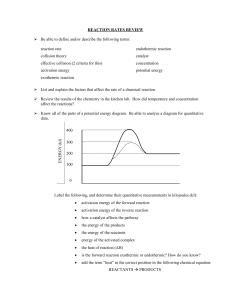
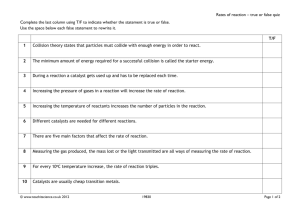
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Regional Office IX, Zamboanga Peninsula 10 Z est for P rogress Z P eal of Science Grade 10 Quarter 4 - Module 7 Collision Theory and the Factors Affecting the Rates of Chemical Reactions: Catalyst and Temperature Name of Learner: __________________________________ Grade & Section: __________________________________ Name of School: ___________________________________ 1 artnrship Module Collision Theory and the 7 Factors Affecting the Rates of Chemical Reactions: Catalyst and Temperature What I Need to Know This module is prepared to facilitate your understanding and learning of some of the essential concepts and explain how the factors affecting rates of chemical reactions are applied in food preservation and materials production, control of fire, pollution, and corrosion (S10MT-IVh-j-24). The primary goal of this module is to engage you in simple interactive activities to explore concepts related to chemical reaction and how it is being applied to real-life situations. After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. Describe Collision Theory; 2. Discuss how temperature and catalyst affect the rate of chemical reactions; 3. Explain how temperature and catalyst are applied in food preservation and materials production, control of fire, pollution, and corrosion Among the questions, most people ask about the daily occurrences in life: Why does raising the temperature shorten the cooking time? Why does a log of wood take a longer time to burn than small pieces of wood? Why do fruits ripen when kept in a warm place? Why does a baker put yeast in baking? How does yeast help in fermentation, specifically in winemaking? What does a chemical reaction rate tell you? It tells you how fast the reaction takes place. What factors cause chemical reaction rates? Factors that affect the chemical reaction rate include temperature and catalyst. 2 What’s In 10 Activity 1A: When Collision Takes Place Direction: Complete the table by indicating whether each of the scenarios would increase or decrease the rate of chemical reaction. Scenario Increase or Decrease 1. Increasing the temperature 2. Decreasing the temperature 3. Adding an enzyme/ catalyst 4. Decreasing the enzyme/ catalyst 5. Lower the activation energy Activity IB. Direction. Complete the table by indicating what factor would have the most significant impact on a chemical reaction rate. Write the word catalyst and temperature. Scenario Factor that has a great impact on the rate of chemical reaction 1. Carbohydrates are broken down in the small intestine by the enzymes sucrase and lactase. 2. Increasing the temperature while cooking. 3. Blowing air on fire to help it keep going. 4. In a polluted atmosphere where sulfur dioxide concentration is high, calcium carbonates deteriorate more rapidly than in less polluted air. 5. Putting food inside the refrigerator to prevent it from spoiling. 3 What’s New 5 These simple science activities describe how collision theory takes place and demonstrate how catalyst and temperature affect the rate of chemical reaction. Activity 2A: When Particles Collide.. Task: Analysis of molecular representation of collision theory Source: http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/3082/3156859/blb1404/bl14fg16.jpg accessed: Oct.29, 2014 Source: http://i.ytimg.com/vi/OkGzaSOkyf4/maxresdefault.jpg (accessed: Oct.29, 2014) The illustrations above show the effective and ineffective collision of molecules to effect a chemical reaction. Guide Questions: 1. What causes a chemical reaction? ( 1pt.) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 2. What must happen for a chemical reaction to take place? (2 pts.) ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 4 3. Describe an effective chemical reaction resulting to a formation of products. (2 pts.) _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Activity 2B: Relax, Have a Coffee Break 5 Materials Needed: 2 Sachets Coffee powder 2 Cups Coldwater Hot water 2 tsp sugar 2 tsp of milk Hot Coffee Cold Coffee Procedure: 1. Pour the coffee into the cups. (Hot water for Cup A and Cold Water for Cup B). Pour 1 tsp of sugar and milk in each cup 2. Stir the contents of Cup A and do not stir the contents of Cup B 3. Taste the mixture in each cup. Guide Questions: 1. Which coffee mixture tastes better? Why? (2 pts.) ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 2. Does temperature affects the taste of the mixture? Why? (2 pts) ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. Does stirring affect the taste of the mixture? Why? (2 pts) ___________________________________________________________ 5 ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Activity 2C. Let’s Make Some Bubbles! Materials Needed: Transparent Glass • • 3% Hydrogen Peroxide ( Agua Oxinada) Detergent solution (Mix 1tsp of detergent powder/liquid to 2 tsp. of water) • • • Yeast Dropper Popsicle stick Procedure: 1. Add 10 ml of hydrogen peroxide to a transparent glass. Add 1 drop of detergent solution. Stir gently and watch the solution for bubbling. 2. Use the end of the Popsicle stick to add a small amount of yeast to the hydrogen peroxide. Stir the solution. 3. Observe the solution. Guide Questions: 1. What will happen to the hydrogen peroxide if you add the yeast to it? (2 pts) ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. What is the catalyst in the activity? (2 pts) ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 6 What is it COLLISION THEORY Collision theory explains how the collision between reactant molecules may or may not result in a successful chemical reaction. There must be an effective collision of particles for a chemical reaction to take place. Based on this theory, not all collisions between the molecules result in the formation of products. Effective collisions between molecules, which result in the formation of products, only occur when the following two conditions are met: (a) the colliding molecules should possess minimum kinetic energy, known as activation energy, to start a chemical reaction. (b) the reactant molecules should be in the correct orientation when they collide In 1888 Svante Arrhenius suggested that particles must possess. A certain minimum amount of kinetic energy to react. The energy diagram is shown below. Energy diagrams are used to analyze the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. The energy of the reactants must be raised over an energy barrier. Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a reaction and force the reactants to form an activated complex. The activated complex is located at the peak of the energy diagram for a reaction. 7 Catalysts It is a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions. The very common examples for this are the Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration. Biological systems use catalysts to increase the rate of the oxidation reaction so that it can occur at a faster rate at lower temperatures. Catalysts are everywhere! Many biochemical processes, such as the oxidation of glucose, are heavily dependent on enzymes, proteins that behave as catalysts. Catalysts increase the rates of chemical reactions. This is due to lowering of the activation energy for the reaction. Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction so in theory, they can be used over and over again. In practice, they are often contaminated and/or some is lost in a process. Temperature Chemical reactions typically occur faster at higher temperatures. Food can spoil quickly when left on the kitchen counter. However, the lower temperature inside of a refrigerator slows that process so that the same food remains fresh for days. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of reaction. At higher temperature, atoms have higher kinetic energy, making the particles move faster and therefore increase the chance for the particles to come in contact with each other. Key point: at a higher temperature more molecules have energy greater than the activation energy. 8 This is also the reason why most fruits and vegetables ripen in the summer when the temperature is much warmer. When a banana ripens, numerous reactions occur that produce all the compounds that we expect to taste in a banana. But this can only happen if the temperature is high enough to allow these reactions to make those products. Food storage is a prime example of how the temperature effect on reaction rate is utilized by society. Consumers store food in freezers and refrigerators to slow down the processes that cause it to spoil. The decrease in temperature decreases the rate at which food will break down or be broken down by bacteria. What’s More 5 Activity 3: Tell Me What Directions: Tell whether the following images are related to temperature or catalyst.(5 pts.) Refrigeration 1. ___________________________ 2. _________________________ Pollution 9 3. _______________________________ Photosynthesis Yeast 4. _______________________________ ______________________________ 5. 5 What I Have Learned Activity 4: Let’s see what you have learned! Directions: Complete the statements by underlining the appropriate word or phrase. (2pts each.) 1. For the reaction to occur, reacting particles must (collide, move) and this collision must be effective. 2. (Activation Energy, Enough Energy) is the energy required to initiate a reaction and force the particles to form an activated complex. 3. The (higher, lower) the temperature, the higher the rate of chemical reaction. 4. (Catalysts, Energy) increase the rates of chemical reactions. This is due to lower of the activation energy for the reaction. 5. (Enzyme, Lipids) are proteins that act as a catalyst in biochemical reactions. You did it! Keep up the good work. This would help you understand the factors that affect the chemical reaction. There’s more that you can do. 10 10 What I Can Do Activity 5: You can do great Directions: A. Choose from the words on the box that will make the statement complete. ( 2 pts. each) -collide -Chemical Reaction -effective - Activation Energy - products Collision theory explains how the collision between reactant molecules may or may not result in a successful ___________________.There must be an __________________________ collision of particles for a chemical reaction to take place. Based on this theory, not all collisions between the molecules result in the formation of __________________. Effective collisions between molecules, which result in the formation of products, only occur when the following two conditions are met in which the colliding molecules should possess minimum kinetic energy, known as ______________________, to start a chemical reaction. (b) the reactant molecules should be in the correct orientation when they ______________________________. B. Directions: Study the pictures below. Identify the factor that affects the rate of the chemical reaction. Write catalyst or temperature. 1. 2. Cooking Meat Decomposition _______________________________ ____________________________ 11 3. 4. Air Pollution Corrosion ______________________________ _____________________________ 5. Catalytic Converter ________________________________ Post Assessment (Set A) Directions. Encircle the letter of the best answer. 10 1. It refers to the minimum energy required for reactions to start. A. Activation energy C. Potential energy B. Kinetic energy D. Stored energy 2. Which of the following is not a factor that affects the reaction rates? A. Reactant concentration C. Particle size B. Catalysts D. Shape of particles 3. What is the name of the theory which is used to explain how different factors affect the rate of a reaction? A. Big bang Theory C. Continental Theory B. Collision Theory D. Particle Theory 4. Which of the following would speed up a chemical reaction? A. Adding some water C. Increasing the temperature B. Decreasing the temperature D. Increasing the volume 12 5. What criteria must be met for reactant collisions to result in a successful product formation? A. Activated complex and energy C. Collision, enough energy B. Collision of the reactants D. All of these 6. What does a temperature do to the reactants during a chemical reaction? A. It increases the volume of reactants C. It makes the reactants big B. It increases the average speed of the reactant D. All of these 7. Why does increasing the temperature of the reactants increase the rate of a chemical reaction? A. Heat energy causes the particles of the reactants to move faster, and therefore react with each other more frequently B. Heat energy causes some of the reactants to evaporate, increasing the concentration of the reactants C. Heat energy increases the size of the molecules of reactants, and therefore the molecules react more frequently D. Heat energy helps to lower the amount of overall energy that is required for the reaction to occur 8. Why do foods stored in refrigerators? A. Bacteria do not grow well in dark places B. Refrigerators often contain enzymes that slow the rate of food spoiling C. The lower temperatures cause the chemical reactions that spoil food to occur more slowly than usual D. The volume inside the refrigerator decreases the concentration of the food particles, allowing them to decompose more slowly 9. Enzymes are an important component of the human body. It can affect the rate of a chemical reaction. What are enzymes? A. Catalysts C. Molecules B. Dust particles D. Simple Elements 10. Which of the following situations in which temperature and catalysts are applied? A. Baking C. Decomposition B. Corrosion of metals D. All of these Assessment (Set B) 10 Directions: Encircle the letter of the best answer. 1. What is required for a chemical reaction to occur? A. Collision C. Energy B. Collision with sufficient energy D. Temperature 2. Which of the following will lower the activation energy of a reaction? A. Adding a catalyst C. Removing a catalyst B. Increasing the temperature D. None of these 3. Which of the following would NOT increase the rate of reaction? A. Adding catalyst 13 B. Increasing the concentration of the reactants C. Increasing the volume of the container D. None of these 4. Which of the following statements about collision is correct? A. All colliding particles have the same amount of energy B. Only fast-moving particles collide with each other C. Reactions can happen if the colliding particles have enough energy D. Reaction will occur even without collision of particles 5. Why do fruits easily ripen during the summer season? A. Heat lowers the activation energy of the reactants B. High temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction C. Molecules are heavy during the summer season D. All of these 6. What does incomplete combustion do on the car engine? A. It provides fuel to the engine C. Produces Oxygen B. It Pumps fuel D. Produces Carbon Monoxide 7. What will you do to prevent/ control fires? A. Don’t refuel gasoline-powered equipment while it is hot B. Keep flammable liquids stored in a tightly closed container C. Use flammable liquids in a well- ventilated areas D. All of these 8. What does a catalyst do in a chemical reaction? A. Cools down the reaction C. Increases the rate of the reaction B. Increases the concentration D. Stabilizes the chemical reaction 9. Enzymes are catalysts that hasten the chemical reaction. Which of the following processes involved enzymes? A. Cellular respiration C. Photosynthesis B. Decomposition D. All of these 10. Which of the following is/are considered as polluters come from the burning of fuel? A. Coal C. Oil B. Natural gas D. All of these 14 Additional Activities 10 Activity 6: Let’s add more! Direction: TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE if the statement is correct. If it is incorrect, write false and underline the incorrect word. ___________ 1. Effective collision results to product formation. ___________ 2. Effective collision is defined as one in which molecules collide with sufficient energy and proper orientation. ___________ 3. Collision between reactant molecules may or may not result in successful chemical reaction. ___________ 4. All collisions between molecules result in the formation of products. ___________ 5. The only condition needed for effective collision is the correct orientation of the reactant molecules when they collide. ___________ 6. Activation energy is needed to break the bond between reactant molecules to form new bonds leading to the formation of the products. ___________ 7. Molecules must collide with sufficient energy even with no proper orientation in order for a chemical reaction to occur. ___________ 8. When the temperature of the reactants is increased it will lead to higher activation energy. ___________ 9. Flame is a source of activation energy so firecrackers must be kept/stored in cool dry place to prevent unexpected explosion. ___________ 10. The “No Smoking” signs in gasoline station is irrelevant because gasoline is not combustible. 15 Answer Key- Gr10-Q4W7 Science 16 17