Textbook
advertisement

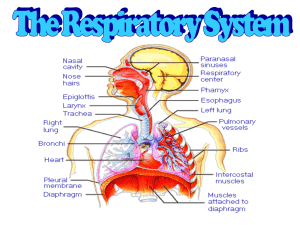
Sachin Panayil 10/10/18 Period 3 EMT HW #3 1. Nasal Cavity: Warms, moistens and filters air entering the respiratory system Pharynx: Path that connects nasal cavity to the trachea Epiglottis: Prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing/prevents air from entering the stomach when breathing in Larynx: To produce sound for communication Trachea: Allows air to pass from the pharynx into the lungs/cartilage rings prevent the trachea from collapsing and provide it with support Lung: The main organs of the respiratory system Bronchi: To carry the air into the lungs Bronchioles: To decrease in size and carry air to the alveoli Alveoli: Are the sites of gas exchange 2. Fast breathing, wheezing, coughing, nasal flaring, blue skin, lips or nails, chest caving or retracting in. 3. Remain calm and do not scare the patient. Attempt to provide humidified oxygen to the face. 4. Any sudden movement could completely block the airway of the patient with difficulty breathing. 5. The signs of difficulty breathing will be present but to a much more severe level which indicates that they need help. 6. Skin returns to regular skin color, breathing looks to be more rhythmic and is more alert 7. The patient is showed to have this medicine or, the patient themselves indicate a medicine they need. 8. Keep the patient as calm as possible. These conditions are hard to tell apart at first sight.