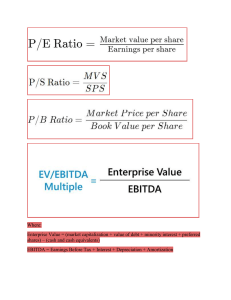
PAS 33 Earnings Per Share Learning Competencies • • Explain how basic earnings per share is computed. Explain how diluted earnings per share is computed. 1 Definition • Earnings per share (EPS) is a computation made for ordinary shares. It is a form of profitability ratio which represents how much was earned by each ordinary share during the period. No EPS is presented for preference shares because these shares have a fixed return represented by their dividend rates. 2 Types of Earnings per share 1. 2. Basic earnings per share Diluted earnings per share 3 Basic Earnings Per Share 4 Considerations in computing “Profit or loss” a. b. Profit or loss should be net of income tax expense Profit or loss should be adjusted for the after-tax amounts of preference dividends, differences arising on the settlement of preference shares, and other similar effects of preference shares classified as equity. 5 Adjustments for preference dividends a. If the preference shares are cumulative, one-year dividend is deducted from profit or loss whether declared or not. b. If the preference shares are non-cumulative, only the dividend declared is deducted from profit or loss. 6 Weighted average number of outstanding ordinary shares • Shares are usually time-weighted from the date consideration is receivable (which is generally the date of their issue). Thus: a. Shares issued outright are averaged from the issuance date. b.Subscribed shares are averaged from the subscription date. c. Treasury shares are averaged i. ii. as reduction to the number of outstanding shares from the reacquisition date; or as addition to the number of outstanding shares from the reissuance date 7 Restatement of EPS • EPS in previous periods are adjusted retrospectively when an entity issues any of the following: a. A capitalization or bonus issue (e.g., share dividend); b. A bonus element in any other issue, for example a bonus element in a rights issue to existing shareholders (also referred to as preemptive stock rights); c. A share split (increase in number of shares with corresponding decrease in par value); and d. A reverse share split (consolidation of shares or decrease in number of shares with corresponding increase in par value). 8 Rights issue 9 Diluted earnings per share • Diluted earnings per share is the amount of profit for the period per share, reflecting the maximum dilutions that would have resulted from conversions, exercises, and other contingent issuances that individually would have decreased earnings per share and in the aggregate would have had a dilutive effect. • Only basic earnings per share is presented if an entity has no dilutive potential ordinary shares (i.e., simple capital structure). 10 • The computation of diluted earnings per share is based on the assumption that the dilutive potential ordinary shares were converted or exercised. It is: 1. “As if” the convertible preference shares or convertible bonds have been converted; or 2. • “As if” the options or warrants have been exercised. The conversion or exercise is assumed to have taken place on the date the potential ordinary shares became outstanding, regardless of the date of actual conversion or exercise. 11 12 Options, warrants and their equivalents • When computing for diluted earnings per share, the “treasury share method” shall be used in computing for the incremental shares. This method assumes that: 1. 2. The options or warrants are exercised and The proceeds received from the exercise are used to purchase treasury shares at the average market price. 3. The difference between the treasury shares assumed to have been purchased and the option shares represents the incremental shares. 13 Treasury share method 14 Financial statement Presentation • Basic and Diluted earnings per share are computed on the following: 1. 2. Profit or loss from continuing operations Profit or loss from discontinued operations, if the entity reports a discontinued operation. 3. • Profit or loss for the year EPS is not computed on other comprehensive income and total comprehensive income. 15 Financial statement Presentation (Continuation) • EPS computed on profit or loss from continuing operations and profit or loss for the year are presented on the face of the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income. If the entity uses a twostatement presentation, EPS is presented only on the separate income statement. 16 17