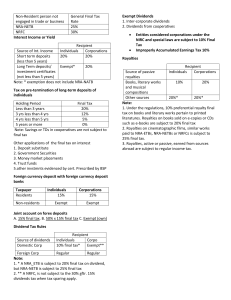
5 - Final Income Taxation 4 features of final income taxation 1. Final tax 2. Tax withholding at sources 3. Territorial imposition 4. Imposed on certain passive income and persons not engaged in business in the Philippines Rationale of final income taxation - Taxpayer and government convenience Items of passive income - those that are earned with very minimal involvement from the taxpayer and are generally irregular in timing and amount and is best used with the final withholding scheme for passive income 2 of the types of taxpayers that have high risk of non compliance, and are thus subject to final income 1. NRA-NETBs 2. NRFCs General final tax rate of NRA-NETBs - 25% General final tax rate of NRFCS - 30% 9 passive income subject to final tax 1. Interest or yield from bank deposits or deposit substitutes 2. Domestic dividends, in general 3. Dividend income from a Real Estate Investment Trust 4. Share in the NI of a business partnership, taxable associations, joint ventures, joint accounts, or co-ownership 5. Royalties, in general 6. Prizes exceeding 10k 7. Winnings 8. Informer's tax reward 9. Interest income on tax-free corporate covenant bonds Final tax rate on interest earned from short term deposits for individuals and corporations - 20% Final tax rate on interest earned from long term deposits for individuals and corporations - Individuals (except NRA NETB) - exempt - Corpos - 20% Deposits made for a period of less than 5 years - Short term deposits Deposits made for a period of 5 years or more - Long term deposits or investment certificates Final tax rate on pre-termination of long-term deposits of individuals - < 3 yrs - 20% - 3-4 - 12% - 4-5 - 5% - > 5 yrs - 0% Exempted savings and time deposits from final tax - Those of cooperatives' 5 other applications of the final tax on interest 1. Deposit substitute 2. Government securities 3. Money market placements 4. Trust funds 5. Other investments evidenced by certificates prescribed by BSP An alternative form of obtaining funds from at least 20 persons at any one time other than deposits through the issuance, endorsement, or acceptance of debt instruments for the borrowers' own account - Deposit substitute Final tax rate on foreign current deposit under foreign currency depositary banks - Residents - 7.5% - Non - exempt (for both indiv & corpo) Final tax rate on interest from joint accounts (by resident and non res) on forex deposits - 50% is exempt while 50% is subject to 7.5% final tax rate 5 interest income subject to regular income tax 1. Lending activities 2. Investment in bonds 3. Promissory notes 4. Foreign sources 5. Penalty for legal delay or default Any distribution made any corporation to its shareholders out of its earnings or profits and payable to its shareholders - Dividends 5 types of dividends 1. Cash 2. Property 3. Scrip 4. Stock 5. Liquidating Cash dividends - dividend paid in cash Property dividends - dividend paid in non cash properties including stocks or securities of another corporation Scrip dividends - dividends paid in notes or evidence of indebtedness of the corporation Stock dividends - dividends paid in stocks of the corporation Liquidating dividends - dividends for the distribution of corporation net asset 2 dividends whose income are not for taxation purpose 1. Stock dividends 2. Liquidating dividends When does substantial alteration in ownership in the corporation occur? - Stock dividends are given in lieu of cash div or when corporation declared an optional stock or cash dividend Exception to the non taxability of stock split - NONE. It is absolutely not subject to income Dividend tax rules for dividends from domestic corporations - Individuals - 10% (nra etb 20%, nra netb -25%) - Corpos - exempt (nrfc -30%, or 15% in some cases) Dividend tax rules for dividends from foreign corporations - Regular tax for both individuals and corporations 2 exempt dividends 1. inter corporate 2. dividends from cooperative dividends Why are corporate (and business partnership) recipients of dividends exempted from taxation? - To eliminate the impact of double taxation 5 entities taxable as corporation and thus subject to 10% final tax 1. Real estate investment trusts (REIT) 2. Business partnerships 3. Taxable associations 4. Taxable joint ventures, joint accounts or consortia 5. Taxable co-ownerships REIT (Real Estate Investment Trust) - a publicly listed corporation established principally for the purpose of owning income-generating real estate assets 3 recipients of reit dividends exempt from final tax 1. Non resident alien or NRFCScs entitled to claim preferential tax pursuant to applicable tax treaty 2. Domestic corporations or RFCS 3. Overseas filipino investors (only until aug 12 2018) For the last or remaining 4 exempted (from final tax) entities, how is net income received? - Deemed constructively received by PARTNERS, MEMBERS, OR VENTURERS For the last or remaining 4 exempted (from final tax) entities, when does the final tax of 10% apply? - Point of determination of income, NOT at the point of actual distribution Inclusions of share in net income of business partnership 1. Share in residual profit (ONLY THIS IS SUBJECT TO FINAL TAX if the other 2 are expensed, and are thus subject to regular tax to receiving partner) 2. Salary provisions 3. Interest & bonus to a partner Penalty tax imposed to corporation that accumulate earnings beyond the reasonable needs of business - 10% Improperly accumulated earnings tax Tax rule for royalties from sources within Ph. for individuals - Books (in print), literary works, and musical compositions - 10% - Other sources - 20% Tax rule for royalties (PASSIVE) from sources within Ph. for corporations - Books (in print), literary works, and musical compositions - 20% - Other sources - 20% Tax imposed for royalties (passive or active) from sources abroad - Regular income tax 2 prizes exempt from final tax 1. Received w/o effort to join contest 2. From sports competitions sanctioned by their respective national sport organizations 2 requisites of exemption for prizes 1. Recipient was selected w/o any action on his part to join 2. He is not req to render substantial future services as a condition to receive prize or reward