Respiratory System: Anatomy, Function, and Gas Exchange
advertisement
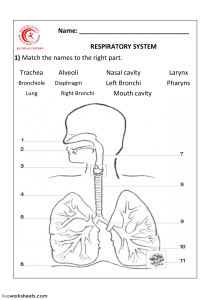
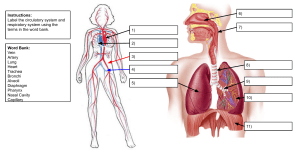
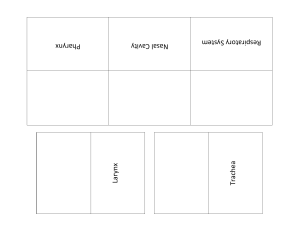
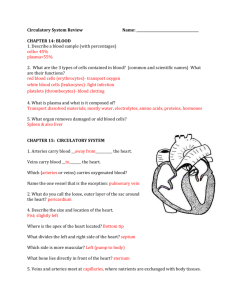
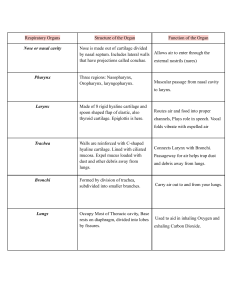
The Respiratory System Purpose of the respiratory system • To provide a constant supply of oxygen to keep your body cells functioning • To remove carbon dioxide from the body cells Organs of the respiratory system • • • • • • Nose / mouth Nasal cavity Pharynx Epiglottis Larynx Trachea • • • • • • Trachea Bronchus (bronchi) Bronchioles Lungs Alveoli Pleura Diaphragm http://www.bbc.co.uk Mouth & Nose • Brings air into the body • Nasal hairs in nostrils trap dust Nasal cavity • Warms & moistens air • Glands that produce sticky mucus line the nasal cavity – cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the back of the throat where it can be swallowed – traps dust, pollen, and other materials that were not trapped by nasal hairs Pharynx • Tube-like passageway used by food, liquid, and air • At the lower end of the pharynx is a flap of tissue called the epiglottis – covers the trachea during swallowing so that food does not enter the lungs Larynx • “Voice box” • The airway to which two pairs of horizontal folds of tissue, called vocal cords, are attached Trachea • Air-conducting tube • Connects the larynx with the bronchi • Lined with mucous membranes and cilia • Contains strong cartilage rings Bronchi • Two short tubes that branch off the lower end of the trachea • Carry air into the lungs. • Singular - bronchus Bronchioles • Tiny branches of air tubes in the lungs • Connect bronchi to alveoli Alveoli • Tiny, thin-walled, grapelike clusters at the end of each bronchiole • Surrounded by capillaries • Where carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange take place • Singular - alveolus http://mhln.com http://www.borg.com/~lubehawk/hrespsys.htm Pleura • Membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity Diaphragm • Muscle wall between the chest and the abdomen that the body uses for breathing http://mhln.com Relationship to digestive system • Cellular respiration requires glucose and oxygen to release energy to the body • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy • Oxygen is provided by the respiratory system • Glucose is provided by the digestive system