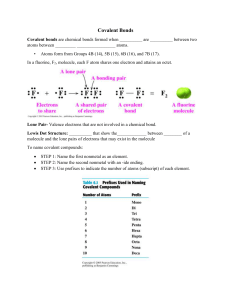
Name:_____________________________ Date:__________ Hour:______ Assignment #_____ ALL ABOUT COVALENT BONDING 1. What is a covalent bond? 2. Why do atoms create covalent bonds with other atoms? 3. When atoms create covalent bonds with other atoms, what is the maximum number of valence electrons they can have (except hydrogen)?__________ 4. Ionic bonds are created between a metal and a non-metal while covalent bonds are created between two _____________________. 5. When two of the same atoms create covalent bonds, they are called ___________________ molecules. 6. List the 7 diatomic elements. ______________________________________________________ 7. A double bond involves ___________ pairs of electrons. 8. N2 is an example of a compound with a _______________ bond. (single, double, or triple) 9. Which of the formulas represent the correct molecule if X and Z were to create a bond? A) XZ B) X3Z C) XZ3 D) X2Z 10. The attraction to electrons that elements have is known as _______________________________. 11. Explain polar covalent molecules (what gives them polarity). 12. Oxygen’s atomic number is ______, it will have ______ valence electrons and it wants to bond to ______ more electrons to fill the energy level. 13. Hydrogen’s atomic number is _______, so it will have ______ valence electrons, and wants to bond to ______ more electron to fill the energy level. 14. Draw a lewis dot diagram to show how 4 Hydrogens bond to one Carbon creating CH4. Draw circles to show shared electrons. 15. Draw a lewis dot diagram to show how 3 Hydrogens bond to one Nitrogen creating NH3. Draw circles to show shared electrons. Use the following diagrams to answer questions 16-21 A) B) C) 16. Which diagram above shows only single bonds?______ 17. Which diagram above shows a double bond?_______ 18. Which diagram above shows a triple bond?_______ 19. How many total electrons are shared between oxygen and carbon in diagram A?______ 20. How many pairs of electrons are shared between carbon and carbon in diagram B?______ 21. How many pairs electrons are shared between carbon and hydrogen in diagram C?_______ 22. List the prefixes used in naming covalent compounds: Number of atoms 1 Prefix Number of atoms 6 Prefix 2 7 3 8 4 9 nona 5 10 deca 23. State whether the following compounds are ionic or covalent. Compound Ionic or Covalent? Compound HgBr Disulfur Trioxide SO3 Nickel (II) cyanide P2O5 Chlorine Tetrafluoride KCl Tin (IV)Bromide Ba(NO3)2 H2O Lead (II) Phosphate NaCl Ionic or Covalent? Name the following covalent compounds: 24. NO2 ______________________________________________________ 25. CO _____________________________________________________ 26. S3Cl5 _______________________________________________________________________________ 27. S8O5____________________________________________________________________________________ 28. Br2I_________________________________________________________ 29. SiF4_____________________________________________________________________________________ Write the formula for the following covalent compounds: 30. Phosphorus trichloride _________________ 31. Phosphorus monoxide _________________ 32. Disilicon tetrachloride _________________ 33. Trinitrogen hexafluoride _________________ 34. Pentabromine heptachloride ________________ 35. Diphosphorus pentoxide __________________ Matching- match each formula on the right to its correct name on the left. _____36. disulfur tetrafluoride a) H3P _____37. carbon trioxide b) CH4 _____38. nitrogen pentoxide c) HCl _____39. nitrogen tribromide d) H2O _____40. dinitrogen heptachloride e) NBr3 _____41. carbon tetrachloride f) NH3 _____42. hydrogen monochloride g) N2Cl7 _____43. trihydrogen monophosphide h) S2F4 _____44. water i) NO5 _____45. methane j) CO3 _____46. ammonia k) CCl4 47-50 on back For numbers 47-50, use the table and information below to tell whether each bond between atoms is polar, or nonpolar. ELECTRONEGATIVITY VALUES OF THE ELEMENTS Difference of 0.0 to 0.5 = nonpolar 47) carbon + sulfur Difference of 0.6 to 1.6 = polar _________________ 48) oxygen + chlorine __________________ 49) nitrogen + hydrogen ___________________ 50) sulfur + fluorine _______________________