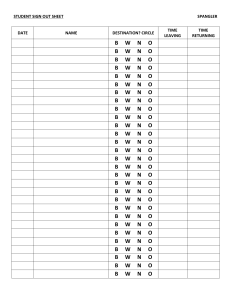
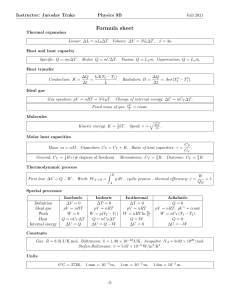
Acceleration: a=Fresultant/m a=(v-u)/∆time Momentum formula: p=m x v F=mv-mu/t F=p/t F= m x a GPE=mgh KE=1/2*mv2 efficiency=useful out / total input work done(Joules or Nm) = force × distance moved W = F× d=P*time in electricity Heat = Work = Energy - IVt power(watts) = energy transferred /time taken P= W/t in electricity P=IV Pressure = Force/Area P=F/A Unit: Pa(1000Pa=1kPa) Pressure In liquids Pressure=Height x Density x Gravitational Field strength pliquid = ρ*g*h Spring formula(Hooke’s Law) F=kx Boyle’s Law: p1xV1=p2xV2 V=volume p=pressure Thermal(Heat) Capacity: C=m*c c is specific heat capacity C is thermal capacity Specific Heat Capacity: E change = m x c x change T c = Heat supplied to substance/m x change T WaveSpeed = WaveLength x Frequency Current = Voltage / Resistance I = V/R Current = Charge / change in time I = Q / delta time Power = Voltage x Current = Energy / time P=VxI P=W/t=E/t Power = Current x Resistance ^2 P = I x R^2 Energy = Work = Current x Voltage x time = Power x time E=W=IxVxt=Pxt EMF = Work / Charge emf = W / Q EMF = sum of pd’s Hand Rules ● Fleming’s Left hand rule (FLHR) next page too!!! ● Right Hand Rotation Rule ● Right Hand Grid Rule ● Fleming’s Right Hand Rule (FRHR) X (cross) is used to show as going INSIDE ● (dot) is used to show as going OUTSIDE For DC motor – FLHR and positive particles (alpha, proton) For AC motor – FRHR and negative particles (beta and electron)