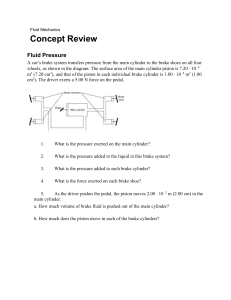
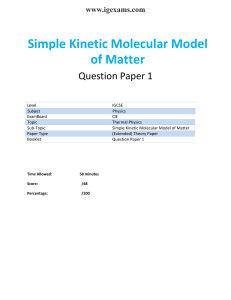
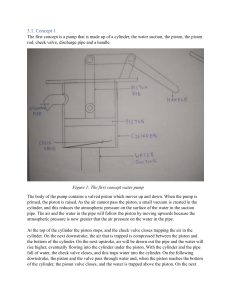
EGN 3343 (Summer 2023) – Homework 1 Submission Deadline 12 June (Monday) midnight th Write your name and page number at the top right-hand corner of each page of your homework. Scan your homework as a single pdf document and upload it in canvas by the submission deadline. Homework Question 1: Homework Question 2: Is the process reversible? Why? Homework Question 3: Is Internal Energy a point or a path function? Is work done a point or a path function? Homework Question 4: What assumptions are we making when we state ∆E = ∆U. 1/4 Homework Question 5: What type of a cycle is it? Homework Question 6: What type of a cycle is it? 2/4 Homework Question 7: You can use any software like Matlab or Excel to find n. Homework Question 8: A piston–cylinder assembly contains air, initially at 2.5 bar, 300 K, and a volume of 2 m3. The air undergoes a process to a state where the pressure is 1 bar, during which the pressure–volume relationship is pV = constant. Assuming ideal gas behavior for air, determine the mass of air, in kg, and the work and heat transfer, each in kJ. Kinetic and potential energy effects can be neglected. 3/4 Homework Question 9: As shown in Figure below, 2 kg of air fills the cylinder of a piston–cylinder assembly. The initial volume and pressure are 2 m3 and 1 atm, respectively. Heat transfer to air occurs at constant pressure until the volume is doubled. Assuming ideal gas behavior for air, determine the heat transfer for the process, in kJ. Kinetic and potential energy effects can be ignored. Homework Question 10: Air contained in a piston–cylinder arrangement, initially at 6 bar and 400 K, undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 K, during which the pressure–volume relationship is pV1.2 = constant. Assuming the ideal gas model for the air, determine the final pressure, in bar, and the work and heat transfer, each in kJ/kg. 4/4