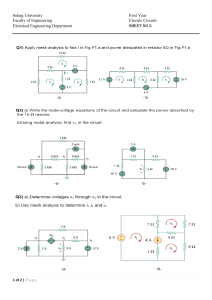
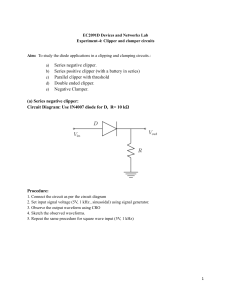
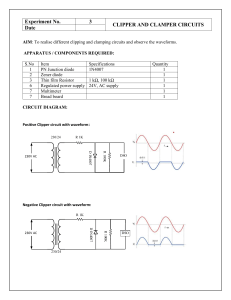
University College of Science and Technology-UCST Department of Engineering and Applied-Art Computer Systems Engineering Electronic Circuits (1) / Lab. Exp. # 5 Name of Exp / clipper and clamper Student Name: Ameer Wael Talat Elfarra Student No.: 120217022 Supervisor : Eng. Yousef Al-Mutayeb Date of Exp. م3/5/2023 2022-2023 Experiment No.6 Clipper and Clamper Objective: The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate the operation of diode clipping and clamping circuits. Theory In addition to the use of diodes as rectifiers, there are a number of other interesting applications. For example, diodes are frequently used in applications such as wave-shaping, detectors, voltage multipliers, switching circuits, protection circuits, and mixers. In this experiment, we will investigate two widely used applications of diode circuits, namely diode clipping circuits and diode clamping circuits Types Of Clipper Diode Circuit : Types Of Clipper Diode Circuit : Equipment: 1. Function Generator 2. Dual-Channel Oscilloscope 3. DC Power Supply 4. Electronic Test Board 5. Resistors 1K , 68K 6. Silicon Diode 1N4007 7. Leads and Adaptors Procedure: 1. Connect the biased series clipping circuit shown in Fig and apply a 6Vpp sinusoidal input waveform with frequency of 1 kHz at the input. Display and sketch the input and the output waveforms. 2. Connect the biased parallel clipping circuit shown in Fig. and apply a 6Vpp sinusoidal input waveform with frequency of 1kHz at the input. Display and sketch the input and the output waveforms. 3. Connect two biases level clippers as shown in the fig and apply 6 vp sinusoidal input waveform with frequency of 1 kHz at the input. Display and sketch the input and the output waveforms 4. Connect the clamping circuit shown in Fig and apply a 10Vpp sinusoidal input waveform with frequency of 1 kHz at the input. Display and sketch the input and the output waveforms Comments : 1. Bias source affect waveform in Clipper circuit as a cut in the wave .2. Clamper circuit is an electronic circuit that shifts the DC level of a signal without changing the shape of its waveform. It moves the whole signal either up or down about the reference level .