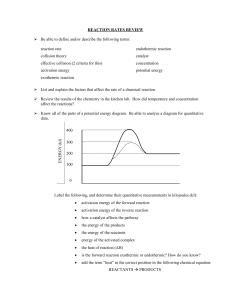
C6 Energy changes in chemical reactions C6 Energy changes in chemical reactions 1 Describe the meaning of exothermic and endothermic reactions 2 Describe bond breaking as an endothermic process and bond forming as an exothermic process 3 Draw and label energy level diagrams for exothermic and endothermic reactions using data provided 4 Interpret energy level diagrams showing exothermic and endothermic reactions and the activation energy of a reaction Energy changes in chemical reactions 1 Describe the meaning of exothermic and endothermic reactions Exothermic reactions When energy is transferred to the surroundings, this is called an exothermic reaction, and the temperature of the surroundings increases. Exo- meaning out , therm- meaning relating to heat Examples combustion reactions Condensation of water vapour Respiration Reaction between acid and metal many oxidation reactions most neutralisation reactions When energy is taken in from the surroundings, this is called an endothermic reaction and the temperature of the surroundings decreases. Endo – meaning in Examples: Thermal decomposition reactions Photosynthesis Cooking an egg Evaporation of water the reaction of citric acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate Everyday uses of endothermic reactions include instant ice packs which can be used to treat sports injuries. Exothermic reaction Mg ribbon is dropped into the conical flask containing HCl. Cotton prevents loss of heat produced. Energy is released during reaction. Chemical energy of the reactants are converted into heat energy. Temperature of the acid increases. Endothermic reaction Sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to the plastic cup containing dilute HCl. Energy is absorbed during reaction. Heat energy of the reactants are converted into chemical energy. The products have more energy than reactants. Temperature of the acid drops. Breaking and making bonds ❑ During a chemical reaction: ▪ bonds in the reactants are broken ▪ new bonds are made in the products ❑ Energy is absorbed to break bonds. Bond-breaking is an endothermic process. ❑ Energy is released when new bonds form. Bond-making is an exothermic process. ❑ If more heat energy is released when making the bonds than was taken in, the reaction is exothermic ❑ If more heat energy was taken in when making the bonds than was released, the reaction is endothermic Energy diagrams ❑ Energy diagrams show the level of energy of the reactants and of the products. ❑ The bigger the difference between the energy of the reactants and the energy of the products, the more energy is given out or taken in. ❑ It is easy to see from an energy level diagram whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic: ▪ in exothermic reactions, the reactants are higher than the products ▪ in endothermic reactions, the reactants are lower than the products An energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction In an exothermic reaction, the products are at a lower energy than the reactants. The difference between the energy of the reactants and the energy of the products is called the enthalpy change (∆H) of the reaction. For an exothermic reaction, the enthalpy change is always negative. An energy level diagram for an endothermic reaction In an endothermic reaction, the products are at a higher energy than the reactants. This means that the enthalpy change of the reaction (∆H) is positive. 3 Draw and label energy level diagrams for exothermic and endothermic reactions using data provided Activation energy When a fuel burns, a spark is needed to start the reaction. A minimum amount of energy is needed in order for a fuel to burn. ❑ The minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to take place is called the activation energy. High and low activation energy In order for two substances to react, their particles must collide with enough energy. The particles in a substance have a range of different energies. ❑ A low activation energy means that a lot of the particles will collide with enough energy to react. The reaction will be fast. ❑ A high activation energy means that far fewer particles will collide with enough energy. The reaction will be slow. 4 Interpret energy level diagrams showing exothermic and endothermic reactions and the activation energy of a reaction A reaction profile for an exothermic reaction A reaction profile for an endothermic reaction