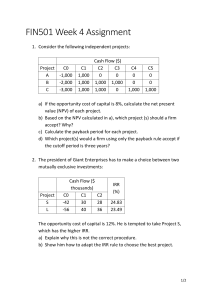
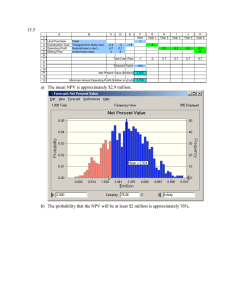
F9 KIT NOTES PE ratio If it increases over the years, the market is increasingly more confident in the future of the company If it decreases over the years the market is not so confident in the future of the company Stakeholders Local community : They will be interested in the financial success of the company as this would potentially generate jobs and wealth in their region. They might also be inclined to understand the treatment and disposal of waste that the company’s production might generate. They will be more aware about the environmental impact of the company and its actions to protect the against the pollution Customers : They would like to keep the pricing of the goods at an optimum and reasonable level according to market standards. They would also like to make sure that they have a constant, safe and reliable supply of water or any other good that they produce. Government : the government will be keen to know if the company performs exceedingly well, in order to improve the tax receipts. Moreover they would be interested in ensuring compliance with environmental legislation and other required laws. They have to make sure that the business is adhering to all the relevant requirements and standards. Government Intervention Monopolistic Market If the company operates in a monopolistic market , the government can see if it is justifiable as some industries require higher degree of investment and therefore there might not be a lot of competition in that sector. This would give the existing company an upper hand to ensure that the company maintains reasonable prices which can be done using government control prices thus this would also limit the return the company can make. Since this company would also be the only provider they government might also impose certain required service standards that it would have to give its customers Other than this the government will also have to ensure that this company works with an acceptable standard and adheres to all the relevant legislation and produces the products without extreme damage to the environment. If the commodity is an essential it would also have to ensure that the country’s anticipated needs for the forthcoming year or the significant future it met without any problems. Nationalized VS Privatisation Nationalized This is when the government decides to nationalize an industry it would generally have different objectives. The main objective being to provide the commodity within a reasonable price or the service to the public. These objectives would be generally tied to the overall development of the society and would have the basis of economic development of the backward or areas which lack infrastructure or access that the government may wish to develop. The secondary objectives would be to meet the minimum rate of return, however sometimes the government might have negative returns for the longer term perspective of development or for political objectives. Privatized The company would have its primary objective to maximize the shareholders wealth. This would be in combination with certain other relevant non financial objectives such as employees work environment, market share and provision of good service to their customers Investment Appraisal Nationalized The nationalized industry would have the strategic planning done by the government. Decisions such as the amount of capital and the source to raise funds are given by the government to the management. The tactical and day to day decisions are taken by the management of the company Therefore the appraisal for such companies would be measures such as budgetary control, return on capital and ensuring whether the government targets are met Privatized The privatized industry would be influenced by the market forces and their main objective would be to ensure that the shareholders wealth is maximized. The management is responsible for both strategic and tactical decisions Appraisal techniques used here would discounted cash flows,budgetary control Failure to meet these objectives may lead to a decline in share price and major losses for the company in the long run Conclusion The objectives of both these industries vary along with prioritization of profits and wealth maximization objectives. The consequence of failure is higher with the private sector Multiple Stakeholders Multiple objectives Objectives of the management conflicting with the objectives of the shareholders Management remuneration package is one way in which goal congruence between managers and the shareholders can be increased. Such packages should motivate managers which still supporting the achievement of the shareholder wealth maximization - Clarity and transparency - Appropriate performance measure : - Quantitative performance measure - Time horizon - Impartiality - Discussion of Interest Rate Risk - Calculate required ratios - Variable interest Payment,Fixed Interest, Fixed Debt/Equity, Total Debt to equity, Interest Coverage ratio, Ratio of the fixed debt in relation to the total debt - It refers to the ratio of debt between fixed and variable interest rates and debt - Compare the percent of debt to equity and the variable and fixed portions of it and see if this is sustainable. Comment on whether the company should halt any further usage of debt in the form of variable debt which can cause concern in the future. - Interest coverage ratio would the number of time the operating profit can be used to cover the financing cost of the company in terms of interest payments, when this has dropped by a number of times in comparison, one can assume that it is a slight cause of concern on being able make the financing cost payments with regard to the debt that the company has taken in the future. - The ratio in which the fixed debt and the variable debt make up the debt structure can also be given importance and commented upon. - When there are long term debts included the debt structure, there exists long term protection against and increase in interest rate risk - Variable interest can also be called floating rate debt and when this increases, it would increase the financial risk of the company. - Further, the increase in interest rate payment can also decrease the profit before tax amounts even though there might be an increase in revenue for the year. - One method that can be used to hedge against the increase in interest rates would be to exchange a portion or all of the variable rate overdraft to a fixed rate long term debt. Although there might be an increase in cost for the payment of the debt since long term debt is more expensive. It would also not be able to benefit from the fall in interest rates if the debt is fixed rather than variable. - Taking steps to decrease the dependency on the variable rate overdraft finance Overtrading Discussion - Overtrading in essence would mean the company is undercapitalised and therefore it would be relevant to calculate financial ratios such as inventory days, receivable days, payable days, current and quick ratio. Along with these ratios the changes in the assets between the two years could be shown in percentage. - Overtrading arises when the company has a small capital base to support the level of activity that it conducts in the business. - Difficulties in relation to liquidity may arise as an overtrading company may have insufficient capital to meet its demands. - Comparing the significant increase in the revenue has to usually match the increase in the required capital to sustain that increase. When such an appropriate increase is not found the company can find it difficult to sustain and manage the liability dues when they fall short - Overtrading can also be found by the deterioration in inventory days. When the inventory days are compared to the revenue it can be found that it is possible that the company has been stockpiling inventory in anticipation of future sales - The significant increase in revenue could be due to relaxation in credit terms. - The liquidity problem can also be seen as the company increases its reliance on short term sources of finance being the overdraft and the trade payables. - Decrease in the current ratio and quick ratio is also an indication of overtrading. - Comparison with other significant ratios with industry standards or benchmarks would give us a better understanding and help establish trends Factors that determine the level of investment in the current assets - The relative importance of each of these factors are given a different level of ranking from company to company - - - - Length of the working cycle: The working cycle or the operating cycle refers to the period of time between when a company settles its accounts payable and when it receives cash from its accounts receivable. Operating activities during this period need to be financed. The longer this period is, the amount of finance also increases. Terms of trade: Although this is an extension of the previous point, the amount of credit period that the company extends to its customers, any discounts offered for early settlement discounts or bulk purchase discounts and any penalties have to be factored in. A company with more generous credit terms would be likely to require more investment in current assets. Policy on the level of investment in current assets will depend on the level of risk the company is willing to take. A conservative approach would be to maintain higher levels of inventory, offer generous credit terms and have a higher cash reserve than a company with a comparatively aggressive approach. An aggressive approach would however be more profitable due to the lower level of investment in current assets Industry in which the organization operates: If the industry has the long term cycle standard. Such as aircraft industry vs grocery. Factoring discussion - Factoring involves a company turning over the administration of its sales ledger to a factor, which is a financial institution with expertise in this area. - The factor will assess the creditworthiness of the new customers, record sales, send out statements and reminders, collect payment,identify late payers and chase them for settlements and take appropriate legal action to recover debts where necessary. - The factor will also offer finance to the company based on the invoices raised of the goods sold or the services provided. - This is usually about 80% of the face value of the invoices raised, the finance is repaid from the settlement of the invoices by the customers,with the balance being passed on to the company with the deduction of the fee that it charges for the services that it provides - If it is factoring without recourse, the factor rather than the company will carry the cost of the bad debts that arise on overdue accounts. It offers credit protection to the company although the factor fee will be comparatively higher. Bad Debts reduction When the bad debts have increased, the company should introduced new policies - Assessing the creditworthiness of the customers and checking for credit history and making appropriate changes - When the average receivable days increase or exceeds from the actual extended period then company would actually incur opportunity costs from not investing that amount and would also incur costs for the short term source of finance interest that it would need in order to fill the requirement - Should encourage accounts receivable to be settled closer to the agreed date - Should check if the receivables are managed appropriately and if it is does in an efficient manner-receivable analysis,credit denied to overdue customer EOQ Assumptions and discussion - The evaluation is based on unrealistic assumptions where the ordering cost and holding costs are constants which are never usually the reality. - Annual demand is also assumed to be constant Working Capital Investment Policy - This is concerned with the level of investment in current assets, with one company being compared to another. - Working capital investment policy has to be assessed on an inter company comparative basis Here the terms aggressive and conservative are used according the amount of investment it has in current assets. The higher the investment in current assets the more conservative and the lower the investment in current assets the more aggressive. This is usually in relation to another company. Working Capital Financing Policy - This is concerned with the relative proportions of short term and long term finance used to source the working capital needs of the firm - This involves assessing the financial information of one company alone - It analysis how the current assets are segregated - permanent current assets and fluctuating current assets - Permanent current assets represent the core level of activity that the company undertakes to support the level of business activity. As the company’s revenue increases the core level of permanent current assets increase. This can be measured by the ratio of revenue to net current assets - Fluctuating current assets represents the changes in the level of current assets that arise due to unpredictability of the business operations - Working capital financing policy relies on the matching principle. This holds that long term assets should be funded using long term finance. Non current assets should therefore be financed through a long term source of finance such as equity or loan note finance. - Fluctuating current assets should therefore be funded using short term sources of finance such as overdraft or short term loan. - The terms conservative, moderate and aggressive are terms used to indicate the type of finance used to match with the type of asset - An aggressive financing policy means that the fluctuating current assets and a part of the permanent current assets are funded through short term sources of finance. This is usually more profitable as the cost of short term finance is lower but however the risk is higher - A conservative financing approach would mean that the permanent current assets and a part of the fluctuating current assets are financed through long term finance. This is usually less profitable as it is a more expensive source of finance. However this is less risky. - Its important to note that short term finance is more flexible than long term finance. Credit granted to foreign customers - The problem that the longer the distance the period of the transaction the more complex the elements become. Longer receivable periods means loss of opportunity costs and the need to finance this gap using other sources of finance and the finance costs that would be incurred in relation to this. - The risk of bad debts is higher with foreign counterparts - Many foreign transactions are on an open account which is an agreement to settle the amount outstanding at a predetermined date. Open account reflects good business relationship between the importer and the exporter. It also carries the highest risk of non payment. - One way to reduce investment in foreign accounts would be to offer early discount payments with an importer such as payment in advance, on delivery, shipment - Another method that can be used is bill finance which can be gotten from the importer to agree for payment on a certain date with the letter of credit , this can then be discounted with the bank to obtain immediate funds - Companies can also manage and reduce risk by checking the overall credit worthiness of the importer with bank references and credit reports. - Insurance for the foreign customers can also mitigate some of the risks - Documentary letters are payment guarantees which are backed by more than one bank. They carry almost no risk, provided the exporter complies with the rules Factors to be considered while formulating trade receivable policy - A key factor would be to analyze the turbulence in the company’s business environment - Credit analysis : this would ensure that credit is granted to customers who settle their accounts at regular intervals in accordance with agreed terms. The risk of bad debts would be minimized - The quality and source for this information should be reliable, such as bank reference, trade reference - Credit control: It is essential that agreed terms and conditions are adhered to while customer credit is outstanding. This can be achieved by monitoring customer accounts and period preparation of aged receivables analysis - Collection procedures:Ensure timely transfer of funds - Usual credit period offered in the industry Profitability and liquidity are twin objectives of working capital Factors that determine working capital policy - Industry - Management attitude and efficiency - Working capital investment policy : This can be either conservative while giving out generous credit terms and keeping high levels of inventory Advantages of using factoring - Scale of economies - Economies of the industry - Free up management time - Bad debt insurance - Accelerate cash flow - Finance through growth ROCE - Disadvantages - ROCE can be expressed in a variety of ways: this is therefore more susceptible to manipulation. Each of the various methods would give rise to different ratios and computed rate of return - ROCE is also susceptible to variation in accounting policy by the same firm over time or as between firms at the same point of time. DIfference in treatment of depreciation would produce different profit figures and hence different rate of return - The most fundamental disadvantage would be that is based on accounting profits expressed net of deduction for depreciation provisions rather than cashflow, the capital cost is allowed for twice, both in the numerator and the denominator. This is likely to depress the measured profitability of a project and result in rejection of some worthwhile investment. - It simply averages the profit instead of considering the time value of the returns of the project Although there are the above stated disadvantages, - The continued usage of ROCE can be attributed to its usage of manager friendly terms of the financial statement such as profit and capital employed. - The impact of the project on the company’s financial statements can also be specified - It is the most common way that a company evaluates its business project and it is the most visible to the shareholders. - It is more suitable since the managers are more keen on expressing the attractiveness of the project in the same way their performance is assessed by the shareholders. Dangers of lenient receivables collection policy - It implies that credit will be extended to customers for whom the ability to repay might be a little lower - This would increase the chance of higher default rates - Capital would be tied up in current assets and therefore would forego opportunity cost - The financing cost of higher receivable days Sensitivity Analysis - Indicates which project variable is the key or critical variable, that is the variable in which the smallest change could make the NPV of the project zero. NPV advantages - Other methods such ROCE compare the average profits with the initial investment, however NPV considers cash flow which is often preferred in financial management - This is mainly because profits can be manipulated, furthermore cash flows are capable of adding wealth to the shareholders in the form of increased dividends. IRR and payback also consider cash flows - NPV considers the whole investment: with respect to Payback, which considers only the cashflows during the payback period, not before and after. This is also a drawback of discounted payback - NPV considers time value of money: Discounted payback considers TVM but ignores cash flows outside the period. IRR and NPV consider TVM. This is essential as otherwise cash flows arising from different times cannot be distinguished from one another from the perspective of the current value - NPV is an absolute measure of return: IRR and ROCE provide a relative measure of return, however NPV is able to reflect the absolute increase in corporate value - NPV links directly to the objective of maximizing shareholders wealth: It represents the change in the market value that will occur if the project is accepted. The increase in wealth of each shareholder can therefore be measured by the increase in the value of their shareholding as a percentage to the overall issue share capital of the company - NPV offers correct investment advice: with respect to mutually exclusive projects NPV always indicates which project to be selected in order to maximize the shareholder’s wealth. This is the drawback of IRR which offers incorrect advice at rates which are less than the IRR of the incremental cash flows - NPV can accommodate discount changes whereas IRR completely ignores them since the IRR is independent of the cost of capital in all time periods. - Reinvestment of the intermediate cash flows at the company’s cost which is a reasonable assumption, whereas the assumption for IRR is that the cashflow is reinvested at the IRR which is not the investment rate available in practice. - NPV can accommodate non conventional cashflows which exist when negative cash flows arise during the life of the project. For each change in sign, there is potentially one additional IRR. With non conventional cashflows, IRR can suffer from the technical problem of giving multiple rates of return. NPV disadvantages - Methods of incorporating risk into the investment appraisal process Risk and uncertainty - Investment project risk therefore increases with variability of returns and uncertainty increases with the longer duration of the project life - Sensitivity analysis shows how the NPV of an investment project is affected by the project variable to the point where the variable makes the NPV of the project zero. This helps identify critical project variables. However sensitivity analysis does not assess the probability of the changes in the project and therefore is dismissed as a way of incorporating risk into the investment appraisal process - Probability analysis refers to the assessment of the separate probabilities of a number of specified outcomes of an investment project` An investment with multiple IRRs - When an investment project has unconventional cash flows, that is cash flows that change sign over the life of the project. - Example when there is an initial investment(cash outflow) followed by many years of successful cash inflow before the decommissioning and repair which would be an outflow. This technical difficulty makes it difficult to use IRR as an investment appraisal method to give out advice. - It would be better to use NPV as it can accommodate unconventional cashflows Projects with significantly different business risk to current operations - WACC cannot be used as the discounting rate for such NPV calculations. - WACC can only be used when the financial and business risk are not significantly affected by the undertaking of the new project - When it changes drastically it is better to use CAPM which takes into account the systematic risk of the investment project Hard Capital Rationing and Soft capital rationing Assessment of Risk of a project Probability analysis CAPM Simulation - A computer based method of evaluating an investment project whereby the probability distribution associated with individual project variables and interdependencies between project are incorporated - Random numbers are assigned to a range of different values of a project variable to reflect on its probability distribution. Each simulation runs randomly selects values of project variables using random numbers and calculates the ENPV - A picture of the probability distribution of the mean ENPV is built up from hte results from the repeated simulation. - The project risk can be assessed from the probability distribution as the standard deviation of expected returns, together with the most likely outcome and the probability of negative NPV Achievement of stakeholder objectives by managers - This can be encouraged by managerial reward schemes - share options and performance related pay (PRP) - This can also be achieved by regulatory requirements such as corporate governance codes of best practice and stock exchange listing regulations - Share option schemes: the agency problem due to the separation of ownership and control where managers pursue their own goals rather than the objectives of the shareholders. They can be encouraged to align their own goals with those of the shareholders. This increased goal congruence can be achieved by turning managers into shareholders through share option schemes - Performance related pay: part the remuneration of the managers can be made conditional upon their achievement of specified performance targets, so that achieving these performance target assists in achieving stakeholder objectives - Corporate governance codes of best practice: these codes have been developed over time into recognised methods of encouraging managers to achieve stakeholder objectives. It can be applied in key areas of corporate governance relating to executive remuneration, risk assessment, auditing and internal control - Stock exchange listing regulations: they ensure the fair market for trading. They encourage disclosure of price sensitive information in supporting price efficiency and help decrease information asymmetry Systematic and unsystematic risk in relation to portfolio theory and CAPM CAPM - Project specific Cost of equity - When the project specific equity is higher than the current cost of equity, it would indicate that a higher return would be needed by the shareholders to compensate for the higher risk of the new venture. - Appraising the project using the old cost of equity would result in overstatement of the project’s NPV and would potentially lead to an incorrect decision being made. High gearing Problems Islamic Finance Increase in Dividend payment to equity shareholders - When the dividends are increased, the dividend cover will most likely reduce. - If this dividend payment was made to make the shares more attractive to equity shareholders, it would be debatable as there are a lot of factors that go into making equity investments - They will consider the business risk as well as the financial risk associated with the company when deciding the required rate of return - Furthermore, MM model show that in a capital market, the share price are independent of the dividend paid out. The value of the company is based on its operations income and not the dividends paid out