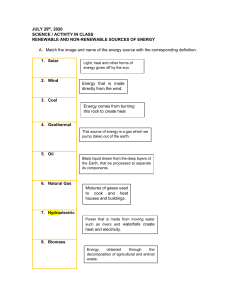
ENERGY SOURCES Renewable and non-renewable sources • Renewable - an energy source that can be replenished in a short period of time • Non-renewable - an energy source that cannot be recreated in a short period of time • Both can be used to produce secondary energy sources - electricity and hydrogen. Renewable and non-renewable sources (cont.) Renewable energy sources include: solar energy, which comes from the sun and can be turned into electricity and heat wind geothermal energy from inside the earth biomass from plants hydropower ocean energy Renewable and non-renewable sources (cont.) Non-renewable energy sources include: fossil fuels - oil, natural gas, and coal uranium, whose atoms when split (nuclear fission) create heat and ultimately electricity. Secondary Energy Sources Secondary energy refers to the more convenient forms of energy which are transformed from other, primary, energy sources through energy conversion processes. Electricity is a secondary energy source - from the conversion of primary sources of energy like coal, natural gas, oil, nuclear power and etc. Secondary sources of energy (energy carriers) -- store, move & deliver energy to consumers. e.g. We convert energy to electricity because it is easier for us to move and use. Secondary Energy Sources (cont.) • Hydrogen is an energy carrier too, especially for the future. • Sending electricity a long way costs four times as much as shipping hydrogen by pipeline. About 9 million metric tons of hydrogen are produced in US annually, enough to power 20-30 million cars or 5-8 million homes. NASA is the primary user of hydrogen as an energy fuel; it has used hydrogen for years in the space program. Hydrogen batteries, called fuel cells, power the shuttle’s electrical systems. The only by-product is pure water, which the crew uses as drinking water. Top 10 Energy Sources of the Future 1. Nuclear fusion 2. Flying Wind Farms 3. Bio-fuels (algae) 4. Solar Windows 5. Nuclear Waste 6. Geothermal heat from underground lava beds 7. Hydrogen (fuel cells) 8. Tidal Power 9. Human Power ALTERNATIVE ENERGIES – (Existing) • Solar • Ocean Wave • Hydropower • Ocean Tides • Biomass • Geothermal • Wind • Ocean Thermal Energy • Ice Harbour Dam Solar energy – thermal devices Solar thermal devices use direct heat from the sun, concentrating it in some manner to produce heat at useful temperatures. Currently, solar thermal devices do everything from heating swimming pools to creating steam for electricity generation. Solar Water Heaters Solar energy – photovoltaic devices Photovoltaic devices use semi-conducting materials to convert sunlight directly into electricity. Solar radiation - varies with changing atmospheric conditions (clouds and dust) & the changing position of the Earth relative to the sun. Wind • Winds are created by uneven heating of the atmosphere by the sun, irregularities of the Earth's surface, and the rotation of the Earth. • As a result, winds are strongly influenced and modified by local terrain, bodies of water, weather patterns, vegetative cover, and other factors. • The wind flow, or motion of energy when harvested by wind turbines, can be used to generate electricity. Geothermal energy • Geothermal energy is contained in underground reservoirs of steam, hot water, and hot dry rocks. • Hot water or steam from geothermal reservoirs in the Earth's crust is supplied to steam turbines at electric utilities that drive generators to produce electricity. • Moderate-to-low temperature geothermal resources are used for direct-use applications such as district and space heating. • Lower temperature, shallow ground, geothermal resources are used by geothermal heat pumps to heat and cool buildings. Biomass energy • Biomass energy is derived from 3 distinct energy sources: wood, waste, and alcohol fuels. • Wood energy is derived both from direct use of harvested wood (chips) as a fuel and from wood waste streams. • The largest source of energy from wood is pulping liquor or “black liquor,” a waste product from processes of the pulp and paper industry. • Waste energy is the second-largest source of biomass energy. The main contributors of waste energy are municipal solid waste (MSW), manufacturing waste, and landfill gas. • Biomass alcohol fuel, or ethanol, is derived almost exclusively from oil palm, rice husk, bagasse and forest residue. Hydropower • Water - leading renewable energy source used by electric utilities to generate electric power. • Hydroelectric plants operate where suitable waterways are available. • Generating electricity using water has several advantages water is a source of cheap power no fuel combustion, less air pollution compared to fossil fuel plants. • Limitations include environmental impacts caused by damming rivers and streams, which affects the habitats of the local flora and fauna. Ice Harbour Dam Ocean energy • Ocean energy draws on the energy of Ocean waves Ocean tides thermal energy (heat) stored in the ocean Wave Energy • Wave energy is generated by the movement of a device either floating on the surface of the ocean or fixed to the ocean floor. • Wave conversion devices that float on the surface have joints hinged together that bend with the waves. This kinetic energy pumps fluid through turbines and creates electric power. • Stationary wave energy conversion devices use pressure fluctuations produced in long tubes from the waves swelling up and down. This bobbing motion drives a turbine when critical pressure is reached. Tidal Energy • Tidal energy traditionally involves building a dam across the opening to a tidal basin. • The dam includes a water-gate that is opened to allow the tide to flow into the basin; the watergate is then closed. • As the sea level drops, traditional hydropower technologies can be used to generate electricity from the elevated water in the basin. Ocean energy (cont.) Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) Systems – A great amount of thermal energy (heat) is stored in the world's oceans. Each day, the oceans absorb enough heat from the sun to equal the thermal energy contained in 250 billion barrels of oil. – OTEC systems convert this thermal energy into electricity; often while producing desalinated water. Fuel-mix for electricity generation – Malaysia Source: Oh et al., 2010 Assessment Criteria Source: Ahmad and Tahar, 2014