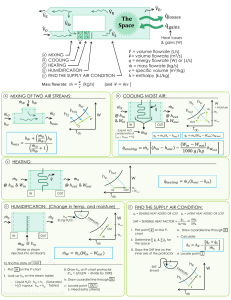
Name (printed):......................................... PHY 317K Signature:......................................... Some Equations for Final Exam • Temperature conversions for T in Kelvin: TC = T − 273.15◦ and TF = 59 TC + 32◦ . • Conductive heat flow for a material with thermal conductivity k: H = −kA • Heat capacity C = ∆T . ∆x Q C Q C Q ; specific heat c = = ; molar specific heat c = = . ∆T m m∆T n n∆T • Thermal expansion of solids: if α is the coefficient of linear expansion, ∆L = αL∆T . • Phase changes: for solid ↔ liquid, Q = mLF , for liquid ↔ gas, Q = mLV . • Boltzmann constant: k = 1.38 × 10−23 J/K; Avogadro constant: NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol−1 gas constant: R = kNA = 8.31 J/mol·K; molar mass: M = NA m, if m is the mass of one molecule. • First Law of Thermodynamics: ∆Eint = Q + W , where Q is the heat into the system and W is the work done on the system. For a closed system, ∆Eint = 0. • For an ideal gas: pV = nRT = N kT , where n = N/NA and N is the number of molecules. • Work by a gas: W = • Isothermal process: Isobaric process: Isochoric process: Adiabatic process: Z Vf p dV . Vi T = const; p = const; V = const; Q = 0; pV γ = const, W = −nRT ln( VV21 ), W = −p(V2 − V1 ), W = 0, 2 −p1 V1 W = p2 Vγ−1 , where γ = Cp /CV Q = −W , Q = ∆Eint − W , Q = ∆Eint , ∆Eint = W , T V γ−1 = const, pV = const Q = nCp ∆T Q = nCV ∆T and • Internal energy: Eint = f2 nRT , where f is the number of degrees of freedom. Molar specific heat: CV = f2 R, and Cp = CV + R. • For a monatomic ideal gas: vrms = p (v 2 )ave = q 3p ρ = q 3RT M = q 3kT m . • Second Law of Thermodynamics: for a closed system, ∆S ≥ 0, where entropy change is given Z f Z b dQ dx b by ∆S = . Recall: = ln( ). T x a i a work performed W = ; heat used |Qh | Tc Qc for a Carnot engine: e = 1 − =1− . Th Qh • Efficiency of a heat engine: e = 1