Uploaded by
Keanna Ashley Grace Guting
Accounting Fundamentals: Key Concepts & Financial Statements
advertisement

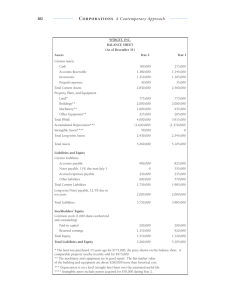
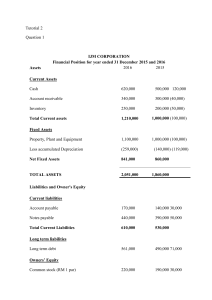
Fundamentals Accounting of Accounting- art of recording, classifying, and summarizing in a significant, manners and in terms of money, transactions and events, and interpreting the result Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)- widely accepted set of rules, concepts and principles of accounting procedures. Separate Entity/ Economic Entityassumes that all the business transactions are separate from the business owner’s personal transactions. Cost principle- all assets acquired should be values and recorded based on acquisition cost not the prevailing market value. Matching Principle- principles that requires that expenses be matched with revenue in a given accounting period. Time Period Principle- requires the business to complete the whole accounting process over a specific operating period. Current Assets- considered short term assets, convertible into cash within a year. Non-current Assets- are long term investments, convertible into cash not only within a year. Current liabilities- paid over a short period of time. Non-current liabilities- paid over a long period of time. Financial Statements documents that describe a company’s operations and financial performance. collection of records that demonstrates the financial standing of your business at a given period. provides important information regarding to the assets and depths of a certain business. Government organizations, accounting companies, etc. frequently audit financial statement to guarantee accuracy and for tax, financing, or investing purposes. Financial Statements includes: 1. Balance Sheet/ Statement of Position 2. Income Statement/ Comprehensive Income 3. Cash Flow Statement 4. Statement of changes in equity 1. Balance Sheet/ Statement of Position Accounting Equation Assets= Liabilities + Shareholder’s Equity It lists the assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s equity of a business at a particular period. So called “book value”, which is determines by deducting all of its obligations(liabilities) and shareholder equity from its total assets. Assets- anything that a business owns which holds some amount of quantifiable value, meaning that it could be liquidated and turned into cash. These are the goods and resources owned by the business. Current Assets Cash Cash Equivalents Prepaid Expenses Inventory Marketable securities Accounts Receivable Non-current Assets Land Equipment Building Furnitures and fixtures Difference: Fixed assets or non-currents assets experience or undergo depreciation, which divides and led a business’s cost for non-current assets to expense them over their useful lives. Customer Deposits Current Position Debt Payable Deferred Revenue Income Taxes Payable Interest Payable Payroll Expense Payable Salaries Payable Sales Taxes Payable o Non-current Liabilities Bonds Payable Loan Payable Notes Payable Deferred tax liability Owner’s Equity- represents the owner’s investment in the business minus the owner’s draws or withdrawals from the business plus the net income or minus, since the business began. o Capital Retained earnings Owner’s drawings Depreciation- refers to an accounting method used to allocate the cost of a tangible or physical assets over its useful life. It represents how much of an asset’s value has been used and allows business/ companies to earn revenue from the assets they own by paying for them over a certain period of time. 1. Accumulated Depreciation – refers to the sum of all depreciation recorded on an asset to a specific date. Depreciation= Cost – Residual Value Life Spa Example: Equipment: Delivery Truck Purchase price: 1,000,000 Purchase Date: March 1, 2018 1. Calculate the depreciation per month 2. Calculate the accumulated depreciation on February 28, 2021 Depreciation= 1,000,000 – 100,000 5 years or 60 months = 900,000 60 Depreciation per month = 15,000 March 1, 2018 – February 28, 2021= 3 years or 36 months = 15,000 x 36 = 1,000,000-540,000(dep.) =460,000 Liabilities- company owes, usually a sum of money. These are settled over time through transferring of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. Can also mean legal or regulatory risk or obligation to asset. o Current Liabilities Accounts Payable Accrued Liabilities Accrued Wages 2.Income Statement/ Profit and Loss Net Income= (Total revenue + Gains) Contains the revenue and expenses items of the company that has not been realized. Typically presented after the income statement within the financial statements. Elements of Income Statement o Revenues and Gains o Operating Revenue o Non-Operating Revenue o Gains o Expenses and Losses o The cost for a business to continue operation and turn a profit is known as an expense. o Primary Activity Expenses o Secondary Activity expenses o Losses as expenses