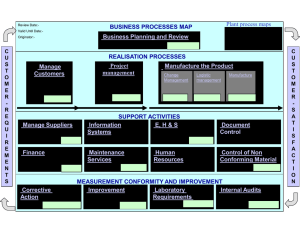
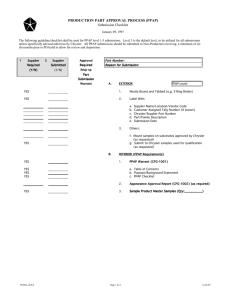
Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford GLOBAL PURCHASING Supplier Technical Assistance Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased Production Part Approval Process Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Motor Company Supplier Technical Assistance December 2004 Acknowledgements: The Phased PPAP development represents the efforts of Ford and its suppliers. Acknowledgement should be made to the core team which comprised of: Erin Bates, Chris Burford, Volker Domdei, Matthias Duex, Timo Golzio, Brian Grandstaff, Russ Hopkins, Tim Jolly, Debra Keller, Tom Miller, Jim Polman, Ranga Rajan, Aricka Long, Hans Pettersson, Julian Taylor and Steve Walsh. This core team gratefully acknowledges the contributions made by employees at Ford and its suppliers who have developed and continue to support effective implementation of Phased PPAP. XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Table of Contents Page Phased PPAP Introduction 3 Phased PPAP Overview 4 Process Flow Overview 5 Phased PPAP Key Definitions 6 Phase 0 PPAP – Run–at-Rate 7 Phase 1 PPAP – Quality Verification 8 Phase 2 PPAP – Production Verification 9 Phase 3 PPAP – Capacity Verification 10 Customer Approval of Phased PPAP 11 Expectations 12 Appendix A - STA Roles & Responsibilities 13 Appendix B – Exception Management Process 14 – 17 Appendix C – Phased PPAP Submission Warrant 18 Appendix D – PPAP Requirements Listing 19 Appendix E - Acronym List 20 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Phased PPAP Introduction In order to improve launch performance, Ford has structured the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) into a phased approach that will require an organization to demonstrate manufacturing capability, product quality and production capacity prior to Job #1. Phased PPAP will provide Ford and the supplier with an improved understanding of supplier manufacturing process and part readiness. Phased PPAP organizes the Production Part Approval Process into four phases: Phase 0: 'Run-at-Rate' Phase 1: 'Quality Verification' Phase 2: ‘Production Verification' Phase 3: ‘Capacity Verification’. Benefits of Phased PPAP Phased PPAP will benefit Ford and its Suppliers by: • Dividing PPAP activities into more manageable segments • Providing a structured approach aligned with manufacturing process development • Providing a program team with earlier and additional measures to forecast program/product readiness • Providing a consistent mechanism for a supplier to demonstrate their ability to support Ford production volume requirements/capacity Teamwork Ford Motor Company and its Suppliers must work together to deliver a quality part, produced ontime, that meets all Ford engineering requirements. To drive flawless execution in launching and delivering products that surpass customer expectations, Ford and its suppliers must place trust, integrity and accuracy above all else in the Production Part Approval Process. What Phased PPAP Means to Ford Motor Company Successful completion of Phased PPAP: • Confirms that all customer engineering design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the supplier, and that ALL production streams have the potential to produce product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate. AND • Verifies that the supplier's production system can support the Daily Production Volume declared by the customer. 3 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Phased PPAP Overview Scope • Phased PPAP must be completed for any of the situations already specified by the current edition AIAG PPAP Manual. In addition, any increase in the Daily Production Volume declared by the customer above the verified declared DVP will require the supplier to re-complete any affected Phased PPAP phases. Summary Phase 0: Run-at-Rate Objectives: To confirm that all production input requirements are available and understood, and can support a limited production run. To provide an early indicator that the design of the process/tool/facility has the potential to produce at rate the required number of acceptable parts as determined by the pre-launch control plan. Phase 1: Quality Verification Utilizes parts produced during Phase 0. Objectives: To confirm all customer design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the supplier. To provide an early indicator that the design of the process/tool/facility has the potential to produce product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate by operating a minimum of one selected production stream. Phase 2: Production Verification Objectives: To confirm all customer engineering design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the supplier, and that ALL production streams have the potential to produce product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate. Phase 3: Capacity Verification Objective: Verify the supplier's production system can support customer declared DPV while meeting Phase 2 requirements. 4 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Ford T h e p ro c e s s b e lo w is n o t to s c a le b e tw e e n tim in g p o in ts START C o m p le te s s o u rc in g o f s u p p lie r s ite p e r P u rc h a s in g P ro c e d u re 2 .1 o r lo c a l p ra c tic e H a v in g c o m p le te d P S W 0 0 9 , a g re e s H ig h Im p a c t P a rts d e s ig n a tio n w ith S ite E n g in e e r. In fo rm s a ffe c te d s u p p lie rs o f H I p a rt s ta tu s a n d d e s ig n a tio n o f P P A P S u b m is s io n L e v e l 5 A s s ig n s P P A P le v e l to S u p p lie r S ite (p e r P S P -0 1 1 : T a b le 1 ). A g re e s w ith P ro g ra m e n g in e e r o n H ig h Im p a c t P a rts N o te : In s o m e re g io n s th e P ro g ra m m e E n g in e e r m a y b e re s p o n s ib le fo r a s s ig n in g s ite P P A P s u b m is s io n le v e l a n d m a y b e th e re s p o n s ib le P a rt A p p ro v a l A c tiv ity . In p u ts P h a s e d P P A P P ro m is e d a te s in to V PP per Phased P PA P H andbook < P le a s e re fe r to P h a s e d P P A P H a n d b o o k fo r T im in g E x p e c ta tio n s b y P h a s e > P h a s e 0 - C a p a c ity A n a ly s is R e p o rt P h a s e 1 - W a rra n t P h a s e 2 - W a rra n t P h a s e 3 - W a rra n t & C a p a c ity A n a ly s is R e p o rt C o m p le te s P h a s e d P P A P R e q u ire m e n ts (P h a s e 0 , 1 , 2 o r 3 ) & D o c u m e n ta tio n d e fin e d fo r P h a s e b e lo w P hase 0 W e re a ll re q u ire m e n ts o f th e P h a s e m e t? No R e q u ire m e n ts Yes <1PP> Phase 1 D o c u m e n ta tio n d e fin e d fo r Phase E n te r "Y " c o d e in V P P fo r P h a s e & s u b m it d o c u m e n ta tio n d e fin e d fo r P h a s e to S T A a c tiv ity th a t m u s t b e c o m p le te d to m e e t P h a s e 1 T im in g o f P h a s e 0 is d e te rm in e d b y lo n g e s t le a d 5 T h e p ro c e s s b e lo w is n o t to s c a le b e tw e e n tim in g p o in ts No W a s th e D o c u m e n ta tio n A p p ro v e d ? Yes S ig n e d -o ff D o c u m e n ta tio n a s d e fin e d b y P hase E n te rs "R " (R e je c te d ) in V P P w ith in 2 4 h o u rs R e fe r to th e P h a s e d P P A P E x c e p tio n M a n a g e m e n t P ro c e s s , e le m e n t 4 .2 .3 in th e P hased PP AP H andbook b) R e je c t R e c o rd s S T A D e c is io n in V P P < P le a s e re fe r to P h a s e d P P A P H a n d b o o k fo r T im in g E x p e c ta tio n s b y P h a s e > R e v ie w & S ig n D o c u m e n ta tio n d e fin e d fo r P h a s e N o te s a) R e fe r to R o le s a n d R e s p o n s ib ilitie s M a tric e s to d e te rm in e m in im u m e x p e c ta tio n s b y s u b m is s io n le v e l a n d p h a s e . b) P ro d u c t D e v e lo p m e n t (C re a tio n ) h a v e th e a u th o rity to a u th o ris e a n A le rt (o r re g io n a l e q u iv a le n t) w h e re a d e v ia tio n to s p e c ific a tio n e x is ts , a n d In te rim A p p ro v a l is re q u ire d . c ) L a u n c h te a m ty p ic a lly c o n s is ts o f S T A , P u rc h a s in g , P ro d u c t D e v e lo p m e n t (C re a tio n ), N e w M o d e l L a u n c h a n d M a te ria l P la n n in g & L o g is tic s (M P & L ). d) D a ta in p u t in to V P P m a y b e c o n d u c te d b y a n a d m in is tra tio n te a m c o n s is te n t a s d e fin e d b y lo c a l p ro c e d u re . If S T A d e c is io n o n P h a s e d P P A P W a rra n t is e n te re d b y th e s u p p lie r, S T A m a y o v e rrid e s u p p lie r V P P e n try a t a n y tim e . T h is a ls o a p p lie s in th e c a s e s o f P P A P S u b m is s io n L e v e l 1 ("S u p p lie r S e lf C e rtific a tio n "), w h e re A p p ro v a l is re g is te re d in V P P a u to m a tic a lly w h e n th e s u p p lie r e n te rs "Y " c o d e e) D o c u m e n ta tio n is n o t lim ite d to th a t d e fin e d in th is P ro c e s s F lo w c h a rt. T h e F o rd P h a s e d P P A P 4 -P a n e l P ro c e s s M a p (s e e P h a s e d P P A P H a n d b o o k ) d e fin e s th e d o c u m e n ta tio n th a t is re q u ire d to b e c o m p le te d a t e a c h P h a s e . S u b m is s io n to th e C u s to m e r A p p ro v a l A u th o rity (S T A ) is d e fin e d in th e A IA G P P A P M a n u a l. Buyer S T A P ro g ra m E n g in e e r S T A S ite E n g in e e r a ),d ), e) S u p p lie r d ),e ) Launch Team c) FPDS T im e lin e A p p ro v e E n te rs "A " (A p p ro v e d ) in V P P w ith in 2 4 h o u rs <FEU> P hase 2 No A re a ll P hases c o m p le te ? Yes END <Job #1> Phase 3 This process flow (an extract from Ford Internal Procedure PSP-011) is intended to link the activities in Phased PPAP to include 4-Panel Process Flow, Roles & Responsibilities Matrices & Exception Management Process with the AIAG PPAP Reference Manual and any related Ford Internal procedures. Process Overview Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Definitions: Production Stream A single production stream is a sequence of a minimum of one line, machine, tool, cavity, facility, equipment, gage, operator and other required items at the intended location and with the intended layout that will be used to produce parts that meet Ford specifications. All production streams must include any additional items not included in the single production stream that are required to meet the Ford Capacity Planning Volume (CPV) requirements of the intended program being launched (e.g. additional tools, cavities, lines, conveyors, machines) Line Stream Conveyor Cavity Gages Others EOL Tester Tool Facilities Operators CPV (Capacity Planning Volumes) Capacity Planning Volumes are the volumes for which Ford requires suppliers to facilitize and tool-up for. CPV's are approximately 10 percent higher than "production planning volumes," in order to cover spares (service requirements) and volume spikes. The CPV is communicated to Suppliers on a part level basis through the Ford Purchasing “Request for Quotation” (RfQ). CPV's are typically expressed as weekly volumes. Suppliers are expected to satisfy the production weekly demand based on a maximum 5 days/3 shifts manufacturing operating pattern. DPV (Daily Planning Volume) DPV's are the maximum planned requirement for this part per day and are broken down by plant and Brand (e.g. Volvo). Acceptable Parts (referenced in Phase 0 objectives) Acceptable Parts are defined as parts produced using the required PPAP inputs for Phase 0 as identified on the Process Map and manufactured in conformance with the relevant control plan, either Pre-Launch or Production. Interim Accepted Part meets customer specifications and includes valid Temporary Engineering Specification for temporary exception. Temporary Engineering Specification Temporary specification provided by the customer engineering release organization. The Ford Brand specific method for communicating these specifications is as follows: • WERS Alert (Ford/Jaguar); • Temporary Part Change Management (Land Rover); • Temporary Part Deviation (Volvo). 6 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Process Map Phase 0 Run-at-Rate Objectives: To confirm that all production input requirements are available and understood, and can support a limited production run. To provide an early indicator that the design of the process/tool/facility has the potential to produce at rate the required number of acceptable parts as determined by the Pre-Launch control plan. Refer to web link https://web.qpr.ford.com/sta/Capacity_Analysis_Report.xls for Capacity Analysis Report and supporting documentation. Phase 0 Run-at-Rate START INPUTS Trained supplier production operators Are the Run-at-Rate input requirements in place for the production stream? Outputs from the event Required Inputs STATUS: Phase 0 Completed No Sub-supplier(s) material status from Tier-x Run-at-Rate Supplier EVENT: Conduct Runat-Rate Yes No Quantity of parts required as defined by customer (default 300 consecutive parts) Was the Pre-Launch Control Plan followed? Yes No Job 1 Location (final site & line) Capacity Analysis Report Were the prescribed number of acceptable parts produced? Submit to Customer Yes Production process including control plan, flow diagram instructions & Process parameters [#5,6 & 7] No Planned production cycle times required to support Daily Production Volume Were the parts produced in the defined period? Status Tracking Database Yes Production Tools, Facilities & Gauging [#8,16 & 17] No Implement Corrective Action on Input Did all operations meet their planned cycle time ? 1 Proceed to next page Released design [#1,2,3 & 4] Yes 4 Note: refer to Appendix D which lists the PPAP requirements number (#x) noted in the 4-Panel Process Map 7 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Process Map Phase 1 Quality Verification Objectives: To determine if all customer engineering design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the supplier. To provide an early indicator that the design of the process/tool/facility has the potential to produce product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate by operating a minimum of one selected production stream. Phase 1 Quality Verification Continue Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) using parts from Phase 0 1 - Dimensional measurements [#9] Material Tests [#10] Statistical process package [#11] Performance Tests [#12] Appearance criteria [#13] Sample parts [#14] Master samples [#15] Customer Specific Requirements[#17] as defined by PPAP Have the PPAP requirements been satisfied? Yes STATUS: Phase 1 Completed 2 No Phase 1 Warrant [#18] Proceed to next page Submit to Customer Status Tracking Database Important notes: For suppliers with only one production stream completion of Phase 1 & 2 occur at the same time utilizing the Production Control Plan. It is required that prior to Phase 1 submission that sub-supplier(s) material status from Tier-x has also achieved Phase 1. Return to Phase 0 for corrective action 4 4 8 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Process Map Phase 2 Production Verification Objectives: To determine if all customer engineering design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the supplier, and that ALL production streams have the potential to produce product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate. Note: The approach adopted for PPAP of multiple production streams is scenario-specific and must be agreed between the Supplier and STA. In general terms each production stream should be assessed for Run-at-Rate and Quality Verification separately. Consideration should also be given to the risk that the introduction of further production streams may impact the validity of the Phase 1 approval. (e.g. Phase 1 achieved on cavity #1 of a four cavity tool - the introduction of cavity #2, 3 & 4 may impact the cavity #1 part and it may no longer be to specification). P h ase 2 P ro d u ctio n V erificatio n 2 Have Run-at-Rates (Phase 0) been conducted and Q uality Verifications (Phase 1) been satisfied for ALL production stream s ? Y es STATUS: Phase 2 Com pleted 3 No S u b m it to C u stom er Status Tracking Database Im porta nt note : Pha se 2 a nd Pha se 3 c a n ha ppe n c onc urre ntly if a ll Inputs a nd Outputs a re sa tisfie d. E x pe c ta tion tha t the Produc tion C ontrol Pla n is follow e d during this Pha se . 4 9 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Proceed to next page Phase 2 W arrant [#18] Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Process Map Phase 3 Capacity Verification Objective: Verify the supplier's production system can support customer declared DPV while meeting Phase 2 requirements. Update process flow with latest version to include nomenclature 'Capacity Analysis Report' Refer to web link https://web.qpr.ford.com/sta/Capacity_Analysis_Report.xls for Capacity Analysis Report and supporting documentation. Phase 3 C a p a c ity V e rific a tio n A re the C V input requirem ents in plac e for all produc tion s tream s ? A ll pers onnel for all s hifts , trained Q uantity required is c us tom er DP V for one full day Required Inputs 3 Y es No E V E N T: Conduc t C apac ity V erific ation R un S TA TUS : P has e 3 C om pleted W as the P roduc tion c ontrol plan follow ed & ac c eptable parts produc ed? P has e 3 W arrant [#18] & Capac ity A naly s is R eport Y es P has e 2 W arrant S c heduled down tim e defined (TP M , c hange over, B reak s etc .) No D id th e vo lu m e o f a c c e p ta b le p a rts p ro d u c e d m e e t o r e xc e e d th e re q u ire d D P V? S ub m it to C us to m e r S tatus Trac k ing Databas e Y es S ub s upplier m aterial s tatus from Tier-x P has e 3 C om plete C apac ity A naly s is W ork s heet D eterm ine Root Caus e & P lan Correc tive A c tion Return to affec ted phas e and s tart c orrec tive ac tion P has e 0 P has e 2 P has e 1 P has e 3 10 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 E ND Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Customer Approval of Phased PPAP Phased PPAP Approval Phase 0 does not require a Phased PPAP Submission Warrant, however a Capacity Analysis Report (Refer to web link https://web.qpr.ford.com/sta/Capacity_Analysis_Report.xls for Capacity Analysis Report and supporting documentation) must be submitted with the Run-at-Rate box ticked indicating Phase 0. In addition, the supplier should have results from Run-at-Rate readily available for STA Engineer review and approval where required (see roles & responsibilities section, appendix A). Phase 1, 2 and 3 each require a Phased PPAP Submission Warrant and customer approval in line with the AIAG PPAP submission level requirements or as otherwise specified by STA (see roles & responsibilities section, appendix A). Phase 3 requires Suppliers to complete the Capacity Analysis Report in addition to the Phased PPAP Submission Warrant. Suppliers to Ford and its affiliates will utilize the Phased PPAP warrant (Appendix C). For suppliers designated as non-Q1 and suppliers/parts identified as High-Impact, STA will review and either approve or reject the PPAP submission warrant within 48 hours of the supplier indicating the PPAP is "Ready-for-STA-Inspection" in the Vehicle Parts Progress (VPP) database. Once STA has determined the PPAP status and signed the Warrant (Phase 1, 2 and 3) and Capacity Analysis Report (Phase 0 and 3), the supplier or STA's designate will enter the PPAP decision status in the Vehicle Parts Progress (VPP) database within 24 hours of receiving a STA's signed copy of the warrant. Any temporary exception due to non-compliance with a PPAP element or build timing requirement is handled in line with the Exception Management Process (refer to Appendix B). Transition: Phase 1 Approval to Phase 2 Approval - Status and Part Supply In cases where more than two production streams are to be used to support Ford's capacity requirements, the degree of complexity regarding the declaration of Phased PPAP Status and the ability to supply parts during the transition from Phase 1 to Phase 2 inevitably increases. In order to illustrate how this should be managed please consider the following example: • A supplier will be introducing a total of four production streams. In line with Phased PPAP methodology, the supplier will only be ready to submit the Phase 2 Warrant when they are able to prove that the PPAP requirements have been met for all 4 production streams. • 3 months prior to 1PP the supplier has achieved Phase 1 Warrant approval for one production stream. • As 1PP approaches the PPAP requirements for the second and third production streams have been satisfied, and the supplier wants to supply parts for 1PP from the three streams. • In order to supply these parts the supplier must have an approved, updated, Phase 1 Warrant, that declares that the PPAP requirements for the 3 production streams have been met (plus supporting data as per submission level requirements). The date for which Phase 1 requirements were achieved is not affected in reporting metrics. 11 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Expectations Phased PPAP Achievement by Build Milestone 1PP (PV1) Phase 1 100% Completed FEU (PV2) Phase 2 100% Completed Job #1 Phase 3 100% Completed The decision to progress through the FPDS Milestones is determined by the Global Launch QOS; refer to New Model Launch Team for latest version. Note: Phased PPAP achievement by Volvo build event is Phase 1: Tryout, Phase 2 and Phase 3: Job 1. Phased PPAP Reporting Expectations The preferred system to track and report Phased PPAP is VPP (Vehicle Parts Progress in CMMS3). Phased PPAP now requires suppliers to track and report on multiple promise dates. Suppliers operating in VPP must enter any remaining open Phased PPAP promise dates (Phase 0 – 3) within one full working day of the part appearing in the supplier work queue. Supplier's Approval submission via VPP is the electronic equivalent to a signed PPAP Warrant. Tier 1 Suppliers shipping to Ford must use a production part approval process for their subsuppliers. Additionally, suppliers are required to verify their sub-supplier can meet required volumes at the required time; suppliers and/or sub-suppliers may use the Ford Capacity Analysis Report and documentation. 12 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix A STA Phased PPAP Roles & Responsibilities Minimum STA Review Requirements a, b) Site Status Regardless of Site Status d) Non-Q1 Site Q1 Site f) PPAP Part Phase 0 Submisssion Run-At-Rate Status c) Level Review must be on site Phase 1 Quality Verification Phase 2 Production Verification Phase 3 Capacity Verification Review must be on site HighImpact 5 Non HighImpact 3 Phase 0, 1, 2 and 3 must be at least a desktop review Non HighImpact 1 None Documentation Capacity Analysis Report At least a desktop review PPAP submission Warrant (Phase 1), Supporting Documentation and Sample Parts PPAP submission Warrant (Phase 2), Supporting Documentation and Sample Parts Capacity Analysis Report and PPAP Submisssion Warrant (Phase 3) PPAP Outcome d, e) Approve or Reject Warrant requiring an Temporary Engineering Specification No change to the assessment requirements as defined in table above. a) For Programs utilizing Supply Base launch Teams (SBLT's) 100% of STA Tier 1 reviews will be conducted On Site for a minimum of 3 of 4 Phases. Any deviation from the minimum requirements listed above must receive STA management authorization. b) For ongoing running changes, MCR, or resourcing action: Phase 0 (Run-at-Rate), Phase 1 (Quality Verification), Phase 2 (Production Verification) and Phase 3 (Capacity Verification) will follow the minimum STA review requirements stated in the table. c) PPAP submission level is assigned per STA procedure PSP-011. d) Site may be designated Q1 or Non-Q1. e) Input into VPP is executed by the Supplier, or their Ford internal administrator, upon receipt of a signed warrant. f) Submission Level 1 suppliers self approve submission 13 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix B Exception Process Purpose The purpose of this instruction is to identify the supplier and customer responsibilities when PPAP is not complete and approved material is required to support customer manufacturing. Also, this instruction defines the process steps for achieving Interim Accepted of a part with a valid Temporary Engineering Specification. Process Flow -- Deviations to PPAP Element(s) or Timing Team Supplier New Model Launch / Manuf. Plant Product Development STA Deviation to PPAP Element(s) or PPAP Timing requirements Develop, Agree and Implement Corrective action Plan Correctable prior to Build need? Consider risks that affect successful completion and monitor accordingly Implement Corrective Action Plan No Is there a deviation to PPAP Elements? Yes Raise Temporary Engineering Specification* No Does Local Practice require Temporary Engrg. Spec. for part status that fails to support customer Timing requirements?** Approve or Reject Temporary Engrg. Spec.? Yes No Yes Update control plan & implement process control changes accordingly No Complete PPAP process and address Temporary Engineering Specification No Does this Temporary Engrg. Spec. apply to parts required for Integrated Build ***? Consider risks that affect successful completion and monitor accordingly No Yes Approve Warrant per PPAP Submission Level? Submit Warrant to the Temporary Engineering Specification with Documentation Yes Supplier develops Support/Containment Plan and submits to NML Approve Support Plan in 'Open-to-Go'? NML & Chief Engineer Supplier inputs plan information into VPP Yes Permission to Ship for Build * Notes: Temporary EngineeringSpecification: Ford = WERS Alert Land Rover = Temporary PCM Volvo = Temporary Part Deviation **Notes: If Phased PPAP timing has not been achieved as per customer requirements (normally specified in the Launch QOS) refer to NML Team for clarification on requirement for Temporary Engineering Specification. ***Notes: For programs following FPDS this refers to IB build and after. Refer to web-link: https://web.qpr.ford.com/sta/Exception_Management.pdf 14 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 No No Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix B Definitions "Approved Material" – parts with Warrant declaring "Approved" in the customer use block of the PPAP Warrant. "Temporary Engineering Specification" – temporary specification provided by the customer engineering release organization. The Ford Brand specific method for communicating these specifications is as follows: • WERS Alert (Ford/Jaguar); • Temporary Part Change Management (Land Rover); • Temporary Part Deviation (Volvo). "Full Approval" – part meets all customer specifications and requirements. "Interim Accepted" – part meets customer specifications and includes valid Temporary Engineering Specification for deviation. "Process Flow Diagram" – Deviation to PPAP Element(s) or Timing Process Flow Description Deviation to PPAP Requirements: It is the responsibility of the supplier to complete the 19 requirements of PPAP prior to the date when the customer requires approved material. Typically, there are four situations that prohibit PPAP completion: • Incomplete PPAP Element – e.g. PV testing not complete; • Deviation to requirement – e.g. dimension out of tolerance; • Parts not produced using intended production flow – e.g. rework due to urgent change, use of temporary tooling/facility, not all equipment on home-line. • Deviation to required cycle time. The team should develop, agree and implement a corrective action plan. If this plan is not complete prior to the build requirements then a Temporary Engineering Specification is needed. Deviation from PPAP Timing: It is the responsibility of the supplier to complete the appropriate Phase by the required timing as determined by the customer. If this timing is not achieved then the team should develop, agree and implement a Corrective action plan. If this plan is not complete prior to the build requirement then a support plan should be developed. Local practice determines whether a Temporary Engineering Specification is required for Deviations to PPAP Timing. Corrective Action Plan: It is the responsibility of the supplier to develop a corrective action plan that achieves Approved Material status by the required part submission date. The supplier should seek input from the customer's product development, manufacturing, and launch management to assure their concurrence with the planned corrective actions. Support Plan: If the PPAP is not complete on time a Support Plan must be developed that identifies how the supplier will support the build volume requirements, as well as, the activities to support Full Approval 15 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix B Temporary Engineering Specification: Shipment of production level parts with an incomplete PPAP requires a supplier's PPAP Warrant consistent with the requirements stated in a Temporary Engineering Specification. The Temporary Engineering Specification must describe the specific PPAP Element(s) (or timing deviations per local practice) that are not completed, the modified specification(s) that the part satisfies and the justification why the modified specification is acceptable. Additionally, the Temporary Engineering Specification shall describe how the supplier will assure quality of parts (e.g. extra ordinary controls/inspection process and robust measurement system) to the modified specification. The Temporary Engineering Specification is effective for a limited period of time, typically reflected in terms of days, quantity, or specific launch build event. Examples of Temporary Engineering Specifications: • Geometry – expanded tolerance or mean shift • PV Testing – partial completion • Functional Testing - Use of surrogate test results The Temporary Engineering Specification processes and originators differ by brand as follows: Brand Process Originator Ford Worldwide Engineering Release System (WERS) Alert Ford Product Development or Supplier with WERS access Jaguar Worldwide Engineering Release System (WERS) Alert Ford Product Development or Supplier with WERS access Land Rover Temporary Product Change Management (Temporary PCM) Land Rover Product Development Volvo Temporary Part Deviation (TPD) Volvo Research & Development, Purchasing, or Manufacturing Approve/Release Temporary Engineering Specification: The customer is responsible to approve and release engineering deviations. Typically, the customer's Product Development, Launch Management, and Manufacturing will (electronically) sign-off on the deviation, and it will be approved by the releasing activity. This approval is authorization to the supplier to proceed with the corrective actions necessary to achieve Approved Material status on a time-limited basis. Update quality control documents: Upon receiving the approved Temporary Engineering Specification from the customer, the supplier is responsible to update all affected quality control documents. The PFMEA shall be updated to determine if there are any new or changed failure modes. Additionally, items such as Gage R&R, Controls Plans, Operator Instructions and Visual Aids shall be reviewed. 16 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix B Provide PPAP Warrant: It is the responsibility of the supplier to complete a PPAP Warrant per the specifications provided in the Temporary Engineering Specification. The purpose of this Warrant is for the supplier to declare that inspections and tests on production parts show conformance to customer specifications including the Temporary Engineering Specification. The supplier must indicate the following on the PPAP Warrant section addressing Interim Status: • In the Interim Status section, check the box indicating Interim Submission • Enter the Temporary Engineering Specification number against Engineering Authorization • Provide a brief description of the reason(s) for the Temporary Engineering Specification Approve or Reject Warrant: If the Temporary Engineering Specification applies to parts to parts required for Integrated Build and subsequent builds (or Brand equivalent Build Phase) then the customer approval authority is required to either Approve or Reject the submission. Prior to this build phase the customer approval authority may choose to review the documentation at their discretion. Approval of the Warrant is the supplier's permission to ship products for a specified time period or quantity. Rejection of the Warrant means customer requirements were not fulfilled and requires the supplier to make corrections and submit a new warrant. Upon review of the Warrant and supporting evidence, the Customer Part Approval Activity completes the Customer Use section of the Warrant. • If Interim Accepted, check Interim Accepted against Phased Part Warrant Status • If Reject, check Reject against Part Warrant Disposition Warrant disposition is communicated by local practice. If a submission at any phase is due to be, or has been, rejected the STA Program Manager should be notified. The STA Program Manager may choose to utilize this Exception Management process to gain approval for the submission Actions to achieve Full Approval: The supplier is responsible to implement the corrective actions necessary to achieve a Full Approval. If Full Approval is not complete by the next launch build event, the customer should process a new or updated Temporary Engineering Specification. If the conditions within the Temporary Engineering Specification are changed, a new Warrant is required from the supplier. Timing Approved material requirements vary based upon customer as follows: • Ford, Jaguar, and Land Rover vehicle programs by the 1PP build event. • Ford, Jaguar, and Land Rover Powertrain programs by the PV (or "Powertrain 1PP") build event. • Volvo Vehicle and Powertrain programs by Try-out. 17 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix C Phased PPAP Submission Warrant 1/ Phase 1 Phase 2 PPAP Submission Warrant Status Phase 3 PART INFORMATION Part Name Customer Part Number Shown on Drawing Number Organization Part Number Engineering Change Level Date Additional Engineering Changes Date Optional Tracking Number Safety and/or Government Regulation Yes Checking Aid Number Purchase Order No. No Weight (kg) Checking Aid Change Level Dated ORGANIZATION MANUFACTURING INFORMATION Organization Name and Supplier Code Customer Name/Division Street Address Buyer/Buyer Code State/County/Province City Zip Country Application REASON FOR SUBMISSION Initial submission Change to Optional Construction or Material Engineering Change(s) Sub-Supplier or Material Source Change Tooling: Transfer, Replacement, Refurbishment, or additional Change in Part Processing Correction of Discrepancy Parts produced at Additional Location Tooling Inactive > than 1 year Other - please specify below REQUESTED SUBMISSION LEVEL (Check one) Level 1 - Warrant only (and for designated appearance items, an Appearance Approval Report) submitted to customer. Level 2 - Warrant with product samples and limited supporting data submitted to customer. Level 3 - Warrant with product samples and complete supporting data submitted to customer. Level 4 - Warrant and other requirements as defined by customer. Level 5 - Warrant with product samples and complete supporting data reviewed at supplier's manufacturing location. DECLARATION and SUBMISSION RESULTS I affirm that the samples represented by this warrant are representative of our parts which were made by a process which meets all current edition Production Part Approval Process Manual requirements including all Ford-specific requirements. I further affirm that hours using these samples were produced at the production rate of ________ / production streams. I also certify that documented evidence of such compliance is on file and is available for review. I have noted any exceptions from this declaration below. EXPLANATION/COMMENTS List Molds / Cavities / Production Processes: (Attach a separate page if additional space is necessary) Supplier Authorized Signature Date Print Name Phone No. Title Fax Email FOR FORD USE ONLY PPAP Phased PPAP Warrant Status: Non-PPAP . Approved Rejected Interim Status (to be completed by Supplier) a/ . Interim Accepted Interim Submission: Engineering Customer Signature Print Name . Date . . Alert, Temp. PCM, TPD Number Description: . a/ Non-PPAP indicates the part does not satisfy one or more PPAP requirements and is considered incomplete until all PPAP requirements are satisfied. 1/ Authorization: . (Open Issues) Refer to web-link: https://web.qpr.ford.com/sta/Phased_PPAP_Warrant.xls 18 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 . Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix D PPAP Requirements as Noted in the Phased PPAP Process Map # Requirement 1 Design Records 2 Engineering Change Documents 3 Customer engineering Approval 4 Design FMEA 5 Process Flow Diagrams 6 Process FMEA 7 Control Plans 8 Measurement System Analysis Studies 9 Dimensional Results 10 Records of Material/Performance Test Results 11 Initial Process Studies 12 Qualified Laboratory Documentation 13 Appearance Approval Reports 14 Sample Production Parts 15 Master Sample 16 Checking Aids 17 Customer-Specific Requirements 18 PPAP Warrant 1/ Bulk Material expectations are not addressed within Global Phased PPAP requirements. 19 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005 1/ Phased PPAP Requirements Handbook Ford Appendix E Acronym List STA - Supplier Technical Assistance PPAP - Production Part Approval Process PSW - PPAP Submission Warrant TACT - Total Actual Cycle Time EOL - End of Line DPV - Daily Production Volume CPV - Capacity Planning Volume IPD - In Plant Date (to a program build event) 1PP - 1st Production Prove-Out Units (at customer plant) FEU - Field Evaluation Units (at customer plant) VPP - Vehicle Parts Progress AIAG - Automotive Industry Action Group FPDS - Ford Product Development System WERS - Worldwide Engineering Release System PM Parts - Part Process Modification TIKO - TidsInformationKöpOrder (Part Information and Order System) PTIS - Part Tracking Information System 20 XOFRD004 - Rev. Date 12/04 - Eff. 5/5/2005