Clippers -- Overview Lab Overview Equipment Theory
advertisement

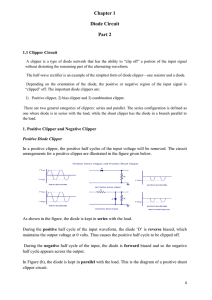
Clippers -- Overview Lab Overview After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: • Design positive and negative shunt clipper • Design positive and negative series clipper • Build the clipper circuit and observe the output Equipment To carry out this experiment, you will need: • TBS 1000B-EDUOscilloscope from Tektronix. • Voltage probe (provided with oscilloscope) / BNC cables • Breadboard and connecting wires • Circuit components - Resistor 1K, 0.25W, Diode 1N4002 /IN4148/equ, Regulated DC supply 0-30V DC, Signal /Function generator 10Hz to 1 Mhz Theory • Clipping circuits are used to select and transmit a part of the given waveform. The other parts of the waveform are clipped or removed by the diode clipper circuit. • These circuits are also known as voltage or current limiters, amplitude selectors or slicers. • The piecewise linear model of diode characteristic exhibits a discontinuity in slope at the cut off voltage Vk. and this point of slope discontinuity is called a break point. • For silicon diode the break point occurs at VK ~ 0.7V. This concept can be used to explain the transfer characteristics of a clipper circuit, which is a plot of output voltage against the input voltage. Design • The limiting resistor R in the circuit can be designed in the following manner. • From the diode forward and reverse characteristics, the resistance in either direction can be determined, respectively, as Rf and Rr. It can be shown that limiting resistor R = . • The ratio Rr/Rf can be called the figure of merit of the diode. From V-I characteristics of diode, we have Rf= 20 Ω and Rr = 1 MΩ. From these values, limiting resistor required is R = 3.3 KΩ (std), ½ watt and we can use 1KΩ to 5K Ω. Circuit Diagram Biased Clipping Circuits Clippers -- Procedures Step 1 Study the circuit, expected waveform and transfer characteristic. Step 2 Place the components on bread board or connection board and connect them as per given circuit diagram. Use patch cords/ wires for connection as required. Step 3 Switch on the signal generator and set voltage to 10V P-P and frequency to 1kHz Step 4 Set DC voltage to 2 V in case of biased circuits Step 5 Connect the input and output of the circuit to the two channels of the CRO. Observe the input and output ( in DC mode only) waveforms and ensures that it matches with expected wave form. Step 6 Measure the voltage amplitude, clipping voltage using CRO. Keep CRO setting in XY mode and observe the transfer characteristic. Step 7 Draw the waveform on graph sheet. Step 8 Repeat this for all clipping circuits. Step 9 Expected Input and Output waveforms Step 10 Result Clipper circuits have been tested and out put wave forms match with the expected waveforms.