?
R =?
R =?
1
2
3
P =R
1
(1 + j)
j
n
R=
=
P
1 (1+j)
j
n
100, 000
1 (1+0.08)
0.08
3
= 38, 803.35
F = Rsn = R
(1 + j)n
j
P = Ran = R
P
1
1
(1 + j)
j
n
F
0.2
365
30
30 ⇥ 365
•
12%
10%
=
=
•
•
•
0
R
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
5
···
···
R
n
j
0
R
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
5
F =R
(1 + j)n
j
1
···
···
F
R
n
,
R
j
n
R = 1, 000
n = 12(15) = 180
i(4) = 0.06
m=4
F
0
1, 000
1, 000
1, 000
1
2
3
···
···
1, 000
F
1, 000
179
180
P
i(12)
1+
12
i(12)
1+
12
F1 = F2
!12t
!12t
i(12)
1+
12
1+
!12
!4t
i(4)
=P 1+
4
!4t
i(4)
= 1+
4
= (1.015)4
i(12)
= [(1.015)4 ]1/12
12
i(12)
= (1.015)1/3 1
12
i(12)
= 0.004975 = j
12
(1 + j)n 1
j
(1 + 0.004975)180
= 1, 000
0.004975
= 290, 076.28
F =R
R = 5, 000
n = 2(10) = 20
i(12) = 0.25% = 0.0025
m = 12
F
1
0
5, 000
5, 000
5, 000
1
2
3
P
···
5, 000
5, 000
19
20
···
F1 = F2
!2t
!12t
i(12)
=P 1+
12
!2
!12
i(2)
i(12)
1+
= 1+
2
12
!2
i(2)
1+
= (1.00020833)12
2
i(2)
1+
2
1+
i(2)
= [(1.00020833)12 ]1/2
2
i(2)
= (1.00020833)6 1
2
i(2)
= 0.00125063 = j
2
(1 + j)n 1
j
(1 + 0.00125063)20
= 5, 000
0.00125063
= 101, 197.06
F =R
1
j
P
0
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
P =R
1
···
5
(1 + j)
j
R
···
n
n
,
R
j
n
R = 38, 973.76
i(4) = 0.08
m=4
n=3
P
P =?
0
R = 38, 973.76
R = 38, 973.76
R = 38, 973.76
1
2
3
P
F 1 = F2
!(1)t
!4t
i(4)
=P 1+
4
! ✓
◆
i(1)
0.08 4
1+
= 1+
1
4
i(1)
1+
1
i(1)
= (1.02)4 1
1
i(1)
= j = 0.082432 = 8.24%
1
j
(1 + j) n
j
1 (1 + 0.082432)
= 38, 973.76
0.082432
P =R
1
= 100, 000.00
R = 3, 000
i(2) = 0.09
m=2
n=6
P
3
P
i(12)
1+
12
F1 = F2
!(12)t
i(12)
1+
12
i(12)
1+
12
1+
!12
!12
!(2)t
i(2)
=P 1+
2
✓
◆
0.09 2
= 1+
2
= (1 + 0.045)2
i(12)
= [(1.045)2 ]1/12
12
i(12)
= (1.045)1/6 1
12
i(12)
= 0.00736312 = j
12
j
◆
(1 + j) n
j
✓
1 (1 + 0.00736312)
= 3, 000
0.00736312
P =R
✓
1
= 17, 545.08
6
◆
50, 000
1, 000, 000
0
1
2
3
···
20
50, 000
40, 000
40, 000
40, 000
40, 000
0
1
2
3
···
···
20
t=0
P = F (1 + j)
n
= 1, 000, 000(1 + 0.05)
= 783, 526.17
= 50, 000 + 783, 526.17
= 833, 526.17
5
P
F1 = F2
!(4)(t)
!(1)(t)
i(1)
=P 1+
1
!4 ✓
◆
i(4)
0.05 1
1+
= 1+
4
1
i(4)
1+
4
1+
i(4)
= (1.05)1/4
4
i(4)
= (1.05)1/4
4
i(4) = 0.012272
1
(1 + j) n
j
1 (1 + 0.012272)
= 40, 000
0.012272
= 705, 572.68
P =R
1
=
20
+
= 50, 000 + 705, 572.68
= 755, 572.68
833, 526.17
755, 572.68 = 77, 953.49
t=5
F = P (1 + j)n
= 50, 000(1 + 0.05)5
= 63, 814.08
= 63, 814.08 + 1, 000, 000
= 1, 063, 814.08
(1 + j)n 1
j
(1 + 0.012272)20
= 40, 000
0.012272
= 900, 509.40
F =R
1
= 63, 814.08 + 900, 509.40
= 964, 323.48
1, 063, 814.08
964, 323.48 = 99, 490.60.
P = 99, 490.60(1 + 0.05) 5 = 77, 953.49
0
1
0
2
1
3
2
4
···
···
3
P1 = F (1 + j)
5
20
n
= 150, 000(1 + 0.04)
6
= 118, 547.18
P2 = F (1 + j)
n
= 300, 000(1 + 0.04)
10
= 202, 669.25
= P1 + P2
= 118, 547.18 + 202, 669.25
= 321, 216.43
P
i(4)
1+
4
F1 = F2
!4(5)
i(4)
1+
4
1+
!20
!2(5)
i(2)
=P 1+
2
✓
◆
0.08 10
= 1+
2
i(4)
= (1.04)1/2
4
i(4)
= (1.04)1/2 1
4
i(4)
= 0.019803903
4
(1 + j) n
j
1 (1 + 0.019803903)
= 25, 000
0.019803903
= 409, 560.4726
P =R
P
1
F
20
•
•
15, 000 = 2, 000
1
(1 + j)
j
8
j
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
P
0
R
R
R
R
R
1
2
3
4
5
P = Ran = R
1
···
R
···
n
n
(1 + j)
j
,
R
j
n
R = 2, 500
i(12) = 0.09
t=1
m = 12
P
P =?
2, 500
2, 500
1
2
0
···
···
R
n
i(12)
0.09
=
= 0.0075
m
12
n = mt = 12(1) = 12
j=
P = Ran = 2, 500
1
(1 + 0.0075)
0.0075
12
= 28, 587.28.
n
j
P =?
0
2, 500
2, 500
···
R
···
R
···
1
2
3
4
5
2, 500
2, 500
2, 500
2, 500
2, 500
1
2
3
4
5
P 0 =?
0
···
P0
P 0 = Ran = R
1
P ⇤ = Ran = R
(1 + j)
j
1
P = P0
(1 + j)
j
n
= 2, 500
1
n
= 2, 500
P ⇤ = 35, 342.49
(1 + 0.0075)
0.0075
1
(1 + 0.0075)
0.0075
15
= 35, 342.49
3
= 7, 388.89
7, 388.89 = 27, 953.60
R⇤
k
0
R⇤
R⇤
1
2
···
R⇤
R
R
k
k+1
k+2
R
R
k+1
k+2
···
···
R
···
k+n
P
0
1
2
P = Rak+n
R
i
n
k
···
Rk = R
k
1
(1 + j)
j
(k+n)
R
1
···
···
(1 + j)
j
R
k+n
k
,
R = 10, 000
i(4) = 0.08
t=5
m=4
P
k = mt = 4(20) = 80
n = mt = 4(5) = 20
i(4)
0.08
j=
=
= 0.02
m
4
P
0
1
P = Rak+n
···
2
80
10, 000
10, 000
81
82
(1 + j) (k+n)
1
R
j
1 (1 + 0.02) 100
= 10, 000
0.02
= 33, 538.38
Rak = R
1
10, 000
···
100
k
(1 + j)
j
10, 000
···
1
(1 + 0.02)
0.02
80
R = 4, 000
i(12) = 0.10
t=2
m = 12
P
k=2
n = mt = 12(2) = 24
i(12)
0.10
j=
=
= 0.00833
m
12
k + n = 2 + 24 = 26
P
0
1
2
4, 000
4, 000
3
4
···
···
4, 000
26
(1 + j) (k+n)
1 (1 + j) k
R
j
j
26
1 (1 + 0.00833)
1 (1 + 0.00833)
= 4, 000
4, 000
0.00833
0.00833
= 85, 260.53
P =R
1
2
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
= 30, 000, 000
= 700, 000
=
=
30, 000, 000
700, 000
= 42.86
= 3%
= 500
= 200
15
⇥ 200
500 ⇥ 0.03 =
= 3, 000.
15
⇥
=
⇥
= 0.03(500)(200)
= 3, 000
= 8
= 12
= 52
= 95
=
=
8
=
52
= 0.1538 = 15.38%
=
12
95
= 0.1263 = 12.63%
•
•
•
•
r
P
•
F
P =F
P <F
P >F
•
•
F = 300, 000
r = 10%
300, 000(0.10) = 30, 000
30, 000
1
2
= 15, 000
F = 100, 000
r = 5%
= 10
= 2(10) = 20
= 4%
100, 000
0.05
2
= 2, 500
t = 10
P =
F
100, 000
=
= 67, 556.42
n
(1 + j)
(1 + 0.04)10
1
(1 + 0.04) =
i(2)
1+
2
!2
i(2)
= 0.019804
2
P =R
1
(1 + j)
j
n
= 2, 500
1
(1 + 0.019804)
0.019804
20
= 40, 956.01,
= 67, 556.42 + 40, 956.01 = 108, 512.43.
=
⇥
⇥
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
57.29
57.19
•
•
•
•
0.10 =
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
P = 1, 000, 000
j = 0.07
n=1
F
F = P (1 + j)n = 1, 000, 000(1 + 0.07) = 1, 070, 000
P = 1, 200, 000
= 31, 000
= (31, 000)(12
)(5
= 1, 860, 000
= 1, 860, 000
= 660, 000
1, 200, 000
)
=(
)⇥(
)
(
)
= 0.20(3, 000, 000)
= 600, 000
=(
)
= 3, 000, 000
600, 000
= 2, 400, 000
(0.80)( 3, 000, 000) = 2, 400, 000.
P = 400, 000
i(12) = 0.09
i(12)
0.09
=
= 0.005
12
12
n = 36
j=
R
R=
1
P
(1 + j)
j
n
=
1
400, 000
(1 + 0.0075)
0.0075
36
= 12, 719.89
n
P
0
R
R
1
2
···
R
···
k
R
k
···
R
···
k +n1 k k + 2
k
R
Bk
k+n
Bk
p OBk
R = 11, 122.22
i(12) = 0.12
i(12)
0.12
=
= 0.01
12
12
k = 12
j=
n
k = 48
Bk = R
"
1
(1 + j)
j
(n k)
#
= 11, 122.22
1
(1.01)
0.01
48
= 422, 354.73
P = 3, 200, 000
i(12) = 0.12
i(12)
0.12
=
= 0.01
12
12
n = mt = (12)(20) = 240
j=
R
P =R
R=
1
P
(1 + j)
j
n
(1 + j) n
j
3, 200, 000
=
1 (1 + 0.01)
0.01
1
240
= 35, 234.76
P = 3, 200, 000
R = 35, 234.76
n = 240
240 ⇥ 35, 234.76 = 8, 456, 342.40.
=
= 8, 456, 342.40
3, 200, 000 = 5, 256, 342.40
P = 3, 200, 000
i(12) = 0.12
i(12)
0.12
=
= 0.01
12
12
n = mt = (12)(20) = 240
j=
R = 35, 234.76
B50 = R
1
(1 + j)
j
190
= 35, 234.76
1
(1 + 0.01)
0.01
190
= 2, 991, 477.63
P R51
P R51 = R
I50 = 35, 234.76
29, 914.78 = 5, 319.98
F = (1 + j)n = 100, 000, (1 + 0.08)3 = 251, 942.40
B3 = R
1
(1 + j)
j
2
= 26, 379.75
1
(1 + 0.10)
0.10
2
= 45, 783.04
B1 = R
1
(1 + j)
j
R=
1
R=
R=
B2 = R
1
(1 + j)
j
1
1
5
= 183, 026.37
P
(1 + j)
j
n
P
(1 + j)
j
P
(1 + j)
j
n
n
=
1
=
=
34
= 16, 607.15
1
1
1
1
5
(1.06)
0.06
= 770, 973.65
30, 000
(1 + 0.0075)
0.0075
750, 000
(1 + 0.02)
0.02
500, 000
(1 + 0.01)
0.01
(1 + 0.01)
0.01
= 2, 623.54
12
8
= 102, 382.35
36
= 16, 607.15
34
= 476, 669.63
I3 = i(P2 ) = (0.01)(476, 669.63) = 4, 766.00
P R51 = R
I50 = 16, 607.15
4, 766.7 = 11, 840.45
F = P (1 + j)n = 800, 000(1 + 0.08)2 = 933, 120
R=
R=
B6 = R
1
B8 = R
(1 + j)
j
1
P
(1 + j)
j
1
1
18
P
(1 + j)
j
n
n
=
=
300, 000
(1 + 0.025)
0.025
1
2
61
6
= 29, 994.20 6
4
(1 + j)
j
700, 000
(1 + 0.01)
0.01
1
12
= 32, 073.56
✓
0.10
1+
12
0.10
12
1
◆
(1.025)
0.025
48
20
18
= 18, 433.68
= 19, 244.14
3
7
7
7 = 499, 428.21
5
12
= 329, 003.03
P1 = R
1
P4 = R
(1 + j)
j
1
3
2
✓
61
6
= 11, 485.35 6
4
◆
3
3
7
7
7 = 33, 889.65
5
(1 + 0.08) 1
= 23, 190.42
0.08
I5 = j(P4 ) = (0.08)(23, 190.42) = 1, 855.23
P R5 = R I5 = 25, 045.65 1, 855.23 = 23, 190.42
(1 + j)
j
1
0.10
1+
12
0.10
12
= 25, 045.65
1
T
F
p
p
p1 , p2 , ...
p
q
r
s
t 3 + 2 = 5p
u f (x) =
v
w
p1
x
x+1
p
2
p2
p3
p4
p
p
q
r
r
s
s
t
3+2 = 5
t
22N
100 2 Z
⇡2
/Q
⇡2R
p
2<2
⇡
⇡
N⇢Z⇢Q⇢R
u
f
u
v
w
w
w
w
w
p
p1
2
p1
p2
p2
p3
p4
2x = 1
(x + y)2 = x2 + y 2
x
x
p
q
p
p
p
p
<·>
q
q
q
y
p r t
p
p1
p2
p3
p4
u
2
p1 p2 p3
p4
p1
r
p2
f
i
b
p3
h
g
p4
d
l
p1
p2
p3
p4
p
2
r
f
i
h
d
b
g
l
l
d
2.5
p
p
T
F
p
q
p
q
p
22
q
p q
23
=8
=4
r
p
p
q
T
T
T
F
F
T
F
F
q
p
q
r
T
T
T
T
T
F
T
F
T
T
F
F
F
T
T
F
T
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
2n
n
⇠
p
⇠p:
p, )
p
T
F
p
⇠p
n1
n2
n3
n4
p(x) =
2
x 1
x+2
⇠p
F
T
⇠p
p
⇠ n1
p(x) =
⇠ n2
2
x 1
x+2
p(x) =
x 1
x+2
2
⇠ n3
⇠ n4
⇠ n2
⇠ p
⇠p
n2
⇠p
p
^
p
q
p ^ q : (p
p
p
q, )
p^q
p
q
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
F
T
q
p^q
p
q
p
q
p
q
⇡>3
p^q
p ^ (⇠ q)
⇡3
⇡>3
p^q
⇡>3
p ^ (⇠ q)
⇡3
⇡3
(⇠ p) ^ (⇠ q)
(⇠ p) ^ q
q
⇠q
q:
p ^ (⇠ q)
p^q
(⇠ p) ^ (⇠ q)
p^q
p
p:
_
p
q
p _ q : (p
p
q, )
p_q
p
q
T
T
T
F
T
F
T
T
F
F
F
T
q
p_q
p_q
p q
r
p
q
r
p_q
q _ (⇠ r)
p _ (q _ r)
p
p
q
q
p_q
q _ (⇠ r)
p _ (q _ r)
(p _ q) _ r
(p ^ q) _ r
p _ (q ^ r)
(p ^ q) _ (p ^ r)
p _ (q _ r)
(p _ q) _ r
p _ (q _ r)
(p _ q) _ r
p_q_r
p ^ (q ^ r)
(p ^ q) ^ r
p^q^r
p q
r
(⇠ p) _ (q ^ r)
r
q^r
q
p
(⇠ p) _ (q ^ r)
(⇠ p)
p
q
r
F
F
T
⇠p
T
q^r
F
(⇠ p) _ (q ^ r)
T
p
q
p ! q : ( p,
p!q
q, )
p!q
p
q
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
T
F
F
T
T
p
q
q
p1
p2
p3
p1
p1
p2
p2
p3
p3
p
p!q
p
p!q
q
p
q
p!q
p!q
p!q
p!q
p
q
2>0
2>0
p!q
2<0
2
2>0
2>0
2<0
2<0
2>0
p
q
p $ q : (p
q, )
p$q
p
q
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
T
T
p
q
p
q
p
q
p1
p2
p3
p1
p1
p2
p3
p3
p q
p
q
r
s
r
p ^ (⇠ q)
p ^ (⇠ p)
⇠ (q _ r)
((⇠ p) _ q) ^ r
(p ^ (⇠ q)) _ (r ^ s)
⇠ (q ! r)
(p ^ (⇠ q)) ! (r ^ s)
p $ (⇠ p)
((⇠ p) ! q) $ r
p
q
r
s
T
F
T
T
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
⇠p
p
p
p
p
p
p
p^q
q
p_q
q
p!q
q
p$q
q
q
p
q
(p ! q) ^ (q ! p)
p
q
p
p
q
T
T
T
F
F
T
F
F
q
(p ! q)
p!q
q!p
F
F
T
F
T
T
F
F
F
T
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
(q ! p)
T
(p ! q) ^ (q ! p)
p!q
q!p
(p ! q) ^ (q ! p)
F
F
T
F
F
T
T
F
F
F
F
T
T
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
T
T
(p ! q) ^ (q ! p)
p$q
(p ! q) ^ (q ! p)
p$q
F
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
F
T
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
T
$
[(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)] ! [(p _ q) ! r]
(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)
(p _ q) ! r
p, q
r
23 = 8
p, q
p, q
r
r
(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)
p!r q!r
(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)
p!r
q!r
(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)
F
F
F
F
F
T
T
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
F
T
T
T
T
T
F
T
F
T
F
F
F
F
T
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
T
T
p
q
r
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
(p_q) ! r
(p _ q) ! r
p_q
p!r
q!r
(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)
p_q
(p _ q) ! r
F
F
F
F
T
F
F
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
T
F
F
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
F
T
F
T
F
F
T
F
F
F
T
T
T
T
F
T
F
F
F
T
T
T
F
T
p
q
r
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
s : [(p !
r) ^ (q ! r)] ! [(p _ q) ! r]
p!r
q!r
(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)
p_q
(p _ q) ! r
T
T
F
F
F
F
T
F
T
F
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
T
F
T
F
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
F
T
F
T
F
F
T
F
T
F
F
T
T
T
T
F
T
T
F
F
F
T
T
T
F
T
T
p
q
r
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
s
T
[(p ! r) ^ (q ! r)] ! [(p _ q) ! r]
p, q,
r
⌧
p
q
p_⌧
p^
p ! (p _ q)
(p ^ (⇠ q)) ^ (p ^ q)
⌧
T
p_⌧
p
p
⌧
T
T
F
T
p_⌧
T
T
F
p^
p
p
p ! (p _ q)
(p^ ⇠ q) ^ (p ^ q)
p
T
F
F
F
p^
p^
F
F
q
p_q
p ! (p _ q)
F
T
T
F
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
T
p
q
⇠q
p ^ (⇠ q)
p^q
(p ^ (⇠ q)) ^ (p ^ q)
F
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
p
q
T
T
T
F
((p ! q) ^ q) ! p
((p ! q) ^ (⇠ p)) !⇠ q
((p _ q) ^ p) ! (⇠ q)
(p ! q) ! (q ! p)
(⇠ (p ^ q) ^ (⇠ p)) ! q
(p ! q) ! ((⇠ p) ! (⇠ q))
(p ^ q) ! p
p ! (p _ q)
(p ^ q) ! (p ^ q)
((p ! q) ^ p) ! q
((p ! q) ^ (⇠ q)) !⇠ p
((p ! q) ^ (q ! r)) ! (p ! r)
((p _ q) ^ (⇠ p)) ! q
((⇠ p) ! ) ! p
((p ! r) ^ (q ! r)) ! ((p _ q) ! r)
F
T
F
(p ! q) ^ (q ! p)
p$q
p
(p ! q) ^ (q ! p)
p$q
F
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
F
T
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
p,q
q
p,q
p$q
T
p
(p ! q) , [(⇠ p) _ q]
q
(p ! q)
(⇠ p) _ q
p!q
⇠p
(⇠ p) _ q
F
F
F
F
F
T
T
T
T
F
F
T
T
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
F
(p ! q)
(p ! q) , [(⇠ p) _ q]
T
(⇠ p) _ q
(p ! q) $ [(⇠ p) _ q]
p!q
⇠p
(⇠ p) _ q
(p ! q) $ [(⇠ p) _ q]
F
F
F
F
T
F
T
T
T
T
T
F
F
T
T
T
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
F
T
T
(p ! q) $ [(⇠ p) _ q]
p q
r
(p ^ ⌧ ) , p
(p _ ) , p
(p _ ⌧ ) , ⌧
(p ^ ) ,
(p _ [⇠ p]) , ⌧
(p ^ [⇠ p]) ,
(p _ p) , p
⇠ (⇠ p) , p
(p ^ p) , p
p _ (q _ r) , (p _ q) _ r
p ^ (q ^ r) , (p ^ q) ^ r
p _ (q ^ r) , (p _ q) ^ (p _ r)
p ^ (q _ r) , (p ^ q) _ (p ^ r)
p _ (p ^ q) , p
p ^ (p _ q) , p
p_q ,q_p
⇠ (p _ q) , (⇠ p) ^ (⇠ q)
p^q ,q^p
⇠ (p ^ q) , (⇠ p) _ (⇠ q)
⇠ (p ! q) , [p ^ (⇠ q)]
⇠ (p ! q)
,
,
,
p
q
p ! q q ! p ⇠ p !⇠ q
p ^ (⇠ q)
⇠ (p ! q)
p ^ (⇠ q)
⇠ (p ! q)
⇠ ((⇠ p) _ q)
⇠ (⇠ p) ^ (⇠ q)
p ^ (⇠ q)
⇠ q !⇠ p
p!q
q!p
⇠p
⇠q
⇠ p !⇠ q
⇠ q !⇠ p
F
F
T
F
T
T
F
F
T
T
F
T
F
F
T
F
F
T
T
T
T
T
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
T
F
F
T
T
(p ! q) ,⇠ q !⇠ p
q)
(q ! p) , (⇠ p !⇠
p
q
p!q
q!p
⇠ q !⇠ p
⇠ p !⇠ q
(p ! q) ,⇠ q !⇠ p
,
⇠ q !⇠ p
⇠ (⇠ q)_ ⇠ p
,
q_ ⇠ p
,
p!q
,
⇠p_q
(q ! p) , (⇠ p !⇠ q)
,
⇠ (⇠ p) _ (⇠ q))
,
p ^ (⇠ q)
,
q!p
,
p!q:
⇠ p !⇠ q
(⇠ q) ^ p
q ! p :
⇠ q !⇠ p :
⇠ p !⇠ q :
(⇠ q !⇠ p)
p!q
p!q
p
⇠p
q
⇠q
⇠ (p _ ((⇠ p) ^ q)) , ((⇠ p) ^ (⇠ q))
((p ^ q) ! (p _ q)) , ⌧
⇠ (p ! (⇠ q)) , (p ^ q)
,
,
,
⇠ (p ! (⇠ q))
⇠ (⇠ p_ ⇠ q)
⇠ (⇠ p)^ ⇠ (⇠ q)
p^q
(p ! (q ^ r)) , ((p ! q) ^ (p ! r))
,
,
,
(p ! (q ^ r))
⇠ p _ (q ^ r)
(sin p _ q) ^ (⇠ p _ r)
((p ! q) ^ (p ! r))
(p _ q) , ((⇠ p) ! q)
⇠ (p ! q) , (p ^ (⇠ q))
((p ! r) ^ (q ! r)) , ((p _ q) ! r)
((p ! q) _ (p ! r)) , (p ! (q _ r))
((p ! r) _ (q ! r)) , ((p ^ q) ! r)
(p1 ^ p2 ^ . . . ^ pn ) ! q.
p1 , p2 , . . . , pn
q
p1
p2
pn
)q
p1 :
p2 :
q:
(p1 ^ p2 ) ! q,
p1
p2
)q
A0
A
A0
p!q
q
)p
A
p!q
p
)q
A
p!q
p
q
p!q
p
p
q
p!q
p!q
p
q
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
T
F
F
T
T
A
A0
p!q
q
p
p!q
q
p!q
q
p
p!q
p
q
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
T
F
F
T
T
A0
p!q
q
)p
!
)
q
p1 , p2 , . . . , pn
(p1 ^ p2 ^ . . . ^ pn ) ! q
((p ! q) ^ p) ! q
((p ! q) ^ p) ! q
p!q
(p ! q) ^ p
((p ! q) ^ p) ! q
F
F
F
T
F
T
T
F
T
F
F
T
F
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
T
((p ! q) ^ p) ! q
((p ! q) ^ p) ! q
p!q
p
)q
T
p q
r
(p ^ q) ! p
p ! (p _ q)
(p ^ q) ! (p ^ q)
((p ! q) ^ p) ! q
p^q
)p
p
)p_q
p
q
)p^q
p!q
p
)q
((p ! q) ^ (⇠ q)) !⇠ p
p!q
⇠q
((p ! q) ^ (q ! r)) ! (p ! r)
p!q
q!r
((p _ q) ^ (⇠ p)) ! q
p_q
⇠p
((⇠ p) ! ) ! p
((p ! r) ^ (q ! r)) ! ((p _ q) ! r)
)⇠ p
)p!r
)q
(⇠ p) !
)p
p!r
q!r
) (p _ q) ! r
p:
q:
p!q
⇠q
)⇠ p
p:
q:
p^q
)p
p:
q:
p
) p _ q,
p:
q:
r:
p!q
q!r
)p!r
(p1 ^ p2 ^ . . . ^ pn ) ! q,
p1 , p2 , . . . , pn
q
(p1 ^ p2 ^ . . . ^ pn ) ! q
((p ! q) ^ q) ! p
((p ! q) ^ q) ! p
p!q
(p ! q) ^ q
((p ! q) ^ q) ! p
F
F
F
T
F
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
T
T
p!q
q
p
p
p
p
q
F
T
p!q
T
q
q
(p ! q) ^ q
T
p!q
q
)p
((p ! q) ^ q) ! p
F
A0
B0
p q
r
((p ! q) ^ q) ! p
((p ! q) ^ (⇠ p)) ! (⇠ q)
((p _ q) ^ p) ! (⇠ q)
(p ! q) ! (q ! p)
(⇠ (p ^ q) ^ (⇠ p)) ! q
(p ! q) ! ((⇠ p) ! (⇠ q))
p!q
q
)p
p!q
⇠p
)⇠ q
p_q
p
)⇠ q
p!q
)q!p
⇠ (p ^ q)
⇠p
)q
p!q
) (⇠ p) ! (⇠ q)
p:
q:
p_q
p
)⇠ q
[(p _ q) ^ p] !⇠ q
p
q
p
q
⇠q
⇠q
p
q
T
T
⇠q
F
[(p _ q) ^ p]
q
p_q
T
(p _ q) ^ p
T
[(p _ q) ^ p] !⇠ q
F
p_q
⇠q
)p
(p ^ q) , (q ^ p)
q_p
⇠q
)p
⇠ (p ^ q)
⇠p
)q
p
p
q
p
q
p
F
⇠p
T
q
F
p^q
F
⇠ (p ^ q)
T
⇠ (p ^ q)^ ⇠ p
T
[⇠ (p ^ q)^ ⇠ p] ! q
F
p!q
p
)q
p!q
p
q
(p ^ q) ! r
p^q
)r
(p ^ q) ! r
r
)p^q
p !⇠ q
q
)⇠ p
p !⇠ q
⇠p
)q
(p ^ (⇠ q)) ! r
s!p
q ! (⇠ u)
u^s
)r
(((p ^ (⇠ q)) ! r) ^ (s ! p) ^ (q ! (⇠ u)) ^ (u ^ s)) ! r
24 = 16
p ! (r ^ s)
⇠r
)⇠ p
⇠p
⇠r
⇠p
p ! (r ^ s)
(⇠ r) _ (⇠ s)
⇠r
⇠r
⇠ (r ^ s)
[(⇠ r) _ (⇠ s)] ,⇠ (r ^ s)
⇠r
(⇠ r) _ (⇠ s)
⇠ (r ^ s)
p ! (r ^ s)
⇠p
(p ^ r) ! (⇠ q)
(⇠ q) ! r
⇠r
)⇠ (p ^ r)
(p ^ r) ! (⇠ q)
(⇠ q) ! r
⇠r
⇠r
(p ^ r) ! r
⇠ (p ^ r)
(p ^ r) ! (⇠ q)
(⇠ q) ! r
(p ^ r) ! r
⇠r
⇠ (p ^ r)
(p ^ r) ! r
⇠ r
(⇠ q) ! r
⇠ r
⇠ (⇠ q)
⇠ (p ^ r)
(p ^ r) ! (⇠ q)
⇠r
(⇠ q) ! r
⇠ (⇠ q)
(p ^ r) ! (⇠ q)
⇠ (p ^ r)
p_r
(⇠ r) _ (⇠ s)
s
)p
s
⇠ r_ ⇠ s
⇠s
s
p_r
s
⇠ (⇠ s)
(⇠ r) _ (⇠ s)
⇠r
p_r
p
p
⇠r
p_r
⇠p!r
(⇠ r)_(⇠ s)
r !⇠ s
p_r
⇠p!r
(⇠ r) _ (⇠ s)
r !⇠ s
⇠ p !⇠ s
s
⇠ (⇠ s)
⇠ (⇠ p)
p
b, e, c, d
b:
e:
c:
d:
b!e
c!d
b_c
)e_d
b_c
⇠ (⇠ b) _ c
(⇠ b) ! c
c!d
(⇠ b) ! d
b!e
(⇠ e) ! (⇠ b)
(⇠ e) ! d
(b ! e) , (⇠ e) ! (⇠ b)
⇠ (⇠ e) _ d
e_d
p!q
r!s
p_r
)q_s
t:
d:
s:
t_d
t!s
)d!s
d ! s
t_d
d
s
d
s
t
t!s
t
t
d
s
F
T
F
t_d
T
p_q
⇠q
)p
p_q
⇠q
p
t!s
T
d!s
F
p_q
⇠q
((p _ q)^ ⇠ q)
((p _ q)^ ⇠ q) ! p
F
T
T
T
T
F
T
T
F
F
T
F
F
F
T
F
T
p
q
T
T
T
T
F
F
T
((p _ q)^ ⇠ q) ! p
p
p
q
p_q
p_q
⇠q
q
⇠ (p _ q) ^ (p _ q) ,
m
m = 2k
m
m = 2k
k
m
y
m = 2k
x+y
k
k
x
x
x
y
x = 2k1
y = 2k2
x + y = 2k1 + 2k2 = 2(k1 + k2 )
k1
k2
k1 + k2
x+y
ABCD mA = 90
mB = 90
mC = 85
ABCD
ABCD
D
= 90
360
mA + mB + mC + mD = 360 .
90 + 90 + 85 + mD = 360 .
mD = 95
ABCD
A
B
B
D
ABCD
C
A
mA + mB + mC + mD = 360 ,
90 + 90 + mC + 90 = 360
mC = 90
85
C
ABCD
ABCD
(p _ q) ! r
q
p_q
q
) r
r
(p ^ q) ! r
q
p, r
q
) r
p ! (q ^ r)
) (p ! q) ^ (p ! r)
(⇠ p _ q) ^ (⇠ p _ r)
p ! (q ^ r)
(p ! q) ^ (p ! r)
⇠ p _ (q ^ r)
p ! (q _ r)
r!s
p, q
)p!s
p ! (r _ t)
⇠r
)⇠ p
⇠p
(p _ q) ! r
⇠r
)⇠p
⇠r
⇠ r_ ⇠ t
⇠ (r ^ t)
r, s
⇠r
⇠p
⇠ (p _ q)
⇠ p^ ⇠ q
(p ^ q) ! r
⇠r
p
q, r
)⇠p
m
6
3
3
n = 6k
k
n
m = 3k
k
n
k
6
m
6
6
2k
m = 3k
3
n = 6k
k
m = 6k
3
m
a, b
k
3
c
p
a2 + 62 = (6 2)2
m = 3 · (2k)
a2 + b2 = c2 ABC
p
6 2
ABC
a=6
ABCD
Shirlee R. Ocampo is an Assistant Professor 7 at the De La Salle University, and has been teaching mathematics and statistics courses for about 20 years. She finished B.S. Mathematics for Teachers at the Philippine
Normal University, and M.S. Mathematics at the De La Salle University. She has earned academic units in
Ph.D. Statistics at the University of the Philippines Diliman. She worked as a research proponent and statistician on several projects in education and statistics, a module writer and a book author of high school and
college mathematics and statistics books, and an item writer and evaluator for some standardized tests and
assessment tools. She has served as a mentor on senior high school core courses such as General Mathematics
and Probability and Statistics.