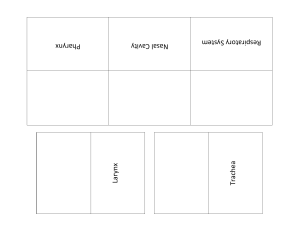
The respiratory system is responsible for providing oxygen to the cells in the body. The purpose of this function is to supply energy for metabolism and to dispel carbon dioxide. The Respiratory system houses the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial system, and lungs Air enters through the nose, where it is warmed, filtered and moistened as it passes over the haircovered mucous membrane of the nasal cavity. Cilia ,which is microscopic hair-like projection, sweeps dirt and foreign materials towards the throat for elimination Inhaled air passes into the throat(PHARYNX) where it mixes with air that enters through the mouth. The pharynx is divided into 3 regions Nasopharynx-superior portion located behind the nasal cavity Oropharynx-middle portion located behind the mouth Laryngopharynx- inferior portion behind the larynx All of the tonsils are located in the vicinity of the pharynx The Larynx “ADAMS APPLE” is a hollow muscular organ that forms an air passage to the lungs, while also holding the voice box(vocal cords) The Trachea “WINDPIPE” is a tube reinforced with C-Shaped rings of cartilage. The trachea connects the pharynx and larynx to the lungs, allowing air flow “BRONCHIAL TREE” is located where the trachea splits in two. At the end of the tree lies a cluster of alveolar ducts, sacs, and the alveoli. This system aids the trachea in air distribution to the lungs The lungs are a pair of spongy, coneshaped organs. Both lungs are different sizes, with the left lung being smaller to accommodate the heart. Once oxygen reaches the lungs it is then spread to all parts of the body. Air is moved into and out of the lungs by a process called breathing, also known as pulmonary ventilation. Breathing consists of a steady cycle of inspiration, expiration, then separated by a rest period Inspiration “INHALING” begins when the phrenic nerve stimulates the diaphragm to contract and flatten, enlarging the chest cavity Expiration “EXHALING” occurs as the breathing muscles relax and the elastic lungs spring back to their original size Oxygen is carried in the blood bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. Carbon dioxide is carried in several ways, but is mainly converted to carbonic acid. The amount of carbon dioxide that is exhaled is important in regulating the bloods acidity. Asthma is a chronic disease that causes surplus production of mucus, inflammation, and narrowing of the bronchial tubes This disorder requires a medical diagnosis, but patients confirmed to have asthma suffer from: Difficulty breathing Chest pain/pressure Shortness of breath Wheezing Dry cough Cough with phlegm Rapid Heart Rate Asthma treatment varies by circumstances; from rescue inhalers( ALBUTEROL) to treat present symptoms. To controller inhalers that prevent symptoms( STERIODS). The main goal of the treatment is to open up clogged, swelled up airways. In most pediatric cases allergy medicine is used in place of steroids due to their mucolytic properties.