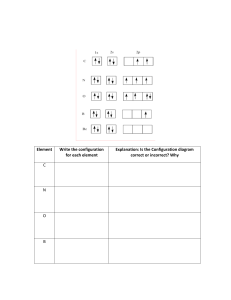
Dumalinao National High School SCIENCE 9 SUMMATIVE TEST NAME: __________________________________________________________________ SECTION: __________________________________SCORE: ______________________ DIRECTION: CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER AND WRITE IT ON THE SPACE PROVIDED BEFORE THE NUMBER. MODULE 1 ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF MATTER _______1. On the basis of Rutherford’s model of an atom, which subatomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom? a. proton and electron c. proton and neutron b. neutron and electron d. proton only _______2. If the first and second energy levels of an atom are full, then what would be the total number of electrons in the atom? a. 6 b. 8 c. 10 d. 18 _______3. Which atomic model is proposed by Schrodinger? a. nuclear model c. raisin bread model b. planetary model d. quantum mechanical model _______4. The symbol “n” in the Bohr Theory of atomic structure refers to…. a. the energy of electron b. the total energy of the atom c. the number of electron in an energy level d. the orbit in which an electron is found _______5. What are the orbitals present in the fifth principal energy level? a. s orbital c. s, p, d orbitals b. s, p orbitals d. s, p, d, and f orbitals DIRECTION: CHOOSE THE ANSWER FROM THE BOX AND WRITE IT ON THE SPACE PROVIDED BEFORE THE NUMBER. Models quantum model atomic orbital Zeeman Effect orbitals uncertainty principle 1 Probability electrons spectroscope 1 stark effect Heisenberg ________________6. An instrument that can analyzed the colors given off by the vapors of elements. ________________7. An atomic model which is considered as the modern atomic model. ________________8. Effect of electrical field on the atomic spectrum ________________9. The volume or region of space around the nucleus where the electron is most likely to be found. ________________10. Effect of magnetic field on the atomic spectrum ________________11. Have specific energy values ________________12. He discovered that for very small particles like electron, its location cannot be exactly known and how it is moving. ________________13. Location of the electron cannot be exactly known and how it moves. ________________14. A measure of the likelihood of an event to occur. ________________15. This are described as occupying fixed energy levels at a certain distance from the nucleus of an atom. ________________16. This is used a way to represent what we cannot see. IDENTIFY THE ELEMENT NAME AND THE SYMBOL THAT CORRESPONDS TO EACH OF THE FOLLOWING ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS. Used a PERIODIC TABLE for references. Electron Configuration Element Name Element Symbol 17. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6,3s2,3p6,3d10, 4s2, 4p5 18. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d6, 4s2 19. 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 20. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p4 21. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 2s2, 3p6, 3d10, 4s2, 4p2 22. 1s2, 2s2, 2p5 23. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d1,4s2 24. 1s2, 2s2, 2p3 25. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2 MODULE 2 CHEMICAL BONDING DIRECTIONS: CLASSIFY THE FOLLOWING PROPERTIES AS IONIC OR COVALENT COMPOUNDS. WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THE SPACE PROVIDED BEFORE THE NUMBER. ________________1. Atoms share electrons to become stable. ________________2. High melting and boiling points. 2 _________________3. Conduct electricity when melted. _________________4. Usually occurs between non-metals. _________________5. Poor electrical conductors in all phases. _________________6. Many soluble in non-polar liquids but not in water. _________________7. Crystalline solids (made of ions) _________________8. Metal atoms give electrons while nonmetal atoms get electrons to become stable. _________________9. Usually occurs between metals and non-metals. _________________10. Hydrogen and another nonmetal chemically combines through covalent bonding. _________________11. Low melting and boiling points. _________________12. Many soluble in water but not in nonpolar liquid. CHOOSE THE LETTER OF THE CORRECT ANSWER AND WRITE IT ON THE SPACE PROVIDED BEFORE THE NUMBER. _______13. Which of the following properties of atoms is the most suitable reference for the kind of bond that will take place between/among them? a. atomic size c. electronegativity b. electron affinity d. ionization energy _______14. When covalent bonding does takes place? a. when atoms attain stability b. when atoms collide with one another c. when the attraction between atoms is strong d. when atoms share electrons with one another _______15. The kind of chemical bond that will form between two oxygen atoms. a. ionic bond c. nonpolar covalent bond b. metallic bond d. polar covalent bond _______16. Which of the following compounds will have the highest melting temperature? a. lead wire b. paraffin wax c. salt d. table sugar _______17. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity because they…. a. break up into ions c. do not dissolve in water b. do not break up into ions d. have high melting points _______18. Nitrogen belongs to family 5A and it is diatomic. How many nonpolar covalent bonds will there be in N2 molecule? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 _______19. Which is a property shared by most covalent compounds? a. high boiling point c. low melting point b. high melting point d. good conductor of heat and electricity 3 _______20. What bond holds the atoms of the elements in group 1 and 2 of the periodic table? a. non polar covalent bond c. metallic bond b. polar covalent bond d. ionic bond MODULE 3 IONIC COMPOUND DIRECTION: CHOOSE THE LETTER OF THE CORRECT ANSWER AND WRITE IT ON THE SPACE PROVIDED BEFORE THE NUMBER. ______1. The ion formed by atom of metal is a (n)… a. cation b. anion c. ionic bond d. ion ______2. What is an ion? a. small atom b. charge atom c. large atom d. cute atom ______3. What type of bond is formed between X and Y? a. covalent b. ionic c. ionic covalent d. metallic ______4. What is the charge of the ion formed when a zinc atom loses two electrons? a. 1b. 2c. 1+ d. 2+ ______5. A charge particle that has gained at least one electron is called a (n) _____. a. cation b. an onion c. anion d. chemistry cat DIRECTION: IDENTIFY EACH AS A CATION, AN ANION, NEITHER. WRITE YOUR ANSWER ON THE SPACE PROVIDED BEFORE THE NUMBER. _______________6. H+ _______________7. Cl_______________8. O2 _______________9. Ba2+ _______________10. CH4 DIRECTION: ENUMERATE THE FOLLOWING. PLEASE USE PERIODIC TABLE FOR REFERENCES. WRITE THE SYMBOL OF THE ELEMENTS ONLY. A. NON METAL ELEMENTS (11-15) B. METAL ELEMENTS (16-25) 11. ______________ 16. _____________ 21. __________ 12. ______________ 17. _____________ 22. __________ 13. ______________ 18. _____________ 23. __________ 14. ______________ 19. _____________ 24. __________ 15. ______________ 20. _____________ 25. __________ 4 MODULE 4-5 THE CARBON COMPOUNDS DIRECTION: CHOOSE THE LETTER OF THE CORRECT ANSWER AND WRITE IT ON THE SPACE PROVIDED BEFORE THE NUMBER. ______1. What happens to the boiling point of hydrocarbon compounds when the number of carbon atoms increases? a. decreases c. increases b. increases then decreases d. remains the same ______2. Which alkene will most likely have the highest boiling point? a. ethane b. hexane c. pentene d. propene ______3. Emmanuel Juan cut his finger accidentally when he was cutting his nails. He has apply something on his wound so that it will not get infected. Which compound should he use? a. formalin b. isopropyl alcohol c. kerosene d. acetone ______4. What is the maximum number of bonds a carbon atom can form? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 ______5. How do carbon atoms form many organic compounds? a. by attracting other elements toward themselves to form the bond b. by forming many bonds with other carbon atoms and other elements c. by sharing their electrons with other metal and nonmetal elements d. by transferring their electrons to the atoms of surrounding elements DIRECTIONS: COMPLETE THE TABLE BELOW BY IDENTIFYING THE TYPE OF CHEMICAL BONDS (IONIC, METALLIC, COVALENT) OF THE FOLLOWING COMPOUNDS. Compound Type of chemical bonds 6. CaF2 7. CBr2 8. Cu 9. CO 10. CH4 11. Al 12. NaCl 13. CS2 14. KCl 15. CH3CH2OH DIRECTION: FILL IN THE CORRECT WORDS FROM THE BOX. WRITE THE WORDS IN EACH BOX TO COMPLETE THE THOUGHT. 5 Double bond carbonyl alkenes Methyl alcohol single bond hydrocarbons Hydroxyl butane pentene Ethyne triple bond isopropyl alcohol Carbon compounds 16. 17. 18. Types of hydrocarbons 19. 20. 21. Types of carbon bonds 22. 23. 24. Examples of carbon bonds 25. 26. 27. Examples of alcohols 28. 29. 30. 6 ethyl alcohol alkanes alkynes